In casting, there is no universal "better" process, only the "right" process for a specific application. Low-Pressure Permanent Mold (LPPC) casting is a robust, high-quality method ideal for many structural components. However, Vacuum Permanent Mold (VPMC) casting offers distinct advantages for parts requiring the absolute highest integrity, thin-walled designs, and superior mechanical properties. The choice depends entirely on your part's performance requirements and economic constraints.
The decision between low-pressure and vacuum casting is not a matter of good versus bad, but a strategic choice between precision and perfection. Low-pressure offers exceptional control and quality, while vacuum adds a level of material purity and detail fidelity that is unmatched.
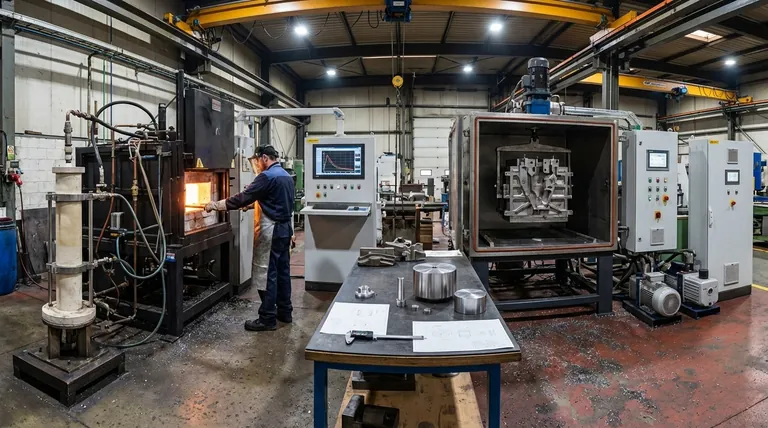

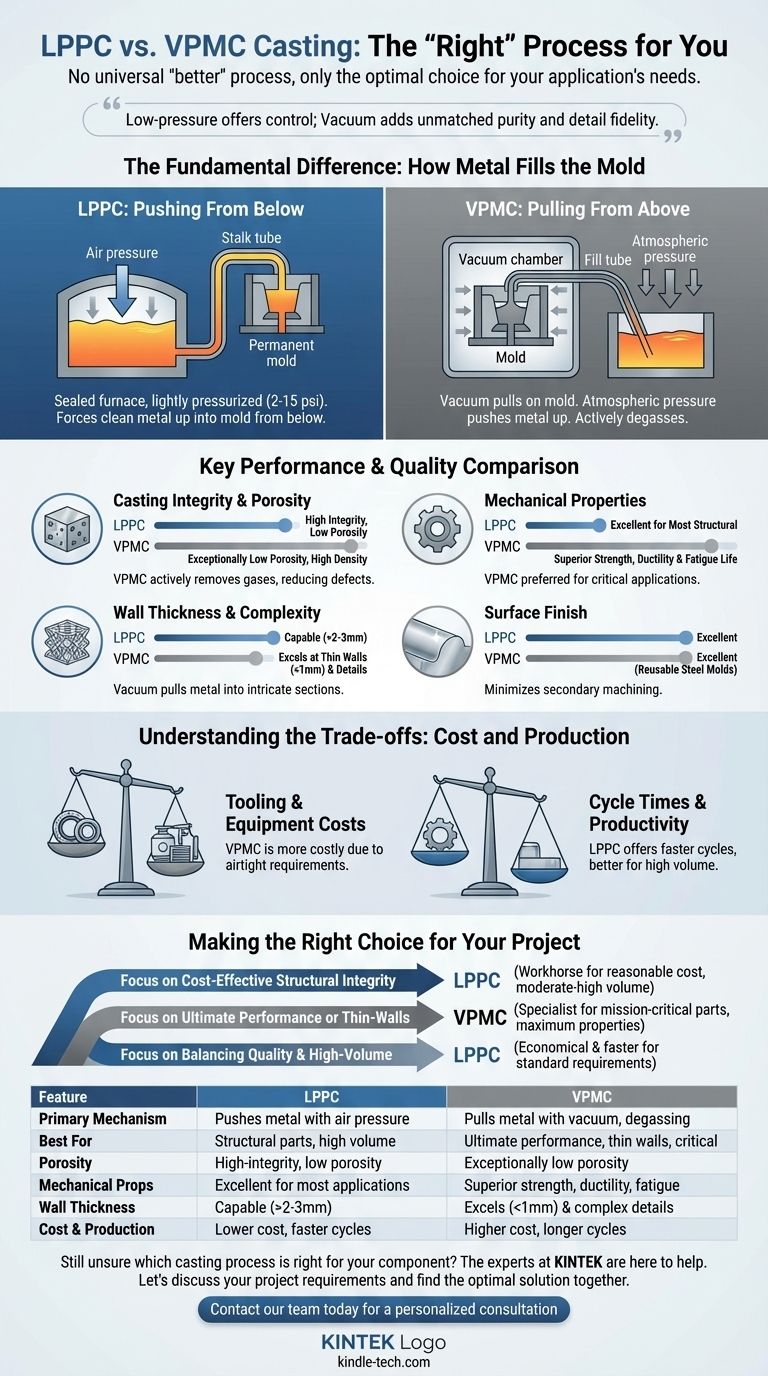
The Fundamental Difference: How Metal Fills the Mold
To choose correctly, you must first understand the core mechanical difference between these two processes. Both use pressure to move molten metal upward into a permanent steel or iron mold, a method far superior to simple gravity pouring. The key is how they generate that pressure.
