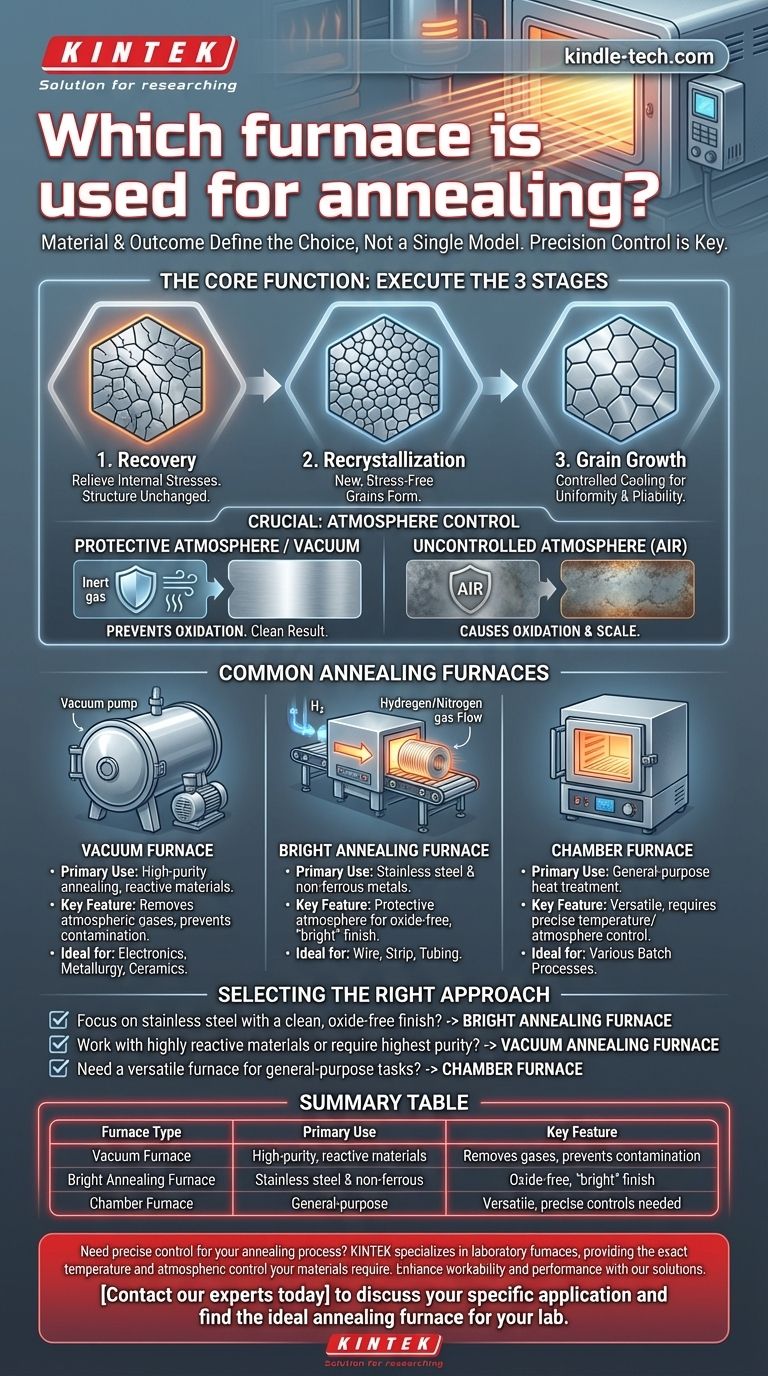
The choice of an annealing furnace is defined by the material and the desired outcome, not by a single universal model. While several types are used, including bright annealing furnaces, vacuum furnaces, and general-purpose chamber furnaces, they all share the essential capability to precisely control temperature and atmosphere to alter a material's properties. The goal is to make the material softer, more ductile, and easier to work with.
The critical factor is not a specific furnace name, but its ability to execute the three stages of annealing—recovery, recrystallization, and grain growth—within a controlled environment that prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.

