To withstand extreme temperatures, furnaces primarily rely on advanced ceramic materials, most notably high-purity alumina fiber. This material, a form of aluminum oxide, serves as the primary insulation and lining, effectively containing the intense heat generated within the furnace while maintaining structural integrity.
A furnace isn't built from a single high-temperature material, but an integrated system of them. While materials like alumina fiber are critical for insulation, other components like heating elements (silicon carbide) and furnace tubes (ceramics) are chosen for their specific roles in generating and containing the heat.
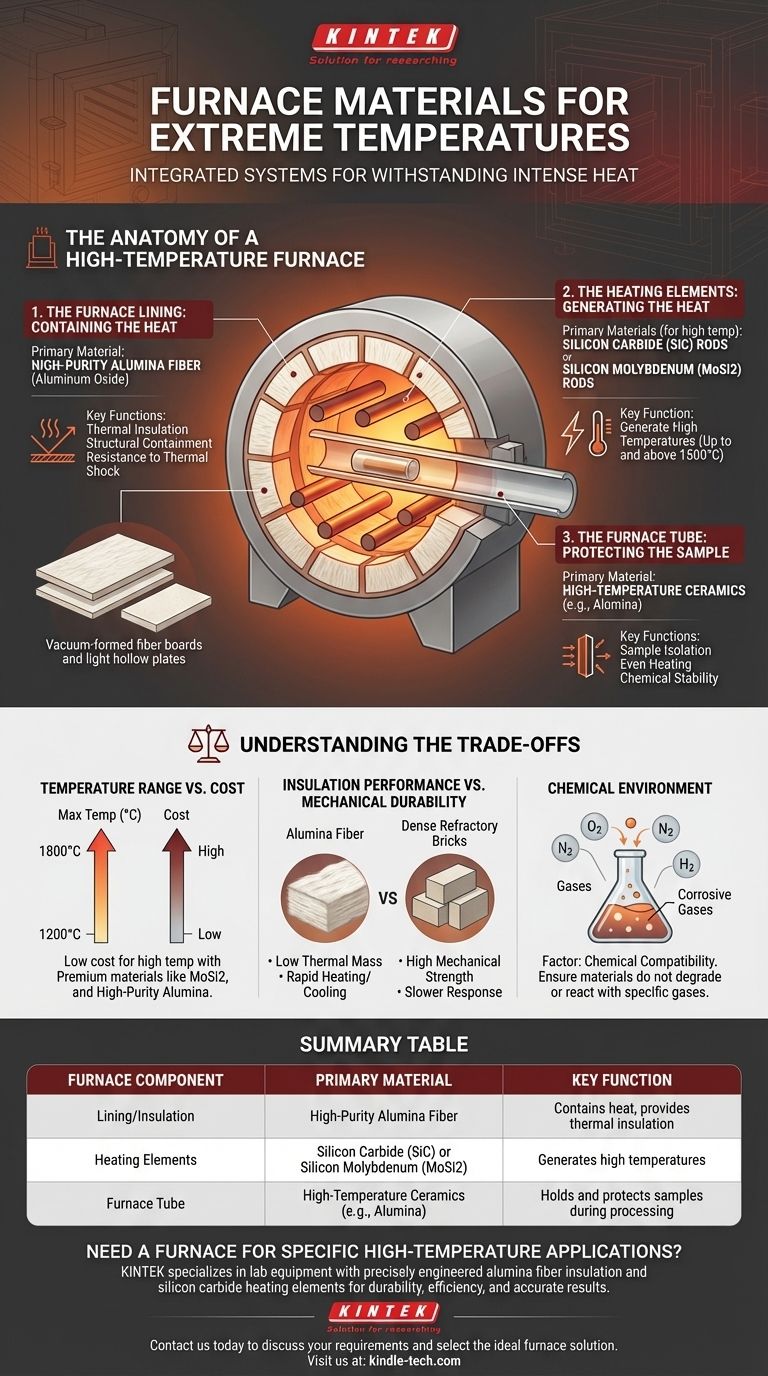
The Anatomy of a High-Temperature Furnace
A furnace is a system where different components work together, each made from materials selected for a specific function under extreme thermal stress. Understanding these parts clarifies why there isn't one single answer.
