Table of Contents
- Introduction to Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
- Components of a Vacuum Hot Press Furnace
- Benefits of Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
- Applications of Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
- Types of Heating Elements and Pressurization Methods
- Material Processing in Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces in Various Industries
- Conclusion
Introduction to Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces (VHPFs) revolutionize material processing by combining the principles of vacuum, heat, and pressure. These furnaces are designed to achieve precise temperature control and create a contamination-free environment, allowing for the creation of high-performance materials. VHPFs offer significant advantages over conventional furnaces, including uniform heating, reduced contamination, enhanced metallurgical properties, rapid cooling, and computer-controlled processes for repeatability. Their applications span various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, where their ability to create advanced materials with exceptional properties is crucial.
Components of a Vacuum Hot Press Furnace
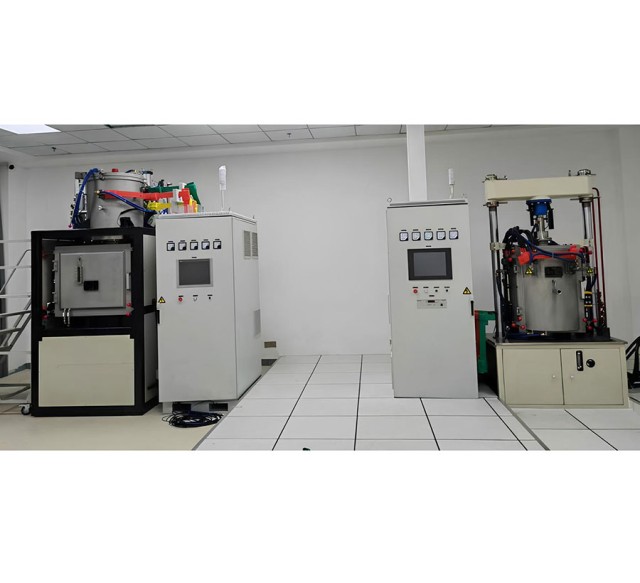
The vacuum hot press furnace is a versatile equipment widely used in various industrial applications. It consists of multiple essential components that work together to achieve the desired heating and pressurization conditions. The primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace include:
-
Furnace Body and Door: The furnace body forms the main structure of the furnace, providing a sealed chamber for the heating process. It is typically made of durable materials such as stainless steel or heat-resistant alloys. The furnace door provides access to the chamber and is designed to maintain the vacuum integrity during operation.
-
Heating and Heat Preservation System: This system is responsible for generating and maintaining the desired temperature within the furnace chamber. It consists of heating elements, insulation materials, and temperature sensors. The heating elements can be electric resistance heaters, induction coils, or gas burners, depending on the specific application. The insulation materials minimize heat loss and ensure temperature uniformity within the chamber.
-
Vacuum System and Air Charging System: The vacuum system creates and maintains a vacuum environment within the furnace chamber. It typically comprises a vacuum pump, vacuum gauges, and valves. The vacuum pump extracts air from the chamber, reaching pressures as low as 10^-6 Torr, enabling the removal of gases and impurities that could affect the heating process. The air charging system allows for the controlled introduction of air or other gases into the chamber when necessary.
-
Water Cooling System and Pressure System: The water cooling system circulates water through the furnace body and door to dissipate heat and prevent overheating. It maintains the integrity of the furnace components and ensures safe operation. The pressure system applies pressure to the chamber, typically using hydraulic or pneumatic means. This pressure helps to distribute the force evenly during the pressing process and achieve the desired compaction or bonding.
-
Control System: The control system monitors and regulates the various parameters of the furnace operation, including temperature, pressure, vacuum level, and heating/cooling cycles. It often employs programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or distributed control systems (DCSs) to automate the process and ensure precise control.
