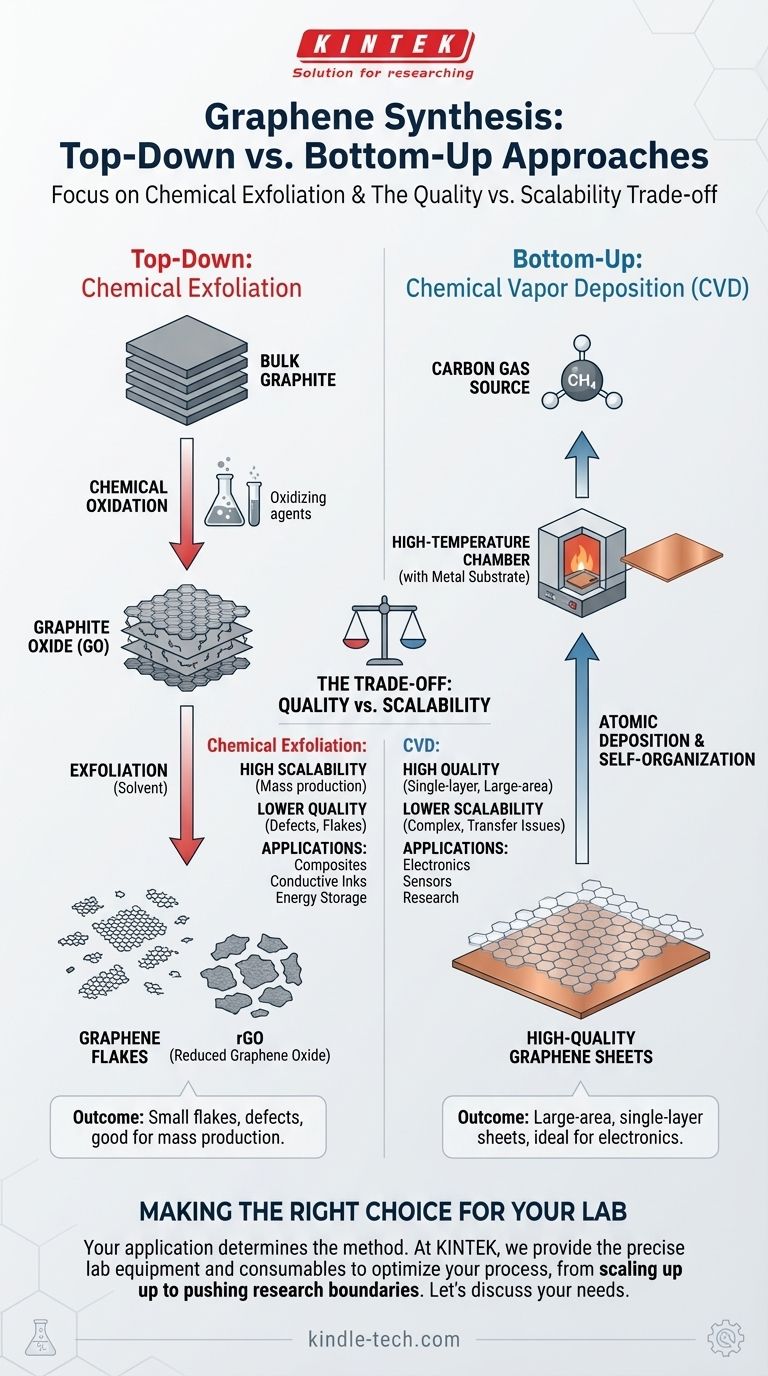
In the synthesis of graphene, chemical exfoliation is a 'top-down' method that begins with bulk graphite and uses chemical processes to separate it into individual or few-layered sheets. This technique primarily involves using strong oxidizing agents to create graphite oxide, which weakens the forces between the layers, allowing them to be exfoliated easily in a solvent. This contrasts sharply with 'bottom-up' methods that build graphene atom by atom.
