Basic Safety Operation
Initial Machine Check
Before initiating any operation with the flat-plate hot press, it is imperative to conduct a thorough initial machine check. This preliminary step is crucial for ensuring both the safety of the operator and the optimal functioning of the machine.
Firstly, inspect the power plug to confirm that it is securely connected and free from any visible damage. A loose or damaged power plug can lead to electrical malfunctions, posing significant safety risks. Additionally, ensure that the machine is correctly plugged into a grounded outlet to prevent potential electrical hazards.
Next, verify that all control panels and indicators are functioning as expected. This includes checking the temperature display, pressure gauge, and any other operational indicators. Ensuring that these components are operational will help in accurately setting and monitoring the machine's parameters during the lamination process.
It is also advisable to perform a brief test run, without any materials loaded, to confirm that the machine operates smoothly. This test run should include checking the movement of the press plates, the responsiveness of the control buttons, and the accuracy of the temperature and pressure settings. Any anomalies detected during this test should be addressed immediately to prevent issues during the actual lamination process.
Furthermore, inspect the work area around the hot press for any debris or obstructions. A clean and organized workspace is essential for safe and efficient operation. Ensure that all necessary safety equipment, such as asbestos gloves and fire extinguishers, are readily accessible and in good condition.
By meticulously following these steps during the initial machine check, operators can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure that the flat-plate hot press is ready for safe and effective use in lamination experiments.
Temperature Setting
Setting the hot press temperature is a critical step that directly impacts the quality of the lamination process. Begin by consulting the sample specifications to determine the optimal temperature for your experiment. This may involve referencing material datasheets or previous successful experiments for guidance.

To ensure accuracy, use a calibrated thermometer or the machine's built-in temperature monitoring system. Regularly check the actual temperature against the set point to minimize deviations. A temperature that is too high can cause material degradation, while a temperature that is too low may result in incomplete bonding.
Consider the following steps for precise temperature control:
-
Initial Temperature Check: Before applying any pressure, verify that the hot press has reached the desired temperature. This preliminary check helps avoid starting the lamination process prematurely.
-
Temperature Adjustment: If the actual temperature deviates from the set point, make necessary adjustments promptly. This may involve increasing or decreasing the heating rate, depending on the discrepancy.
-
Continuous Monitoring: Throughout the lamination process, maintain continuous temperature monitoring. This proactive approach allows for immediate corrective actions if the temperature begins to drift.
By adhering to these steps, you can ensure that the hot press operates at the optimal temperature, leading to successful and consistent lamination outcomes.
Heat Protection
When operating the flat-plate hot press, it is crucial to prioritize heat protection to prevent burns and ensure safe handling of the equipment. Asbestos gloves are a standard safety measure due to their high heat resistance, making them essential for anyone handling the hot press. These gloves provide a critical barrier against the extreme temperatures generated by the machine, allowing operators to manipulate the press without risking severe burns.
In addition to wearing asbestos gloves, it is equally important to avoid direct contact with the machine without proper insulation. The hot press can reach temperatures high enough to cause immediate and severe injury. Therefore, all interactions with the machine, including adjusting settings or placing materials, should be conducted with appropriate protective gear. This not only includes gloves but also may extend to heat-resistant aprons and face shields, depending on the specific requirements of the experiment.
To further enhance safety, operators should be trained to recognize the signs of overheating and know how to respond effectively. Regular maintenance of the hot press, including checking for worn or damaged insulation, is also vital to ensure that the machine remains safe to operate. By adhering to these practices, operators can significantly reduce the risk of heat-related injuries and ensure a safer working environment.
Post-Operation Cleanup
After completing the lamination experiment and ensuring that the flat-plate hot press will not be used for an extended period, it is crucial to perform a thorough post-operation cleanup. This step is essential to maintain the machine's functionality and ensure safety for future use.

Firstly, turn off the machine to prevent any accidental operation or overheating. This step is non-negotiable as it ensures that the machine is not left in an active state, which could pose risks to both the equipment and the personnel.
Next, clean the work area. This involves removing any debris, residual materials, or spillages that may have occurred during the experiment. Use appropriate cleaning agents and tools to ensure that the surface of the hot press and the surrounding area are free from contaminants. This not only helps in preventing contamination of future experiments but also extends the lifespan of the equipment by reducing wear and tear caused by residual materials.
Additionally, inspect the machine for any signs of wear or damage that may have occurred during the operation. This proactive measure helps in identifying potential issues early, preventing costly repairs in the future. Ensure that all components are functioning correctly and that there are no loose parts or connections that could compromise the machine's performance.
Finally, document the cleanup process. Keeping a log of the post-operation activities can be beneficial for future reference, especially in cases where the machine's performance or maintenance history needs to be reviewed. This documentation can also serve as a training tool for new operators, ensuring that they are aware of the proper procedures for post-operation cleanup.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the flat-plate hot press is ready for its next use, maintaining both its operational efficiency and safety standards.
