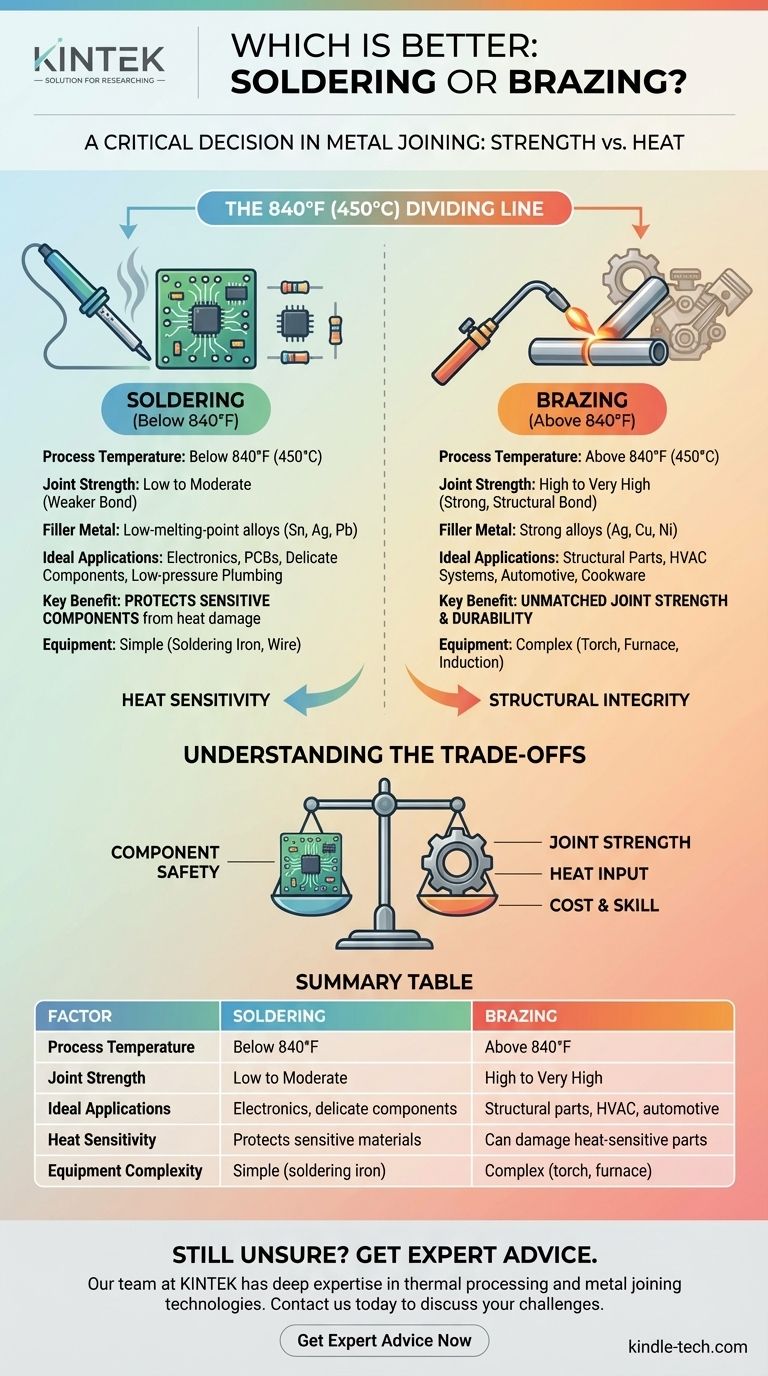
Choosing between soldering and brazing is a critical decision in metal joining, but it is not a matter of one being universally "better." The correct choice is determined entirely by the application's demand for strength and its tolerance for heat. Brazing uses high temperatures (above 840°F / 450°C) to create exceptionally strong, structural bonds, while soldering uses low temperatures to join components without damaging heat-sensitive materials like electronics.
The core difference is a trade-off between strength and heat. Brazing provides superior mechanical strength at the cost of high heat input, making it ideal for structural joints. Soldering provides a weaker bond but uses low heat, making it essential for delicate applications.

The Fundamental Difference: Temperature and Filler Metal
The official dividing line between these two processes is temperature. This single variable dictates the type of filler metal used, the resulting strength of the joint, and the applications for which each process is suitable.