Low-Pressure Permanent Mold (LPPC): Pushing From Below
In LPPC, the holding furnace containing the molten metal is sealed and lightly pressurized (typically 2-15 psi).
This air pressure pushes the metal's surface down, forcing clean metal from below the surface up through a ceramic stalk tube and into the mold cavity above.
The pressure is maintained during solidification, which helps feed the casting as it shrinks, significantly reducing porosity compared to gravity casting. It is a gentle, controlled, and highly repeatable fill.
Vacuum Permanent Mold (VPMC): Pulling From Above
In VPMC, the mold itself is the star of the show. The mold halves are placed in a vacuum chamber, or the mold is designed with seals to create a vacuum-tight enclosure.
A vacuum is pulled on the mold cavity. The entire assembly is then lowered so the fill tube dips into an open, unpressurized furnace. Atmospheric pressure—the weight of the air in the factory—then pushes the molten metal up into the low-pressure mold cavity.
Crucially, the vacuum actively removes gases from the mold cavity and the molten metal stream itself, preventing trapped air and reducing gas porosity.
Key Performance & Quality Comparison
The difference in fill mechanics has direct consequences on the final part's quality, performance, and manufacturability.
Casting Integrity and Porosity
VPMC holds a distinct advantage here. The vacuum environment actively degasses the molten aluminum, pulling out dissolved hydrogen and other gases. This leads to castings with exceptionally low porosity and high density.
LPPC produces high-integrity, low-porosity parts that are excellent for most structural applications. However, it cannot match the gas removal capabilities inherent to the vacuum process.
Mechanical Properties
Due to its lower gas content and potential for a finer, more uniform grain structure, VPMC typically yields parts with superior mechanical properties. This includes higher tensile strength, ductility, and fatigue life.
This makes VPMC the preferred process for critical components where failure is not an option and maximum material performance is required (e.g., aerospace brackets, high-performance automotive suspension parts).
Wall Thickness and Complexity
VPMC excels at producing extremely thin-walled and complex parts. The pressure differential created by the vacuum actively pulls the molten metal into intricate details and thin sections that might otherwise solidify prematurely in other processes.
LPPC is very capable with complex geometries but may face limitations with wall sections below 2-3mm, whereas VPMC can often achieve thicknesses of 1mm or less.
Surface Finish
Both processes produce an excellent surface finish thanks to the use of reusable steel molds. The smooth, non-porous mold surface imparts a clean finish on the casting, minimizing the need for secondary machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost and Production
Your decision isn't purely technical; it's also economic. The superior quality of VPMC comes at a price.
Tooling and Equipment Costs
VPMC is generally the more expensive process. The tooling is more complex and costly due to the absolute requirement for airtight seals around the mold halves and ejector pins. The vacuum equipment itself also adds significant capital expense.
LPPC tooling is simpler and less expensive to build and maintain, making it a more cost-effective choice for a wider range of applications.
Cycle Times and Productivity
LPPC often has faster cycle times and higher productivity. The process is typically simpler, more robust, and easier to automate. Sealing a furnace is less complex than sealing a moving mold for every shot.
VPMC can have longer cycle times due to the added steps of creating and verifying the vacuum seal before each fill. This can make it less suitable for very high-volume production unless the part's value justifies the lower throughput.
Material and Alloy Selection
Both processes are versatile and can handle a wide range of aluminum alloys. However, the high-purity environment of VPMC makes it uniquely suited for specialty and high-performance alloys where minimizing gas content and oxides is critical to achieving desired properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Evaluate your project's non-negotiable requirements to make a clear and confident decision.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective structural integrity: LPPC is the workhorse process, delivering excellent mechanical properties and low porosity for a reasonable cost in moderate-to-high volumes.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance or thin-walled design: VPMC is the specialist, justified for mission-critical parts where maximum strength, ductility, and detail fidelity are paramount.
- If your primary focus is balancing quality and high-volume production: LPPC is often the more economical and faster choice for parts that do not require the absolute pinnacle of material purity.
By aligning the unique strengths of each casting method with your specific engineering and business goals, you can ensure you are selecting the optimal manufacturing path for your component.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Low-Pressure Casting (LPPC) | Vacuum Permanent Mold Casting (VPMC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Pushes metal with air pressure (2-15 psi) | Pulls metal with vacuum, degassing the melt |
| Best For | Cost-effective structural parts, high-volume production | Ultimate performance, thin walls (<1mm), critical applications |
| Porosity & Integrity | High-integrity, low porosity | Exceptionally low porosity, superior density |
| Mechanical Properties | Excellent for most applications | Superior strength, ductility, and fatigue life |
| Wall Thickness | Capable, may struggle below 2-3mm | Excels at thin walls (1mm or less) and complex details |
| Cost & Production | Lower tooling/equipment cost, faster cycle times | Higher tooling/equipment cost, longer cycle times |
Still unsure which casting process is right for your component? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your foundry and materials testing needs, ensuring you achieve the desired quality and performance in your cast parts.
Let's discuss your project requirements and find the optimal solution together.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- Why is precise temperature and pressure control necessary for combustible cartridge cases? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification



