Operational Steps
Startup Preparation
Before initiating the hot pressing process, it is crucial to ensure that both the hot press and the sample surfaces are meticulously cleaned. This step is essential to prevent any contaminants from affecting the quality of the lamination. Once the surfaces are clean, proceed to turn on the power supply.
Setting the required temperature is the next critical step. This should be done according to the specific requirements of the sample to be laminated. It is advisable to monitor the actual temperature closely to avoid any deviations that could compromise the experiment's outcome. Additionally, ensuring that the temperature is stable before proceeding can help in achieving consistent results.
To summarize, the startup preparation involves:
- Cleaning the hot press and sample surfaces.
- Turning on the power supply.
- Setting and monitoring the required temperature accurately.
Material Preparation
To ensure the successful execution of lamination experiments using a flat-plate hot press, meticulous preparation of the materials is essential. This process begins with selecting the appropriate release films, such as silicone oil papers or PET release films, which are crucial for preventing the adhesion of the laminated materials to the hot press plates.
-
Cutting the Release Films: The first step involves cutting the silicone oil papers or PET release films to the required dimensions. This ensures that the films fit perfectly onto the metal plates, providing an even surface for the application of the solution.
-
Applying the Solution: Once the release films are cut, the next step is to apply the solution uniformly onto the films. This solution is typically a mixture of the materials to be laminated, and its application must be precise to ensure consistent results.
-
Pressing with Metal Plates: After the solution is applied, the release films are placed onto the metal plates. These plates are then pressed together using the hot press, which applies both heat and pressure to the materials. This step is critical for ensuring that the solution is evenly distributed and that the materials bond correctly.
The preparation of these materials is a foundational step in the lamination process, directly influencing the quality and success of the experiment. Proper execution of these steps ensures that the subsequent phases of the experiment, such as heating and post-processing, can proceed smoothly and effectively.
Material Heating
Place the prepared materials on the heated workbench with precision. Begin by adjusting the pressure settings to ensure uniformity in the heating process. Preheat the materials to the required temperature, carefully monitoring for any signs of overflow. This step is crucial to prevent material degradation or contamination.
Once preheating is complete and no overflow is detected, apply the necessary pressure to the materials. Set the timer according to the specific requirements of the experiment. Throughout this process, maintain vigilance to ensure that the materials are being heated evenly and effectively, thereby optimizing the lamination results.
Post-Processing
After completing the lamination experiment, it is crucial to follow a systematic post-processing routine to ensure the longevity and efficiency of the flat-plate hot press. This process begins with the immediate shutdown of the machine. Turning off the power not only conserves energy but also prevents accidental overheating or damage to the equipment.
Once the machine is off, the next step involves a thorough cleaning of any debris or residue that may have accumulated during the experiment. This is particularly important for maintaining the integrity of future experiments. Debris can cause uneven pressure distribution, leading to suboptimal results in subsequent tests. Therefore, using appropriate cleaning tools and techniques is essential to remove all traces of materials from the press surfaces.
Additionally, ensuring that the hot press is in a state of readiness for future use involves more than just cleaning. Operators should perform a quick inspection to check for any signs of wear or damage. This includes examining the heating elements, pressure mechanisms, and any other critical components. Addressing any issues promptly can prevent more significant problems down the line.
To facilitate this inspection, a checklist can be employed. This checklist should include items such as:
- Power Supply: Confirm that the power is fully disconnected.
- Surface Cleanliness: Verify that all surfaces are free from debris and residue.
- Component Integrity: Check for any visible signs of wear or damage.
- Safety Features: Ensure that all safety mechanisms are functioning correctly.
By adhering to these post-processing steps, operators can ensure that the flat-plate hot press remains in optimal condition, ready to support the next round of experiments with precision and safety.
Safety Precautions for Hot Press Operation
Operational Safety
To ensure operational safety during the use of a flat-plate hot press, it is imperative to adhere to several critical guidelines. Avoid placing hands in the hot press plate at any time, as the high temperatures can cause severe burns. This precaution is particularly crucial when the press is in operation, as the plates can reach temperatures that are unsafe for human contact.
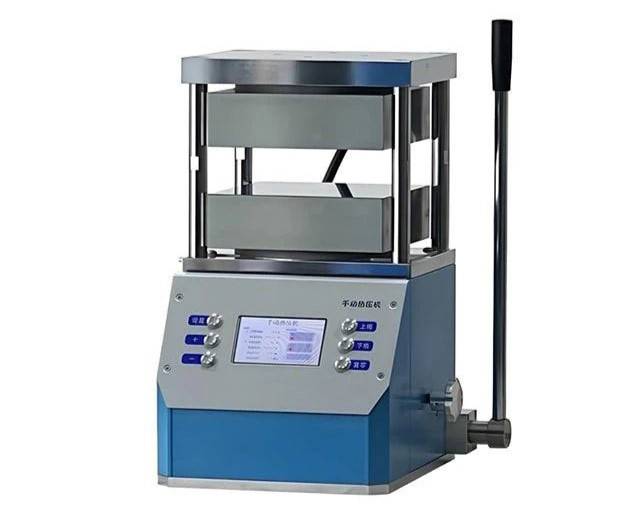

Ensure the operator remains at the station during operation to monitor the process closely. This practice allows for immediate response to any unexpected events, such as material overflow or mechanical malfunctions. Staying vigilant ensures that any issues can be addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of accidents.
| Safety Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Avoid Hand Contact | Do not place hands in the hot press plate to prevent burns. |
| Operator Presence | Maintain an operator at the station to monitor and respond to any issues. |
By following these safety measures, the risk of accidents and injuries is significantly reduced, ensuring a safer working environment for all personnel involved in the lamination experiments.