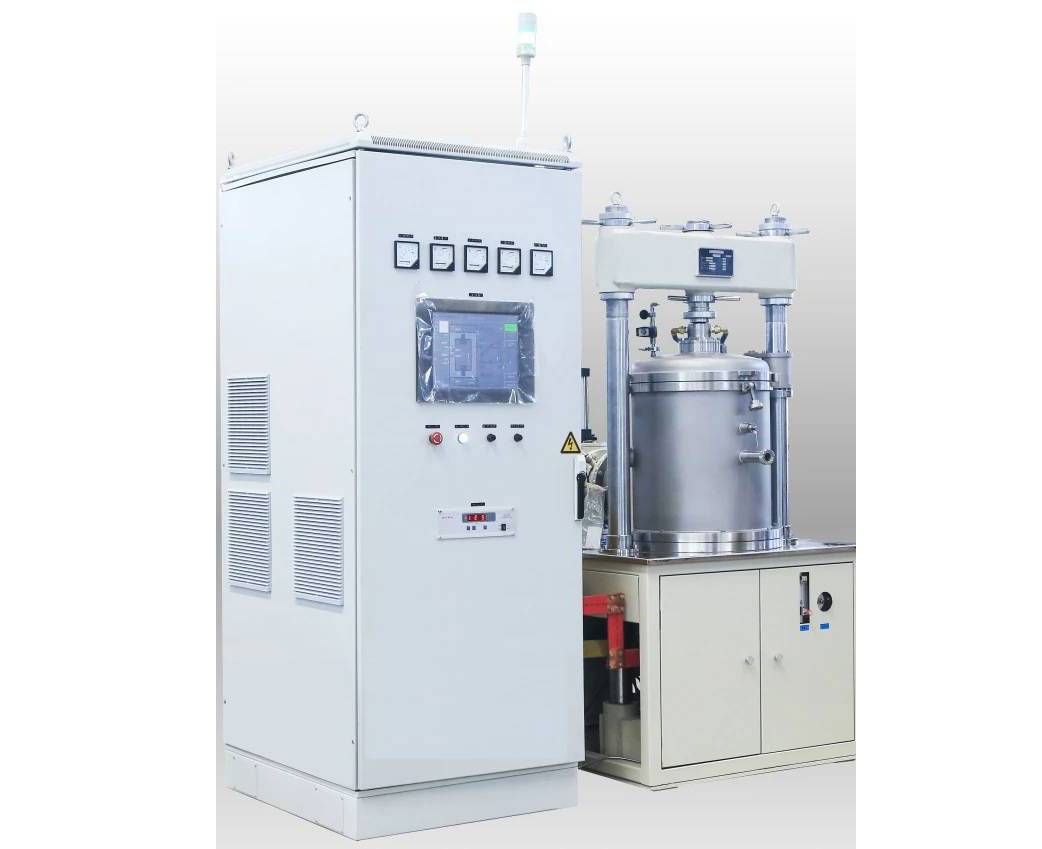

In addition to these essential components, vacuum hot press furnaces may also incorporate additional features or accessories depending on specific application requirements. These can include:
- Atmosphere Control System: Allows for the introduction and control of specific gases within the furnace chamber to create a controlled atmosphere for specialized processes.
- Gas Quenching System: Enables rapid cooling of the workpiece by introducing inert gases into the chamber after the heating process.
- Data Acquisition and Analysis System: Records and analyzes process data for monitoring, optimization, and quality control purposes.
Understanding the components and their functions is crucial for operating and maintaining vacuum hot press furnaces effectively. Proper selection and configuration of these components ensure optimal performance, safety, and reliability in various industrial applications.
Benefits of Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
Vacuum hot press furnaces offer a unique set of advantages over traditional furnaces, making them ideal for a wide range of industrial applications. These benefits include:
Uniform and Precisely Controlled Temperatures: Vacuum furnaces create a controlled environment that allows for precise temperature control within the heating zone. This is achieved by surrounding the heating zone with insulation or thermal barriers, ensuring uniform heat distribution throughout the chamber.
Reduced Contamination of Products: Vacuum furnaces operate in a vacuum environment, which effectively eliminates the presence of oxygen and other gases that can contaminate the products being heated. This results in reduced oxidation and other forms of contamination, leading to higher purity end products.
Enhanced Metallurgical Properties: Vacuum heat treatment prevents oxidation and minimizes the risk of distortion, resulting in improved mechanical properties of the treated materials. It enhances the hardness, strength, and wear resistance of metals while preserving their dimensional stability.
Rapid Cooling Capabilities: Vacuum furnaces allow for rapid cooling (quenching) of the product, which can significantly shorten the process cycle time. This rapid cooling process helps to preserve the desired metallurgical properties and prevent unwanted phase transformations.
