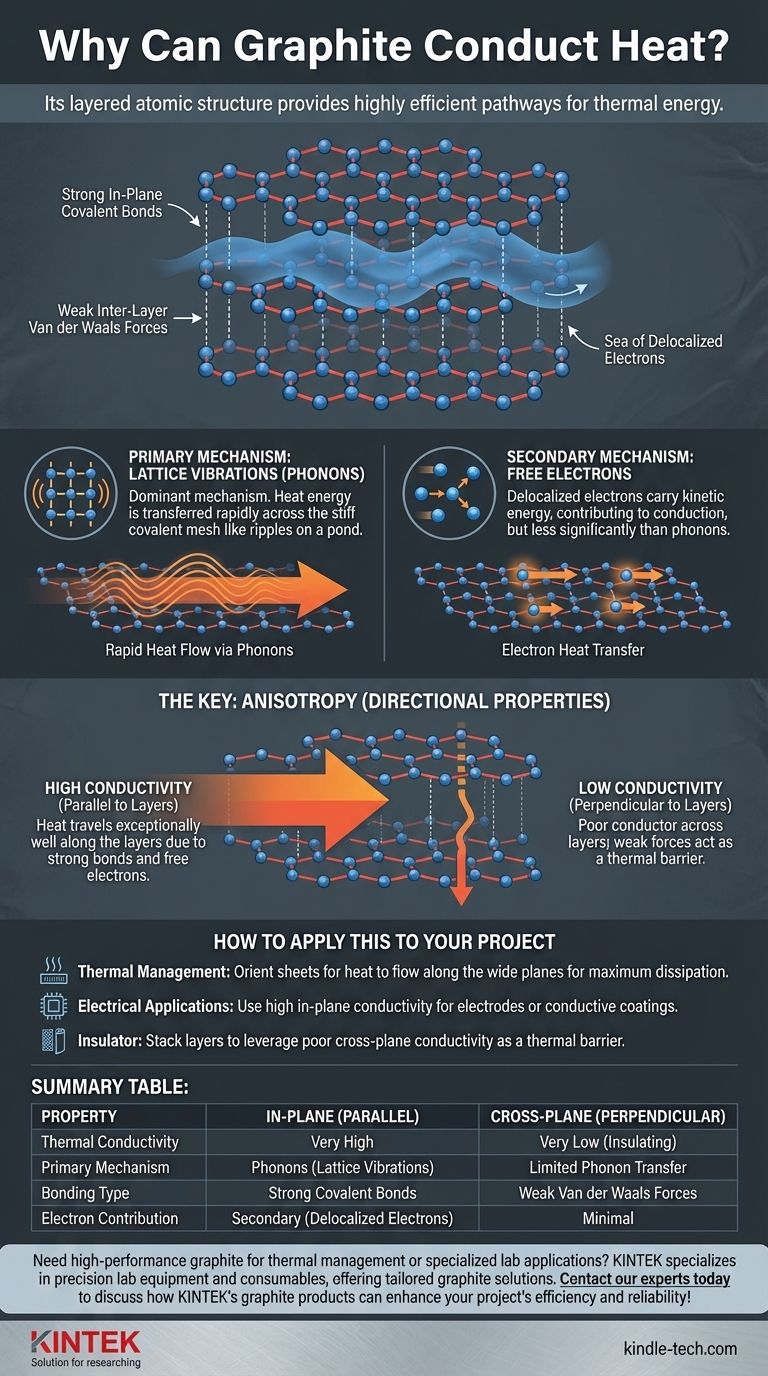
At its core, graphite conducts heat because its unique, layered atomic structure provides highly efficient pathways for thermal energy to travel. This happens primarily through synchronized atomic vibrations, with a secondary contribution from the same free-moving electrons that allow it to conduct electricity.
Graphite's excellent thermal conductivity isn't just about free electrons; it's dominated by the efficient transfer of lattice vibrations (phonons) through its strong, tightly bonded carbon layers. This structure dictates both how and where the heat can flow.

The Unique Structure of Graphite
To understand why graphite is an effective thermal conductor, we must first examine its atomic arrangement. It is an allotrope of carbon, meaning its properties are defined entirely by its structure.
Layers of Carbon Atoms
Graphite consists of vast, two-dimensional sheets of carbon atoms. Each sheet, known as a graphene layer, is arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice.
Strong In-Plane Bonds
Within each layer, every carbon atom is bonded to three others by extremely strong covalent bonds. These bonds are rigid and create a stiff, stable plane.
Weak Inter-Layer Bonds
These flat graphene layers are stacked on top of one another. However, they are held together only by weak intermolecular forces known as van der Waals forces, making it easy for the layers to slide past each other.
A "Sea" of Delocalized Electrons
The bonding within the layers only uses three of carbon's four outer electrons. The fourth electron from each atom is delocalized, forming a "sea" of mobile electrons that can move freely along the plane of the layer, but not easily between layers.
The Two Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
Heat in a solid is simply the kinetic energy of its vibrating atoms. The transfer of this energy happens through two primary mechanisms in graphite, both of which are dictated by its structure.
Primary Driver: Lattice Vibrations (Phonons)
The dominant mechanism for heat transfer in graphite is through phonons, which are quantized packets of vibrational energy.
Think of the strong covalent bonds within a graphene layer as a stiff, taught mesh. When one part of the layer heats up and vibrates, the energy is transferred rapidly across the entire mesh, much like ripples spreading across the surface of a pond.
Secondary Contributor: Free Electrons
The delocalized electrons that make graphite an excellent electrical conductor also play a role in thermal conduction. These mobile electrons carry kinetic energy and transfer it as they move through the lattice.
However, in graphite, their contribution to overall thermal conductivity is significantly less than that of the phonons.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Anisotropy
The most important consequence of graphite's layered structure is that its properties are not the same in all directions. This is known as anisotropy.
High Conductivity Along the Layers
Heat travels exceptionally well parallel to the graphene layers. The strong bonds provide a perfect, uninterrupted path for phonons, and the delocalized electrons move freely within this plane.
Low Conductivity Between the Layers
In contrast, graphite is a poor thermal conductor (an insulator) in the direction perpendicular to the layers. The weak van der Waals forces are inefficient at transmitting vibrations from one layer to the next, creating a thermal barrier.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding this directional property is critical for using graphite effectively in any application.
- If your primary focus is thermal management: You must orient graphite sheets so that the heat source is conducted along the wide, flat planes to achieve maximum dissipation.
- If your primary focus is electrical applications: The high in-plane conductivity makes it ideal for electrodes or conductive coatings where current needs to flow across a surface.
- If your primary focus is using it as an insulator: You can leverage the poor cross-plane conductivity by stacking layers to create a thermal barrier in a specific direction.
Ultimately, graphite's thermal behavior is a masterclass in how a material's atomic structure directly governs its real-world function.
Summary Table:
| Property | In-Plane (Parallel to Layers) | Cross-Plane (Perpendicular to Layers) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Very High | Very Low (Insulating) |
| Primary Mechanism | Phonons (Lattice Vibrations) | Limited Phonon Transfer |
| Bonding Type | Strong Covalent Bonds | Weak Van der Waals Forces |
| Electron Contribution | Secondary (Delocalized Electrons) | Minimal |
Need high-performance graphite for thermal management or specialized lab applications? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored graphite solutions that leverage its unique anisotropic properties. Whether you require superior in-plane conductivity for heat dissipation or controlled insulation, our expertise ensures optimal material performance for your laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's graphite products can enhance your project's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature can graphite handle? Unlocking its extreme heat resistance in inert environments
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab



