Preheating Procedure
The preheating procedure is a critical step in ensuring the effectiveness and safety of the hot pressing process. To begin, close the press plate securely to create an enclosed environment for the heating process. This step is essential as it allows for uniform heat distribution across the materials being pressed.
Next, increase the temperature without applying pressure. This phase allows the materials to reach the required temperature gradually, minimizing the risk of thermal shock and ensuring that the materials are uniformly heated. During this period, it is crucial to monitor the temperature closely to ensure it reaches the desired level without any significant deviations.
Once the required temperature is achieved, start the hot pressing process. At this point, the pressure can be applied, and the timer can be set according to the experimental requirements. This step transitions the process from preheating to active pressing, ensuring that the materials are subjected to both the necessary temperature and pressure for the desired outcome.
Throughout the preheating procedure, it is important to maintain vigilance and follow all safety protocols. This includes wearing appropriate protective gear, such as asbestos gloves, to protect against high temperatures, and ensuring that the operator remains at the station to monitor the process continuously. By adhering to these guidelines, the preheating procedure ensures that the subsequent hot pressing process is both effective and safe.
Material Centering
Ensuring that experimental materials are precisely centered on the movable table is a critical step to prevent biased pressure during the hot pressing process. This alignment is essential for achieving uniform stress distribution across the materials, which is crucial for the integrity and quality of the final product. If materials are not centered, the pressure applied during the pressing process could be uneven, leading to defects such as warping or delamination.
To achieve accurate centering, operators should follow these steps:
- Pre-Positioning Check: Before placing the materials on the table, visually inspect the table to ensure it is clean and free of any debris that could interfere with proper alignment.
- Material Alignment: Carefully place the materials on the table and use alignment tools, such as rulers or alignment pins, to ensure they are positioned correctly.
- Double-Check: After initial placement, double-check the alignment by viewing the materials from different angles to confirm they are centered.
- Secure Placement: Once centered, gently secure the materials to the table to prevent any movement during the pressing process.
By meticulously following these steps, operators can ensure that the experimental materials are perfectly centered, thereby avoiding any potential issues related to biased pressure and ensuring the success of the lamination experiment.
Machine Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the hot press is crucial to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Cleaning is a fundamental aspect of this maintenance routine. After each use, it is essential to remove residues promptly from the hot press surfaces. This practice prevents the buildup of contaminants that could interfere with the even distribution of stress during subsequent operations.

Moreover, maintaining a clean hot press helps in preventing cross-contamination between different samples. Residues left behind can degrade the quality of future experiments, leading to inconsistent results. By adhering to a strict cleaning schedule, you can ensure that the hot press operates efficiently and reliably, contributing to the overall success of your lamination experiments.
In addition to cleaning, periodic inspections should be conducted to identify any wear and tear or potential issues. This proactive approach allows for timely repairs, preventing minor problems from escalating into significant malfunctions. Regular maintenance not only enhances the machine's performance but also ensures the safety of the operator and the integrity of the experiments.
Monitoring and Cleaning
Regular monitoring and cleaning are essential to maintain the integrity and functionality of the flat-plate hot press. During operation, it is crucial to frequently observe both the veneer and the steel plate for any signs of abnormalities. These abnormalities could include warping, discoloration, or residue buildup, which can significantly affect the quality of the lamination process.
To ensure optimal performance, the steel plate should be cleaned as necessary. This involves removing any debris or residue that may have accumulated during the pressing process. Cleaning the steel plate not only helps in preventing contamination but also ensures even stress distribution across the surface, which is vital for achieving uniform lamination results.
| Monitoring Points | Cleaning Steps |
|---|---|
| Check for warping or deformation | Use appropriate cleaning tools to remove debris |
| Look for discoloration or unusual marks | Ensure the surface is free from residue |
| Inspect for residue buildup | Regularly clean to maintain even stress distribution |
By adhering to these monitoring and cleaning practices, operators can significantly enhance the safety and efficiency of the flat-plate hot press, ensuring that each lamination experiment yields high-quality results.
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
Related Articles
- Manual Lab Hydraulic Pellet Press: Comprehensive Guide to High-Quality Pellet Preparation
- Guidelines for Safe Operation and Procedures of Flat-Plate Hot Press in Lamination Experiments
- Optimizing Laboratory Analysis with Split Automatic Heated Lab Pellet Press
- Manual Hydraulic Presses for Laboratory Use: A Comprehensive Guide
- Hydraulic Heated Lab Pellet Press: Comprehensive Guide to Selection and Usage
















