Sieve analysis is fundamentally important because it determines the particle size distribution of a soil. This single property, often called gradation, is the primary indicator used to predict a soil's engineering behavior, including its strength, permeability, and compaction characteristics. It is the first step in classifying a soil and forecasting its performance in any construction project.
The true value of a sieve analysis is not simply measuring particle sizes. It is the key that unlocks our ability to predict a soil's core engineering properties—how it will bear load, manage water, and respond to construction efforts.

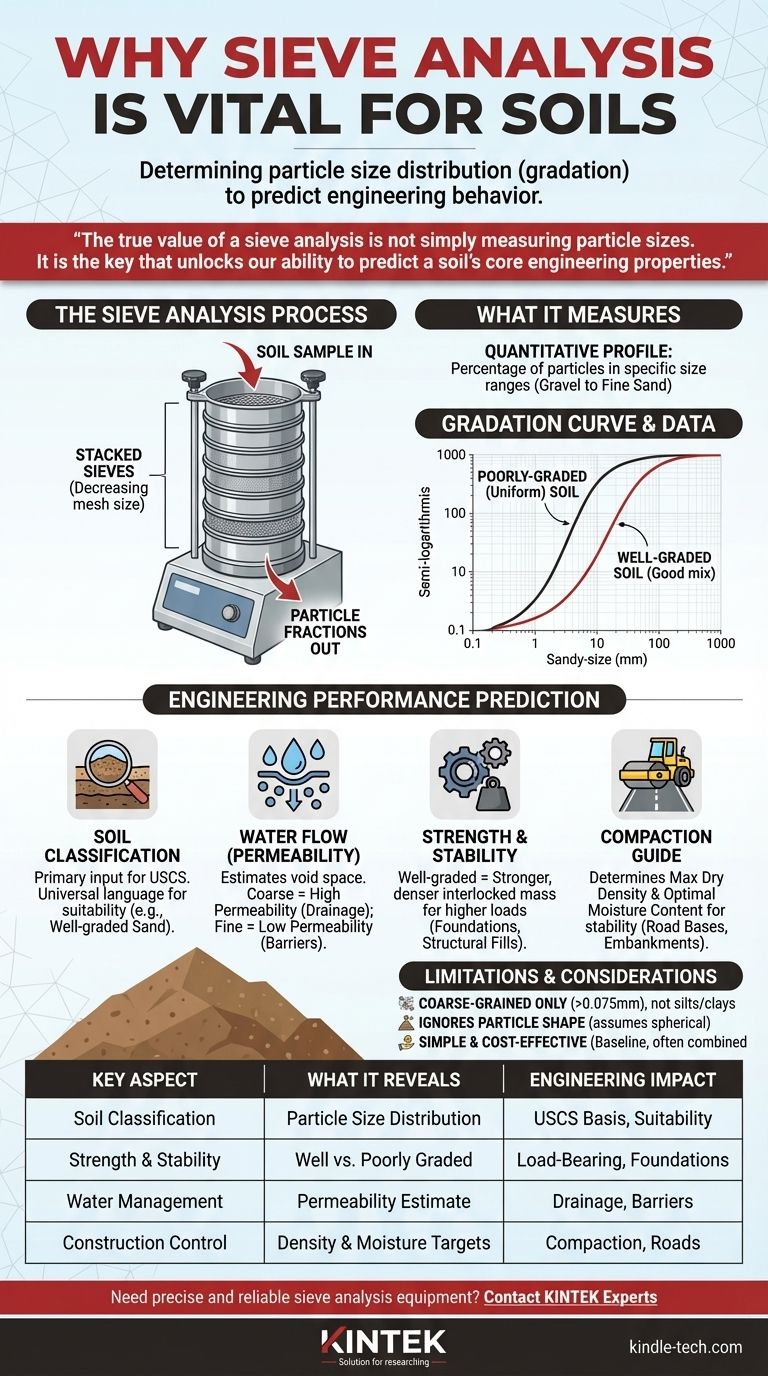
What a Sieve Analysis Actually Measures
A sieve analysis is a straightforward, mechanical process used to separate a dry soil sample into different particle size fractions. The results form the basis for geotechnical classification and engineering analysis.
The Concept of Particle Size Distribution
The test involves passing a soil sample through a series of stacked sieves, each with progressively smaller mesh openings.
By weighing the amount of soil retained on each sieve, we can calculate the percentage of particles that fall within specific size ranges. This creates a quantitative profile of the soil's makeup, from coarse gravels down to fine sands.
