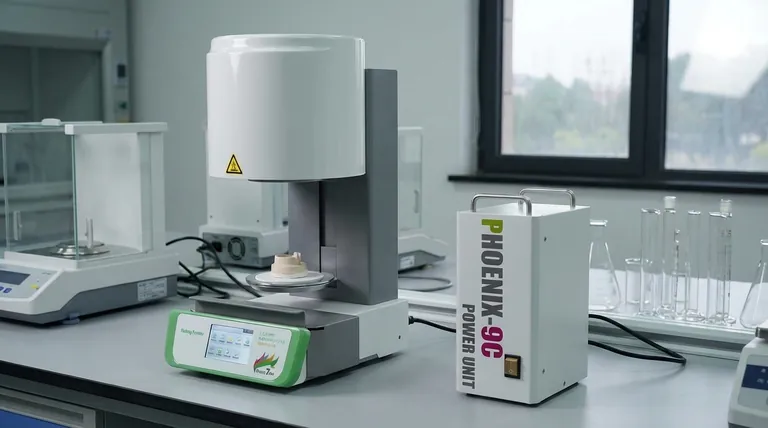
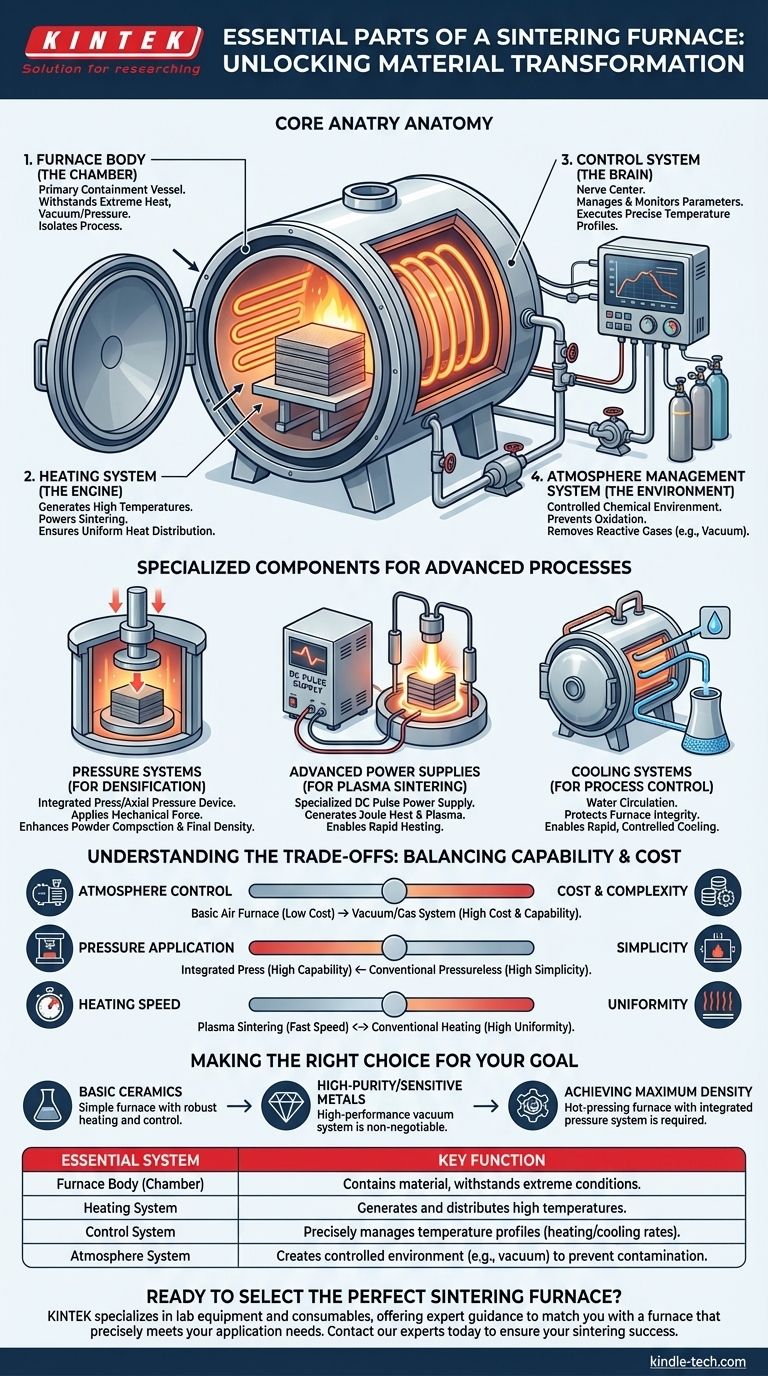
At its core, a sintering furnace is built around four essential systems. These are the furnace body or chamber that contains the material, a heating system to provide the necessary thermal energy, a control system to manage the process parameters, and an atmosphere management system (often a vacuum) to create the ideal chemical environment.
