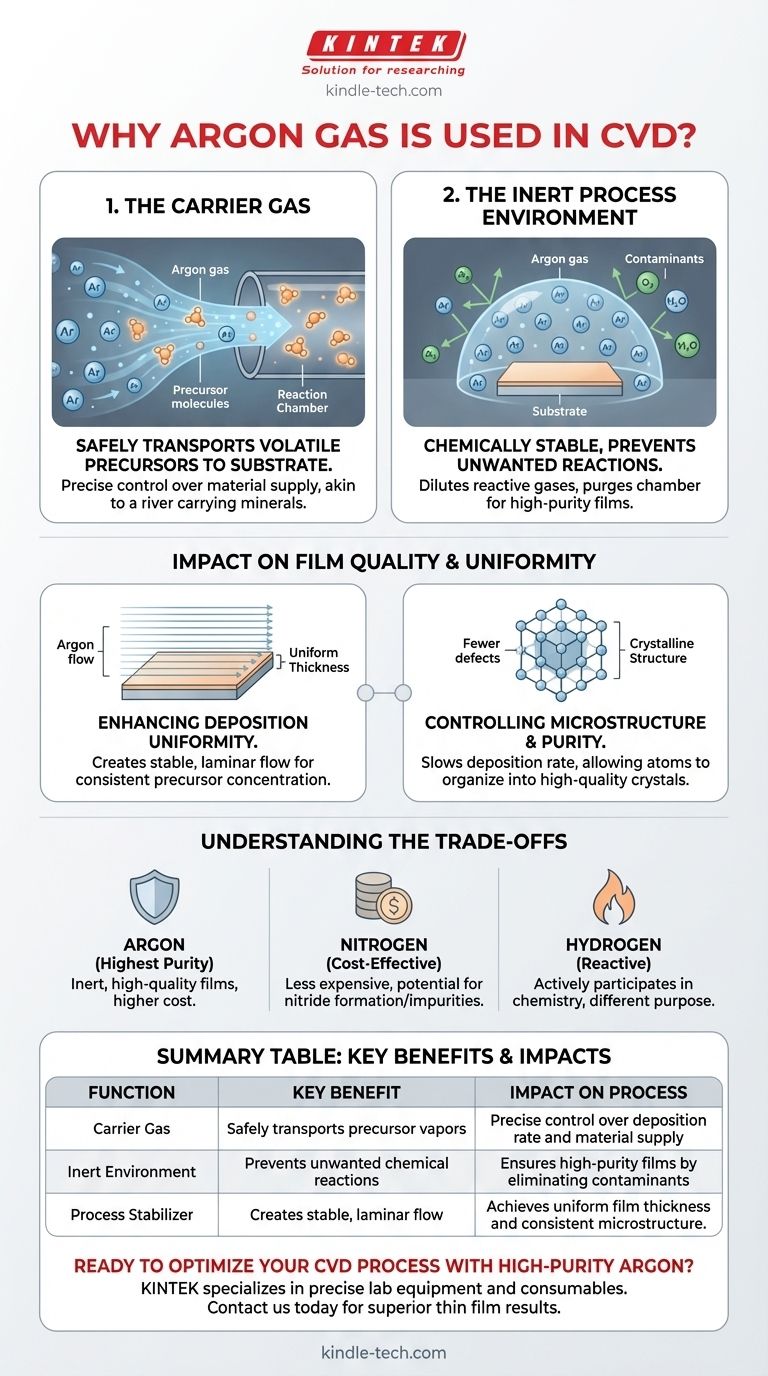
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), argon is primarily used as an inert carrier gas and a process stabilizer. It performs the critical function of safely transporting volatile precursor chemicals to the substrate surface within the reaction chamber. At the same time, its chemically non-reactive nature ensures that it does not interfere with the delicate deposition chemistry, helping to create a controlled environment necessary for growing high-quality thin films.
The use of argon in CVD is not merely for transport; it is a fundamental tool for process control. By managing the flow and pressure of this inert gas, operators can precisely regulate the reaction environment, ensuring the stable and uniform conditions required to produce thin films with high purity and specific microstructures.
