Overview of Warm Isostatic Press (WIP)
Table of Contents
Warm isostatic pressing (WIP) is a variant of cold isostatic pressing (CIP) that includes a heating element. It employs warm water or a similar medium to apply uniform pressure to powdered products from all directions. WIP is a cutting-edge technology that enables isostatic pressing at a temperature that does not exceed the boiling point of the liquid medium.
The WIP process involves using flexible materials as a jacket mold and hydraulic pressure as a pressure medium to shape and press the powder material. The liquid medium is heated and continuously injected into a sealed pressing cylinder through a booster source. To ensure temperature control, the pressing cylinder is equipped with a heating element.
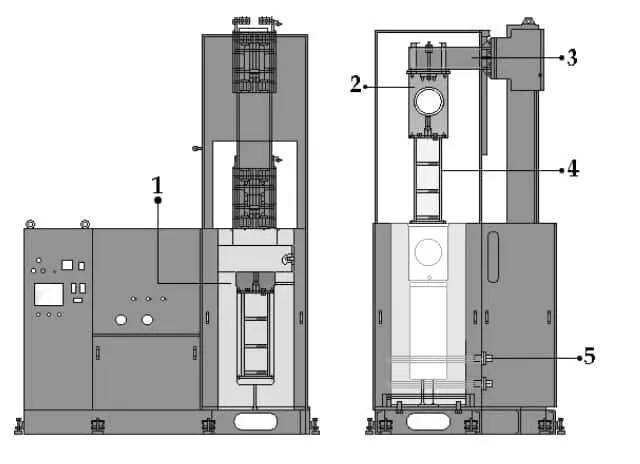
Description of KinTek Autoclave's WIP series
KinTek Autoclave designs and builds Warm Isostatic Presses for various applications, including the semiconductor industry. These systems can be gas or liquid pressurized and are commonly used for plastics and laminated products. WIPs are usually custom-built and can operate at low pressures or extreme pressures. Liquid WIP systems can reach temperatures up to 250°C, while gas WIP systems can go up to 500°C. KinTek also works with companies to develop the necessary molding and technologies for cost-effective and efficient processes. Additionally, KinTek offers toll WIP capabilities and testing for interested parties.
Key components of WIP
The WIP unit is designed for applications requiring artificial pressure. It offers a custom mode for special functions. The system for production uses water or oil thermal fluid and can be heated using an external circulation heater. The WIP unit features a touch screen with computer-based graphical operation and a standard interface. It also includes a high-pressure pump, pressure vessel, and reservoir tank. The pressure vessel is designed and manufactured according to the ASME code for safety and accuracy. Pressure sensors and thermocouples are installed, and a pin closure type is used for user convenience.
Special features for user convenience
The WIP series by KinTek Autoclave includes a heater in the reservoir tank to control temperatures ranging from 50 to 100°C. The system offers various specifications and models to cater to different research and production needs.
Applications of WIP
WIP finds applications in various industries, including:
- Hybrid chips
- MLCC lamination (Muliti-Layer Ceramic Capacitor)
- Bluetooth components
- Fuel cells
- Medical electronics & implants
- Multilayer PZTs (Piezoelectric Transducers)
- LTCCs (Low Temperature Cofired Ceramics)
- Varistors
- Other laminated electronic components
Lamination is a technique used to manufacture materials in multiple layers, resulting in improved strength, stability, appearance, or other properties. It involves permanently assembling different materials using heat, pressure, welding, or adhesives. Lamination is widely used in electronic components such as MLCCs, hybrid chips, ferrites, varistors, Multi-layer PZTs, LTCCs, electronic filters, and ceramics.
Understanding Lamination
Definition of lamination
Lamination is the process of permanently joining two or more layers of material together. It is commonly used to add a protective coating to paper documents, cards, or images by fusing a plastic layer over them using heat or adhesive. Laminating machines are used for this purpose and offer options for different thicknesses of plastic and machine sizes.
How lamination is achieved
Lamination can be achieved using either a cold laminator or a hot laminator. A cold laminator applies the plastic to the document without the use of heat, while a hot laminator fuses the plastic to the document using heat. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the laminating project.