A sintering furnace is not merely a high-temperature oven; it is a precision instrument designed to create a tightly controlled environment. Its essential components work in concert to manage heat, pressure, and atmosphere, fusing powdered materials into a solid mass without melting them.

The Core Anatomy of a Sintering Furnace
Every sintering furnace, regardless of its specific type, is based on a set of fundamental components. Each part serves a distinct and critical function in achieving a successful sintering cycle.
The Furnace Body (The Chamber)
The furnace body is the primary containment vessel. It is engineered to withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures and, in many cases, high vacuum or positive pressure. This chamber isolates the sintering process from the outside environment.
The Heating System (The Engine)
This is the component responsible for generating the high temperatures required for sintering. It typically consists of powerful heating elements that convert electrical energy into thermal energy. The system's design is critical for ensuring uniform heat distribution throughout the material being processed.
The Control System (The Brain)
The control system is the furnace's nerve center. It manages and monitors all critical parameters, most importantly the heating and cooling rates. This system executes pre-programmed temperature profiles with high precision, ensuring the material is processed correctly and repeatably.
The Atmosphere Management System (The Environment)
Sintering often requires a specific atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation. This system can range from a simple gas inlet to a complex vacuum system composed of multiple pumps. Its purpose is to remove reactive gases like oxygen and create a controlled environment, which is crucial for processing sensitive metals and advanced ceramics.
Specialized Components for Advanced Processes
While the four systems above are universal, advanced sintering furnaces incorporate specialized components to handle more demanding materials and applications.
Pressure Systems for Densification
Hot-pressing furnaces include an integrated press system or axial pressure device. This component applies mechanical force to the material during the heating cycle, which significantly aids in compacting the powder and achieving higher final density.
Advanced Power Supplies for Plasma Sintering
Discharge plasma sintering (SPS/FAST) furnaces utilize a specialized DC pulse power supply. This is the most critical component in such a system, as it generates Joule heat and creates plasma within the material, enabling extremely rapid heating rates and unique material properties.
Cooling Systems for Process Control
Nearly all high-performance furnaces use a water cooling system. This system circulates water through the furnace shell and other key components. Its purpose is twofold: to protect the structural integrity of the furnace from extreme heat and to enable rapid, controlled cooling of the sintered part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The specific configuration of a sintering furnace involves balancing capability, complexity, and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is key to selecting the right equipment.
Atmosphere Control vs. Cost
A basic furnace that operates in ambient air is the least expensive but is only suitable for materials that are not sensitive to oxidation. Adding a vacuum or controlled gas system dramatically increases the furnace's capability but also its cost and complexity.
Pressure Application vs. Simplicity
Integrating a pressing system allows for the densification of materials that are otherwise very difficult to sinter. However, this adds significant mechanical complexity and cost compared to a conventional, pressureless sintering furnace.
Heating Speed vs. Uniformity
Specialized systems like plasma sintering offer incredibly fast cycle times. The trade-off can be a greater challenge in maintaining perfect temperature uniformity across larger or complex-shaped parts compared to slower, conventional heating methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material and final product requirements will dictate which furnace components are truly essential for your application.
- If your primary focus is basic ceramics: A simple furnace with robust heating and control systems may be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metals or oxygen-sensitive materials: A furnace with a high-performance vacuum system is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and oxidation.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in advanced materials: A hot-pressing furnace with an integrated pressure system is the required tool.
Ultimately, understanding these core components empowers you to select or operate a furnace that precisely matches the demands of your material and desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Essential System | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Furnace Body (Chamber) | Contains the material and withstands extreme process conditions. |
| Heating System | Generates and distributes the high temperatures required for sintering. |
| Control System | Precisely manages temperature profiles (heating/cooling rates) for repeatability. |
| Atmosphere System | Creates a controlled environment (e.g., vacuum) to prevent contamination. |
Ready to select the perfect sintering furnace for your materials?
The right combination of components is critical for achieving your desired material density, purity, and properties. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to match you with a sintering furnace that precisely meets your application needs, whether you're working with basic ceramics or advanced oxygen-sensitive metals.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure your sintering success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag



















