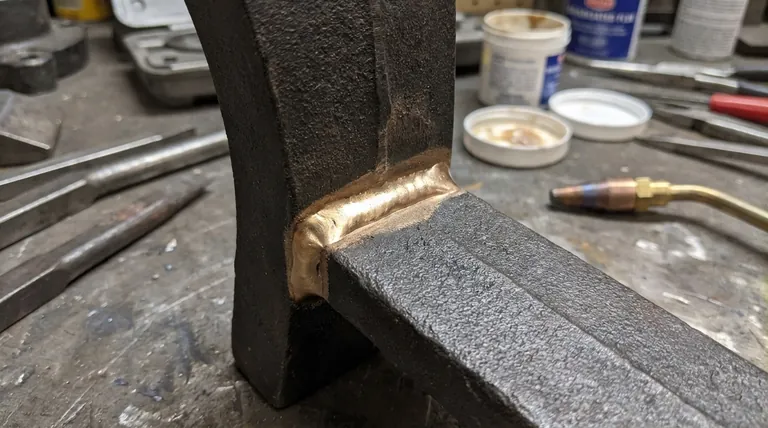
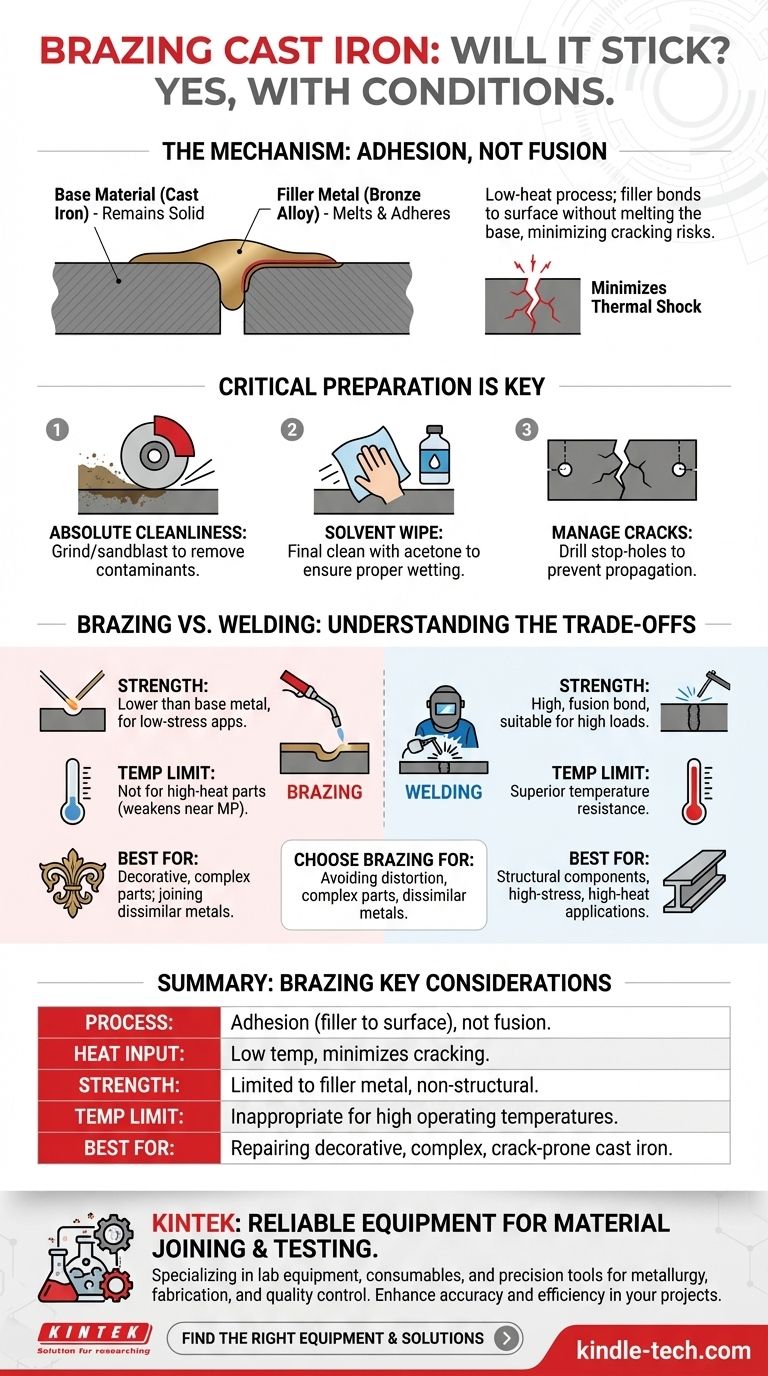
Yes, brazing is a common and effective method for joining cast iron. It works through a process of adhesion, where a filler metal with a lower melting point bonds to the surface of the cast iron without melting the base material itself. This low-heat approach is often preferred because it minimizes the risk of cracking or distorting the brittle cast iron.