Common applications in electronic components
Lamination plays a crucial role in the production of electronic components. Thin-film resistors, which are essential for many electronic applications such as circuit boards, computers, and radiofrequency devices, often utilize lamination. Magnetic thin films are used in electronics, data storage, displays, and optoelectronics. Optical thin films find applications in optical coatings and optoelectronics. Polymer thin films are used for surface metallization, while chemical vapor deposition is a versatile method for depositing thin films.
Lamination presses are hydraulic compression presses used to produce laminates by permanently joining two or more layers of material together. These presses come in various sizes and can apply precise temperature and pressure controls. They are commonly used in industries such as electronic materials, printed circuit boards, decorative laminates, and honeycomb panel manufacturing. Some advanced lamination systems feature computer and process control systems, automated loading and unloading systems, and turnkey installations.
In conclusion, lamination is a process that involves permanently joining layers of material together. It is widely used in various industries, especially in the production of electronic components. Laminating machines and presses provide the means to achieve high-quality laminates for different applications.
Applications of Warm Isostatic Press
Hybrid chips
Hybrid chips are one of the applications of warm isostatic press (WIP). WIP is used in the semiconductor industry for the laminating process. It involves using high pressure and warm temperature (around 50-100°C) to laminate the chips together. This process ensures that the chips are securely bonded and improves the overall performance and reliability of the hybrid chips.
MLCC Lamination
MLCC (Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitor) lamination is another application of warm isostatic press. MLCCs are widely used in electronic components, and the lamination process is crucial for their manufacturing. Warm isostatic press is used to apply uniform pressure to the MLCCs, ensuring proper bonding of the ceramic layers and improving the electrical performance of the capacitors.
Bluetooth components
Warm isostatic press is also used in the manufacturing of Bluetooth components. Bluetooth technology is widely used in wireless communication devices such as smartphones and headphones. The components used in Bluetooth devices need to be compact and reliable. Warm isostatic press helps in achieving the desired compactness and reliability by applying pressure and heat to the components during the manufacturing process.
Fuel cells
Fuel cells are devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. They are used in various applications, including electric vehicles and portable power generation. Warm isostatic press is applied in the manufacturing of fuel cells to ensure proper sealing and bonding of the cell components. This improves the efficiency and durability of the fuel cells.
Medical electronics & implants
Warm isostatic press finds applications in the manufacturing of medical electronics and implants. Medical electronics include devices such as pacemakers, prosthetics, and diagnostic equipment. Warm isostatic press is used to laminate and bond the components of these devices, ensuring their reliability and performance. It is also used in the manufacturing of implants, such as dental implants, to achieve proper bonding and structural integrity.
Multilayer PZTs
PZT (Lead Zirconate Titanate) is a piezoelectric material widely used in sensors, actuators, and transducers. Multilayer PZTs are made by stacking multiple layers of PZT material. Warm isostatic press is used in the manufacturing of multilayer PZTs to ensure proper bonding and alignment of the layers. This results in improved performance and reliability of the piezoelectric devices.
LTCCs (Low Temperature Cofired Ceramics)
LTCCs are ceramic materials used in the manufacturing of electronic components such as filters, antennas, and sensors. Warm isostatic press is used in the fabrication of LTCCs to achieve proper bonding and densification of the ceramic layers. This process ensures the desired electrical and mechanical properties of the components.
Varistors
Varistors are electronic components used to protect electronic circuits from voltage surges and spikes. Warm isostatic press is applied in the manufacturing of varistors to achieve proper densification and bonding of the ceramic material. This process enhances the electrical performance and reliability of the varistors.
Other laminated electronic components
Warm isostatic press is also used in the manufacturing of various other laminated electronic components. These components include ferrites, electronic filters, and ceramics. The process of warm isostatic press ensures proper bonding and alignment of the layers, improving the overall performance and reliability of the electronic components.

Overall, warm isostatic press has a wide range of applications in various industries, including semiconductor, electronics, energy, and healthcare. It plays a crucial role in achieving proper bonding, densification, and alignment of the materials used in these applications, resulting in improved performance, reliability, and efficiency.
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
Related Articles
- The Benefits of Using Isostatic Pressing in Manufacturing
- Understanding the Basics of Isostatic Pressing
- Comprehensive Guide to Isostatic Pressing:Processes, and Features
- How to replace the rubber ring of isostatic press and what precautions should be taken
- Isostatic Pressing Technology in Solid-State Battery Production






