Computer-Controlled Processes for Repeatability: Vacuum furnaces are often equipped with computer-controlled systems that ensure precise temperature control, process monitoring, and repeatability. This automation eliminates human error and ensures consistent, high-quality results across multiple production runs.
Applications of Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
Vacuum hot press furnaces are versatile equipment with a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
-
Aerospace Industry: Vacuum heat treatment is employed in the aerospace industry to enhance the performance and durability of critical components. Processes like solution annealing, aging, and stress relieving are used to achieve desired mechanical properties in materials such as titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and stainless steels.
-
Automotive Industry: Vacuum furnaces are extensively used in the automotive industry for heat treating components like gears, bearings, springs, and engine parts. Through processes like carburizing, nitriding, and quenching, vacuum furnaces impart superior hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength to these components.
-
Powder Metallurgy: Vacuum hot press furnaces are ideal for high-temperature hot forming of new materials such as powder metallurgy and functional ceramics. They enable the sintering of transparent ceramics, industrial ceramics, and other metals, as well as alloy materials composed of refractory metals.
-
High-Temperature Sintering: Vacuum hot press furnaces are suitable for high-temperature sintering of ceramic materials like silicon carbide (SiC) and silicon nitride (Si3N4). These materials are used in a variety of high-temperature applications, such as cutting tools, abrasives, and heat-resistant components.
-
Heat Treatment of Powders and Compacts: Vacuum hot press furnaces can be used to heat treat powders and compacts at temperatures lower than the melting point of the main components. This process improves their strength through metallurgical combination between particles.
-
Consolidation and Densification of Materials: Vacuum hot press furnaces are used to consolidate and densify materials, improving their structural integrity and mechanical properties. This process is particularly useful for materials that are difficult to densify through conventional methods.
-
Brazing and Soldering: Vacuum hot press furnaces are used for brazing and soldering applications, where high temperatures and vacuum environments are required to create strong and reliable joints.
-
Single-Crystal Growth: Vacuum hot press furnaces are used in the growth of single crystals for various applications, including semiconductors, lasers, and optical components.
-
Research and Development: Vacuum hot press furnaces are used in research and development laboratories for various experimental purposes, including materials science, metallurgy, and ceramics engineering.

Types of Heating Elements and Pressurization Methods
A heating element is a device that converts electrical energy into heat energy. In industrial furnaces, heating elements are used to heat the furnace chamber and the materials inside it. There are many different types of heating elements available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Graphite heaters are made of graphite, a form of carbon that is highly conductive and resistant to heat. Graphite heaters can reach temperatures of up to 3,000°C and are often used in high-temperature applications, such as metalworking and glassblowing.
Molybdenum heaters are made of molybdenum, a metal that is also highly conductive and resistant to heat. Molybdenum heaters can reach temperatures of up to 2,500°C and are often used in applications where high temperatures are required, such as in the production of semiconductors and solar cells.
Induction heating is a method of heating that uses an alternating magnetic field to induce an electric current in the material to be heated. Induction heating is a very efficient method of heating and can be used to heat materials of all shapes and sizes.
One-way and two-way hydraulic pressurization are two methods of applying pressure to a material in a hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process. In one-way pressurization, the pressure is applied from one side of the material only. In two-way pressurization, the pressure is applied from both sides of the material. Two-way pressurization is more effective than one-way pressurization, but it requires more equipment and is more expensive.
The choice of heating element and pressurization method depends on the specific application. For example, a graphite heater would be a good choice for a high-temperature application, while an induction heater would be a good choice for a rapid heating application.
Material Processing in Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces
Vacuum hot press furnaces offer a controlled environment for material processing, enabling precise bonding, grain growth, and densification under high temperature, pressure, and vacuum conditions. This process enhances the properties of materials, resulting in reduced voids, grain boundaries, and overall volume shrinkage while increasing density.
The primary goal of vacuum hot pressing is to create compact polycrystalline sintered bodies with tailored microstructures. This technique is particularly advantageous for micro-powder products, as it effectively prevents grain growth and ensures the stability of the final product. For instance, in the production of near-nanometer cemented carbide, vacuum hot pressing has proven successful in restraining grain growth, leading to the formation of nanocrystalline products.
Vacuum hot press furnaces are classified based on their pressurization methods:
- Uniaxial Hot Pressing: Pressure is applied in one direction, typically perpendicular to the surface of the material.