From Raw Data to a Gradation Curve
The results are plotted on a semi-logarithmic graph to create a particle size distribution curve. This curve is a visual "fingerprint" of the soil.
A steep curve indicates a poorly-graded (or uniform) soil, where most particles are the same size. A gentle, S-shaped curve signifies a well-graded soil, which has a good mix of various particle sizes.
From Particle Size to Engineering Performance
The gradation curve is not an academic exercise; it directly informs critical engineering decisions. Understanding the particle mix allows us to predict how the soil will behave under real-world conditions.
Classifying the Soil: The First Critical Step
Sieve analysis data is the primary input for standardized soil classification systems, such as the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS).
Classifying a soil (e.g., as SW for well-graded sand or GP for poorly-graded gravel) provides a universal language for engineers to instantly understand its general properties and suitability for a given purpose.
Predicting Water Flow (Permeability)
The size of the voids between soil particles governs how easily water can flow through it. Sieve analysis allows us to estimate this permeability.
Coarse-grained soils like gravel and sand have large voids and high permeability, making them ideal for drainage applications like trench fills. Fine-grained soils have low permeability and are used for barriers, such as in dam cores or pond liners.
Assessing Strength and Stability
Well-graded soils are generally stronger and more stable than poorly-graded ones.
The smaller particles in a well-graded soil fill the voids between the larger particles, creating a dense, interlocked mass that can support higher loads. This is crucial for designing foundations and structural fills.
Guiding Compaction on Site
For road bases, embankments, and other earth fills, achieving a specific density is essential for long-term stability.
The soil's gradation helps determine its maximum dry density and optimal moisture content—the targets that construction crews must meet during the compaction process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While foundational, a sieve analysis is not a complete picture of soil behavior. It's important to recognize its limitations.
It Primarily Analyzes Coarse-Grained Soils
Sieve analysis is only effective for particles larger than the No. 200 sieve (0.075 mm), which includes gravels and sands.
For finer particles like silts and clays, their behavior is governed by electrostatic forces, not gravity. A different test, the hydrometer analysis, is required to determine their particle size distribution.
Particle Shape Is Ignored
The test inherently assumes particles are roughly spherical. However, angular, flat, or elongated particles can interlock differently, affecting strength and compaction in ways the gradation curve alone won't predict.
It's a Simple, Cost-Effective First Step
The primary advantages of sieve analysis are that it is inexpensive, fast, and highly reproducible, as noted in historical practice. It provides an excellent baseline understanding. However, for critical structures, its results must be combined with other tests that measure plasticity, strength, and consolidation.
Applying This to Your Project
Your interpretation of sieve analysis data should be guided by your specific engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is foundation design: The data helps you classify the soil to estimate its bearing capacity and potential for settlement.
- If your primary focus is earthwork and pavement: The gradation curve is essential for determining compaction requirements and assessing frost susceptibility.
- If your primary focus is drainage and filtration: The analysis allows you to select soils with the correct permeability to manage water flow and prevent clogging.
- If your primary focus is material sourcing: The test quickly verifies if borrow pit material or quarry aggregate meets the project's specifications.
This simple test provides the foundational data upon which sound geotechnical engineering decisions are built.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | What Sieve Analysis Reveals | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Classification | Particle size distribution (Gradation) | Basis for Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) |
| Strength & Stability | Distinguishes well-graded vs. poorly-graded soils | Predicts load-bearing capacity for foundations and fills |
| Water Management | Estimates permeability based on particle sizes | Informs drainage design and barrier applications |
| Construction Control | Determines maximum dry density and optimal moisture | Guides compaction efforts for roads and embankments |
Need precise and reliable sieve analysis equipment for your geotechnical projects? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves and soil testing equipment, delivering the accuracy you need to make critical engineering decisions with confidence. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's soil analysis requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is a sieve used for sieving? A Guide to Precision Particle Size Analysis
- What is the sieve method used for? From Basic Separation to Precise Particle Analysis
- What is the significance of using a standard sieve before the sintering of CaF2 nanopowders? Ensure Optical Clarity
- Which solids can be separated from a solution by sieving? Understanding the Limits of Sieving
- What is the purpose of using precision standard sieves in powder granulation? Maximize Density and Structural Isotropy
- How many ways can sieve analysis be carried out? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- What are the factors affecting sieve analysis? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Distribution
- How does a sieve test work? A Guide to Precise Particle Size Distribution Analysis



