The Furnace Lining: Containing the Heat
The furnace lining is the critical barrier that keeps heat inside the furnace. Its job is both insulation and structural containment.
The most common material for this is high-purity alumina fiber (aluminum oxide). It is used in forms like vacuum-formed fiber boards or light hollow plates.
These alumina-based materials are chosen for their exceptional properties: high service temperature, excellent thermal insulation, and resistance to thermal shock, which prevents cracking during rapid heating and cooling cycles.
The Furnace Tube: Protecting the Sample
Many laboratory furnaces use a tube to hold the material being processed. This tube passes through the center of the heated chamber.
These tubes are generally made of high-temperature-resistant ceramic materials, with alumina being a very common choice. In some applications, specialized metal alloys can also be used.
The key properties for a furnace tube are thermal conductivity, to ensure the sample is heated evenly, and chemical stability, to prevent any reaction with the material being processed.
The Heating Elements: Generating the Heat
The heating elements are the components that actually generate the heat by resisting the flow of electricity. The material used depends entirely on the target temperature range.
For lower temperatures, simple resistance wire is sufficient.
For higher and more demanding industrial or laboratory applications, furnaces use robust elements like silicon carbide (SiC) rods or silicon molybdenum (MoSi2) rods, which can operate at extremely high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The selection of a furnace material is never based on temperature resistance alone. It involves a careful balance of cost, performance, and application-specific needs.
Temperature Range vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between a material's maximum operating temperature and its cost. A furnace designed for 1200°C can use less expensive heating elements and insulation than one built for 1800°C, which requires premium materials like silicon molybdenum rods and high-purity alumina.
Insulation Performance vs. Mechanical Durability
Alumina fiber products offer incredible insulation with very low thermal mass, allowing for rapid heating and cooling. However, they can be more fragile than traditional dense refractory bricks, which offer greater mechanical strength but store more heat and are slower to respond.
Chemical Environment
The chemical atmosphere inside the furnace is a critical factor. Certain materials may degrade or react in the presence of specific gases at high temperatures. The choice of furnace tube and lining must account for the chemical compatibility with the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal determines which material is most important within the furnace system.
- If your primary focus is thermal insulation: High-purity alumina fiber is the definitive material used for modern furnace linings.
- If your primary focus is generating extreme heat (above 1500°C): You need a furnace equipped with specialized heating elements like silicon carbide or silicon molybdenum rods.
- If your primary focus is isolating a sample during processing: The key component is the high-temperature ceramic furnace tube, often made of alumina.
Ultimately, selecting the right material is about matching the component's function to the specific thermal and chemical demands of your work.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Component | Primary Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Lining/Insulation | High-Purity Alumina Fiber | Contains heat, provides thermal insulation |
| Heating Elements | Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Silicon Molybdenum (MoSi2) | Generates high temperatures |
| Furnace Tube | High-Temperature Ceramics (e.g., Alumina) | Holds and protects samples during processing |
Need a furnace built with the right high-temperature materials for your specific application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing furnaces with precisely engineered components like alumina fiber insulation and silicon carbide heating elements to ensure durability, efficiency, and accurate results for your laboratory processes. Contact us today to discuss your high-temperature requirements and let our experts help you select the ideal furnace solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Sheet
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum operating temperature of alumina? The Critical Role of Purity and Form
- What is the most common industrial ceramic? Discover Why Alumina Dominates Countless Applications
- What is the function of alumina setter plates for LATP? Protect Material Purity & Prevent Adhesion
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- What are the process advantages of selecting an alumina plate for CuO nanofilm synthesis? Achieve Superior Purity



