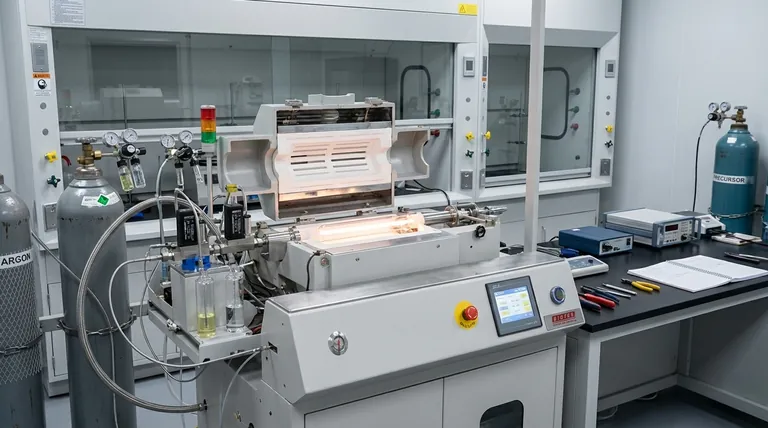

The Core Functions of Argon in Detail
To understand why argon is so prevalent, we must break down its two main roles: transporting the reactants and stabilizing the environment. These functions are essential for achieving the precision that makes CVD a powerful manufacturing technique.
Function 1: The Carrier Gas
The CVD process relies on getting reactive chemical vapors (precursors) from their source to the substrate where the film will grow.
Argon acts as the delivery vehicle. Precursor materials are often heated or bubbled with argon, which picks up the vapor and carries it into the main reaction chamber in a controlled, predictable stream.
This is analogous to a river carrying dissolved minerals. The flow rate of the river (argon) determines how much mineral (precursor) is delivered to a specific location over time, giving engineers precise control over the supply of raw material for film growth.
Function 2: The Inert Process Environment
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically stable and extremely unlikely to react with other elements, even at the high temperatures common in CVD.
This inertness is its greatest strength. It dilutes the reactive precursor gases without participating in the chemical reaction, preventing unwanted side reactions that could create impurities in the final film.
Furthermore, a continuous flow of argon helps purge the reaction chamber of residual atmospheric gases like oxygen or water vapor. These contaminants can cause significant defects, so removing them is critical for achieving high-purity films.
How Argon Impacts Film Quality and Uniformity
The choice to use argon directly influences the final properties of the deposited material. Its role extends beyond simple delivery and purging to actively shaping the film's characteristics.
Enhancing Deposition Uniformity
The flow dynamics inside a CVD reactor are complex. A well-managed flow of argon helps create a stable, laminar flow pattern over the substrate surface.
This ensures that all areas of the substrate are exposed to a consistent concentration of the precursor gas. The result is a thin film with uniform thickness and composition across its entire surface, a key advantage of the CVD method.
Controlling Microstructure and Purity
By diluting the reactive gases, argon can effectively slow down the deposition rate. This slower growth gives atoms more time to find their ideal positions in the crystal lattice.
This control is crucial for producing highly ordered, crystalline films, such as the well-faceted diamond films mentioned in research. The presence and flow of argon become a lever to fine-tune the material's microstructure from amorphous to polycrystalline or even single-crystal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While argon is highly effective, it is not the only option, and its use involves balancing cost against performance. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making informed process decisions.
Argon vs. Other Gases
Nitrogen (N₂) is a common, less expensive alternative. However, it is not truly inert. At high CVD temperatures, nitrogen can react with certain materials to form unwanted nitrides, compromising film purity.
Helium is also inert but is more expensive and has significantly different thermal conductivity, which would alter the heating dynamics of the process. Hydrogen is often used, but it is a reactive gas that actively participates in the chemistry, serving a completely different purpose than argon.
The Cost and Purity Factor
The decision to use argon is often a trade-off between operational cost and the required film quality. For demanding applications in semiconductors or optics where purity is paramount, the higher cost of high-purity argon is justified.
For less sensitive applications, a less expensive gas like nitrogen might be sufficient, provided it is proven not to react with the process chemicals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The selection of a carrier gas should be driven by the specific goals of your deposition process.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest film purity and crystalline quality: Use high-purity argon to create a stable, non-reactive environment and exert fine control over reaction kinetics.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, large-scale production: You can evaluate nitrogen as a cheaper alternative, but you must first verify it will not form undesirable compounds in your process.
- If your primary focus is to actively influence the surface chemistry: Consider a reactive gas like hydrogen, understanding that it is a chemical reactant, whereas argon is chosen for its deliberate non-reactivity.
Ultimately, selecting the right process gas is a fundamental step in mastering the precision and power of Chemical Vapor Deposition.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Benefit | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Carrier Gas | Safely transports precursor vapors | Precise control over deposition rate and material supply |
| Inert Environment | Prevents unwanted chemical reactions | Ensures high-purity films by eliminating contaminants |
| Process Stabilizer | Creates stable, laminar flow | Achieves uniform film thickness and consistent microstructure |
Ready to optimize your CVD process with high-purity argon?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables—including high-purity gases and CVD systems—that your laboratory needs to achieve superior thin film results. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for process control, purity, and uniformity.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific deposition challenges and help you master the precision of Chemical Vapor Deposition.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries



