The 840°F (450°C) Dividing Line
By definition, soldering is a joining process that occurs at temperatures below 840°F (450°C).
Brazing, conversely, takes place at temperatures above 840°F (450°C). In both methods, a filler metal is melted and drawn into a tight-fitting joint by capillary action, bonding the base metals without melting them.
Filler Metals and Joint Strength
The higher temperatures of brazing allow for the use of strong filler alloys, often containing silver, copper, or nickel. These alloys create a metallurgical bond that is exceptionally robust and durable.
Soldering relies on low-melting-point alloys, such as those made from tin, silver, or lead. These create a reliable electrical and mechanical connection but are much softer and weaker than brazed joints.
When to Choose Brazing: The Case for Strength
Brazing is the default choice when the mechanical integrity of the joint is the primary concern. Its applications are centered on structural performance and durability under stress.
Unmatched Joint Strength
A properly executed brazed joint is exceptionally strong. In many cases, the bond is as strong as or even stronger than the base metals being joined. This makes it suitable for parts that will experience vibration, shock, or pressure.
High-Temperature and Structural Applications
You will find brazing used extensively in demanding industries. It is essential for joining pipes in HVAC systems, assembling components in automotive engines, and manufacturing durable cookware.
Versatility and Cleanliness
Brazing can join a wide variety of dissimilar metals, such as copper to steel. Advanced techniques like vacuum brazing prevent oxidation, resulting in a clean, strong, and highly consistent joint ideal for complex geometries.
When to Choose Soldering: The Case for Sensitivity
Soldering dominates in applications where the components being joined cannot withstand high temperatures. Its primary advantage is its gentle nature.
Protecting Sensitive Components
The defining use case for soldering is electronics. The low heat from a soldering iron is just enough to melt the solder without destroying the delicate transistors, resistors, and microchips on a printed circuit board (PCB).
Simplicity and Accessibility
For many tasks, soldering is more accessible. A basic soldering iron is inexpensive and relatively easy to use for simple wire connections or hobbyist projects. Brazing, by contrast, typically requires a torch or furnace and a higher degree of skill to manage the heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong process can lead to immediate failure. A soldered joint will fail in a high-stress structural application, while brazing would instantly destroy an electronic circuit.
Strength vs. Component Safety
This is the central trade-off. Brazing gives you a powerful, permanent bond but generates enough heat to warp thin metals and destroy electronics or plastics. Soldering protects those components but offers a much weaker mechanical connection.
Cost and Equipment
Brazing equipment, like high-temperature torches and specialized furnaces, is more complex and expensive. The filler materials, especially those with high silver content, also carry a higher cost than standard solder.
Thermal Stress and Skill
The intense heat of brazing can introduce stress into the workpieces, potentially causing distortion if not applied correctly. It requires significant skill to heat the joint evenly to the target temperature without overheating and damaging the base metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your process by defining your project's most critical requirement.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and durability: Brazing is the correct choice, as the joint will be suitable for structural and high-stress applications.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive electronic components: Soldering is the only safe and effective option due to its low-temperature process.
- If your primary focus is creating a leak-proof seal in low-pressure plumbing: Soldering is a cost-effective and perfectly sufficient solution.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals for a structural part: Brazing offers superior strength and material versatility for this task.
By understanding this fundamental relationship between temperature, strength, and application, you can confidently select the right joining process for your project.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Soldering | Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Below 840°F (450°C) | Above 840°F (450°C) |
| Joint Strength | Low to Moderate | High to Very High |
| Ideal Applications | Electronics, delicate components | Structural parts, HVAC, automotive |
| Heat Sensitivity | Protects sensitive materials | Can damage heat-sensitive parts |
| Equipment Complexity | Simple (soldering iron) | Complex (torch, furnace) |
Still unsure which process is right for your application?
Our team at KINTEK has deep expertise in thermal processing and metal joining technologies. Whether you're working with delicate electronics requiring precise soldering or structural components needing the strength of brazing, we can help you select the right equipment and consumables for your laboratory or production needs.
Contact us today to discuss your specific metal joining challenges and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source