While brazing reliably "sticks" to properly prepared cast iron, it is not a universal solution. Its suitability depends entirely on the part's final application, as it creates a bond that is less strong and less heat-resistant than a true weld.

Why Brazing Works on Cast Iron
Brazing operates on a different principle than welding. Understanding this distinction is key to knowing when and how to use it effectively for cast iron repair or fabrication.
Adhesion, Not Fusion
The core of the process is that the filler rod (often a bronze alloy) melts at a temperature significantly lower than cast iron. This molten filler flows into the joint and adheres to the cast iron's surface, acting like a powerful metallic glue rather than fusing the two pieces together.
The Advantage of Low Heat
The primary benefit of this low-temperature process is the preservation of the cast iron's properties. Exposing cast iron to the extreme heat of traditional welding can alter its internal structure, making it even more brittle and highly susceptible to cracking as it cools. Brazing avoids this thermal shock.
Critical Preparation for a Strong Bond
A successful braze is entirely dependent on meticulous preparation. The filler metal cannot adhere to a contaminated surface.
Start with Absolute Cleanliness
The joint area must be completely free of any oil, grease, paint, rust, or other contaminants. This typically requires grinding or sandblasting the surface, followed by a final wipe-down with a solvent like acetone. Any residue will prevent the filler metal from wetting the surface and creating a strong bond.
Managing Existing Cracks
When repairing a cracked casting, it is standard practice to drill a small "stop-hole" at each end of the crack. This simple step relieves stress concentration at the crack's tip and prevents it from propagating further during the heating process or future use.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brazing vs. Welding
Choosing to braze a cast iron part involves a clear set of compromises. It is not inherently better or worse than welding; it is a different tool for a different job.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
A brazed joint is not as strong as a properly executed cast iron weld. The strength is limited to that of the filler metal itself. Therefore, brazing is not suitable for parts that will be subjected to high tensile loads, heavy vibration, or significant stress.
Critical Temperature Limitations
The bronze filler alloys used for brazing have a much lower melting point than iron. This makes brazing completely inappropriate for parts exposed to high operating temperatures, such as engine exhaust manifolds, cylinder heads, or furnace components. The joint will weaken and fail as it approaches its service temperature limit.
When Brazing Is the Better Choice
Despite its limitations, brazing is often the superior choice for repairing parts where avoiding heat distortion is the top priority. It is also an excellent option for complex, ornate, or "unweldable" types of cast iron where the risk of cracking from a welding process is unacceptably high.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Use the application of the part as your definitive guide to selecting the correct joining method.
- If your primary focus is repairing non-structural or decorative parts: Brazing is an excellent and often preferred method due to its low heat input and reduced risk of cracking.
- If your primary focus is joining high-stress or high-heat components: You must use a specialized cast iron welding process, as a brazed joint will not have the required strength or temperature resistance.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals to cast iron: Brazing is often the only practical solution, as it can effectively bond a wide range of different metals together.
Ultimately, choosing to braze cast iron is a deliberate technical decision based on its unique advantages for low-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Aspect | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Process | Adhesion of filler metal (e.g., bronze) to surface, not fusion of base metal |
| Heat Input | Low temperature minimizes risk of cracking and distortion in brittle cast iron |
| Strength | Lower than welding; suitable for non-structural, low-stress applications |
| Temperature Limit | Not for high-heat parts (e.g., engine components); filler metal weakens near its melting point |
| Best For | Repairing decorative, complex, or crack-prone cast iron; joining dissimilar metals |
Need reliable equipment for material joining or testing? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories with precision tools for metallurgy, fabrication, and quality control. Whether you're brazing, welding, or analyzing materials, our solutions enhance accuracy and efficiency. Contact us today to find the right equipment for your cast iron projects and ensure durable, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the normal temperature for sintering? Master the 750°C to 1300°C Range for Optimal Results
- What role does a vacuum drying oven play in processing Al2O3/ZrO2 ceramic mixed slurries? Ensure Powder Quality
- What is the application of quenching oil? Achieve Superior Hardness and Durability in Metal Parts
- What is the industrial brazing process? A Guide to Strong, Permanent Metal Joining
- How big is the vacuum furnace market? A Multi-Billion Dollar Industry Driven by High-Tech Demand
- How long should a furnace take to raise the temperature? Key Factors for Optimal Heating Speed
- How high-precision furnaces control TiAl alloy microstructure? Master phase transformations with KINTEK precision.
- Why is a vacuum oven necessary for drying NVOPF electrode sheets? Ensure Battery Stability and Purity



