The Core Function of an Annealing Furnace
An annealing furnace is fundamentally a tool for metallurgical transformation. Its design must support the distinct stages of the process to relieve internal stresses and refine the material's grain structure.
Executing the Three Stages of Annealing
- Recovery: The furnace slowly heats the material to a specific temperature. This initial stage relieves internal stresses locked into the metal from previous processing, without changing its core structure.
- Recrystallization: The furnace holds the material above its recrystallization temperature but below its melting point. At this critical temperature, new, stress-free grains begin to form within the metal's structure.
- Grain Growth: The furnace begins a controlled cooling cycle. As the material cools, the new grains develop, resulting in a more uniform, homogeneous internal structure that makes the material more pliable and less hard.
Managing the Furnace Atmosphere
A controlled furnace atmosphere is crucial for a successful anneal. Exposing hot metal to an uncontrolled atmosphere (like air) causes oxidation, leading to scale formation and potential surface damage.
This is especially critical for materials like stainless steel. The furnace must maintain either a protective atmosphere of specific gases or a vacuum to prevent these unwanted reactions and ensure a clean, reproducible result.
Common Types of Furnaces Used for Annealing
While many furnace designs can be adapted for annealing, a few types are commonly associated with the process due to their specialized features.
The Vacuum Furnace
This furnace is widely used across industries like metallurgy, ceramics, and electronics. By removing atmospheric gases, it creates a clean environment that is ideal for annealing highly reactive materials or when surface purity is paramount.
The Bright Annealing Furnace
This is a specialized furnace primarily used for stainless steel and other non-ferrous metals. It uses a protective atmosphere (often hydrogen or a nitrogen-hydrogen mix) to prevent any surface oxidation during the heat treatment cycle. The result is a finished product that retains a clean, "bright" surface, eliminating the need for post-process cleaning.
The Chamber Furnace
A chamber furnace is a more general-purpose design where the core annealing process of heating, holding, and controlled cooling takes place. Its suitability depends entirely on its ability to provide the precise temperature control and atmospheric management required for the specific material being treated.
Understanding the Key Considerations
Choosing the right approach involves understanding the trade-offs between different furnace environments and recognizing the specific needs of your material.
Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
A protective atmosphere is effective at preventing oxidation for many common metals. A vacuum, however, provides a higher level of control by removing nearly all reactive gases, which is essential for materials that are extremely sensitive to contamination.
Material-Specific Processes
The exact annealing process can vary. For example, solution annealing is a specific high-temperature process used for 300-series stainless steels. It is designed to improve corrosion resistance and ductility by dissolving chromium carbides back into the material's structure. This specific requirement dictates the temperature capabilities of the chosen furnace.
The Ultimate Goal: Workability
Regardless of the furnace, the purpose of annealing is to improve a material's properties. By reducing hardness and relieving internal stress, annealing makes a material easier to machine, form, or cold-work, while reducing the risk of failure during service.
Selecting the Right Approach for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired end-state for that material.
- If your primary focus is processing stainless steel with a clean, oxide-free finish: A bright annealing furnace with a controlled protective atmosphere is the correct choice.
- If you work with highly reactive materials or require the highest purity: A vacuum annealing furnace provides the most controlled environment by removing atmospheric gases.
- If you need a versatile furnace for general-purpose heat treatment: A chamber furnace with precise temperature and atmospheric controls can be adapted for various annealing tasks.
Ultimately, the best furnace is the one that gives you absolute control over the temperature cycle and atmospheric conditions your specific material requires.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Furnace | High-purity annealing of reactive materials | Removes atmospheric gases to prevent contamination |
| Bright Annealing Furnace | Stainless steel & non-ferrous metals | Protective atmosphere for an oxide-free, 'bright' finish |
| Chamber Furnace | General-purpose heat treatment | Versatile; requires precise temperature/atmosphere controls |
Need precise control for your annealing process?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory furnaces and equipment, providing the exact temperature and atmospheric control your materials require. Whether you need the high purity of a vacuum furnace or the clean finish of a bright annealing system, our solutions are designed to enhance your material's workability and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal annealing furnace for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control



