The primary distinction in graphene synthesis is between 'top-down' methods like chemical exfoliation, which are suited for mass production but yield lower-quality flakes, and 'bottom-up' methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which produce high-quality, large-area sheets ideal for electronics.

The Two Fundamental Approaches to Graphene Synthesis
Understanding chemical exfoliation requires placing it within the broader context of how graphene is made. All methods fall into one of two categories: breaking down graphite ('top-down') or building up graphene from carbon atoms ('bottom-up').
The 'Top-Down' Strategy: Starting with Graphite
Top-down methods are fundamentally deconstruction processes. They take a block of graphite, which is essentially a stack of countless graphene layers, and find ways to peel those layers apart.
Chemical exfoliation is a prominent top-down technique. It typically uses chemical oxidation to insert oxygen-containing functional groups between the graphite layers. This increases the spacing and weakens the bonds, making it much easier to separate the layers into graphene oxide flakes, which are then often chemically reduced to form reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
Other top-down methods include mechanical exfoliation (the original "scotch tape" method) and liquid-phase exfoliation, which uses solvents and sonication to overcome the forces between layers.
The 'Bottom-Up' Strategy: Building from Atoms
In contrast, bottom-up methods construct graphene from a carbon-based gas source. This is an additive process, akin to building a structure brick by brick.
The most important bottom-up method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). In this process, a carbon-containing gas like methane (CH4) is introduced into a high-temperature chamber with a metal substrate, typically copper foil.
At high temperatures, the gas decomposes, and carbon atoms deposit onto the surface of the metal, self-organizing into the hexagonal lattice structure of graphene. This allows for the growth of large, continuous, and high-quality single-layer graphene sheets.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Scalability
The choice between a top-down and a bottom-up method is governed by a fundamental trade-off between the quality of the final product and the ease of mass production.
Limitations of Chemical Exfoliation (Top-Down)
While excellent for producing large quantities of graphene-like material, chemical exfoliation has significant drawbacks. The harsh oxidation process introduces defects into the graphene structure, which compromises its exceptional electrical properties.
The output consists of small flakes, typically only tens of micrometers in size, not a continuous sheet. Furthermore, controlling the exact number of layers in these flakes is very difficult.
The Strengths and Hurdles of CVD (Bottom-Up)
CVD is widely regarded as the most promising technique for producing the high-quality, single-layer graphene needed for advanced electronic applications. It allows for the creation of large, uniform sheets that can cover entire wafers.
However, the CVD process is more complex and less scalable for bulk production than chemical exfoliation. A critical challenge is the need to transfer the graphene sheet from the metal foil it was grown on to a target substrate, a delicate step that can introduce wrinkles, tears, and impurities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct synthesis method is entirely dependent on the intended use case. There is no single "best" method; there is only the best method for a specific goal.
- If your primary focus is mass production for applications like composites, conductive inks, or energy storage: Chemical exfoliation is the more viable path due to its scalability, even with the lower electronic quality of the resulting flakes.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics, sensors, or fundamental research: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the superior method for producing the large-area, high-quality, single-layer graphene sheets required.
Ultimately, the best synthesis method is determined not by a universal standard, but by the specific performance and production requirements of your end goal.
Summary Table:
| Method | Process | Key Outcome | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Exfoliation (Top-Down) | Oxidizes graphite to weaken layers, then exfoliates in solvent. | Graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) flakes. | Mass production, composites, conductive inks, energy storage. |
| CVD (Bottom-Up) | Grows graphene from carbon gas on a metal substrate at high heat. | High-quality, large-area, single-layer graphene sheets. | High-performance electronics, sensors, research. |
Ready to choose the right graphene synthesis method for your lab?
The choice between scalable chemical exfoliation and high-quality CVD graphene is critical for your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need to excel in materials science.
Whether you're scaling up production or pushing the boundaries of research, our expertise can help you optimize your process. Let's discuss your specific application needs and find the perfect solution together.
Contact our experts today to get started!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth



