- Isostatic Hot Pressing: Pressure is applied equally from all directions, resulting in uniform densification.
- Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Pressure is applied isostatically under high temperature conditions, promoting densification and eliminating internal voids.
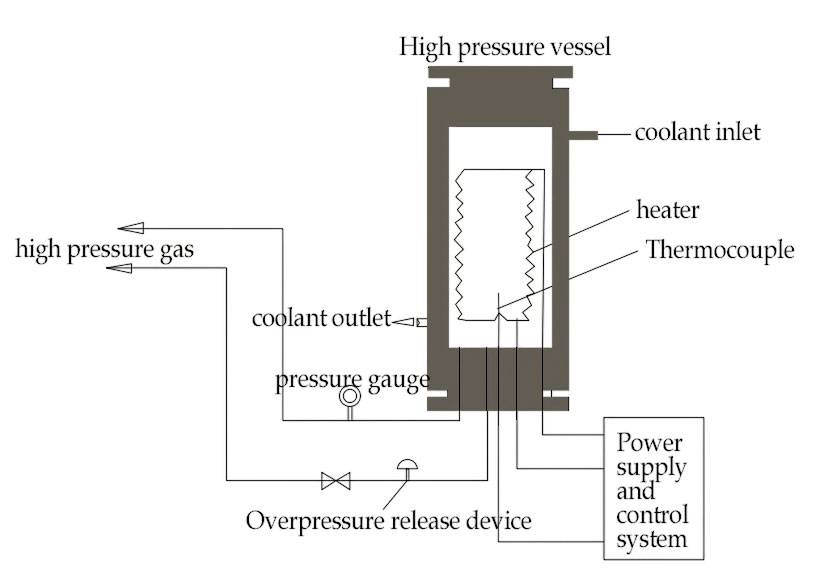
The benefits of vacuum hot pressing extend to various applications:
- Hot pressing sintering of metal and ceramic powders
- Fabrication of ceramic/metal composites and intermetallic compounds
- Diffusion welding process development
- Densification hot press sintering of oxygen/nitrogen/boron/carbon compounds and their mixtures
Vacuum hot pressing furnaces are composed of heating elements, pressurization systems, and a vacuum chamber. Heating elements, such as graphite or molybdenum heaters, provide the necessary temperature for the process. Pressurization can be achieved through hydraulic systems, enabling one-way or two-way pressurization.
The densification process in vacuum hot pressing furnaces involves plastic and viscous flow, diffusion, and creep. These mechanisms facilitate rapid densification and controlled microstructure formation. Under the combined effects of high temperature, pressure, and vacuum or atmosphere, raw material particles bond, grains grow, and voids and grain boundaries diminish. This process leads to the formation of dense, polycrystalline sintered bodies with enhanced mechanical, electronic, and thermal properties.
Vacuum Hot Press Furnaces in Various Industries
Vacuum hot press furnaces play a crucial role in diverse industries, enabling the precise manufacturing and heat treatment of advanced materials. Here are some key industries utilizing vacuum hot press furnaces:
Aerospace and Automotive Industries:
In the aerospace industry, vacuum hot press furnaces are employed to enhance the performance and durability of critical components. Heat treatment processes such as solution annealing, aging, and stress relieving are performed to achieve optimal mechanical properties in materials like titanium alloys, nickel-based superalloys, and stainless steels.
Similarly, in the automotive industry, vacuum furnaces are utilized for heat treating components such as gears, bearings, springs, and engine parts. Processes like carburizing, nitriding, and quenching impart superior hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength to these components.
Medical and Dental Applications:
Vacuum hot press furnaces are employed in the medical and dental fields to manufacture and process various materials. They are used to create dental implants, surgical instruments, and other medical devices made from materials like titanium, cobalt-chromium alloys, and bioceramics. Vacuum hot pressing ensures the production of high-density, biocompatible components with precise geometries.
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing:
In the electronics and semiconductor industries, vacuum hot press furnaces are utilized for the fabrication of electronic components and devices. They are used in processes such as sintering of ceramic substrates, bonding of semiconductor wafers, and encapsulation of microelectronic components. Vacuum environments are critical for preventing contamination and ensuring the reliability of these components.

Research and Development Laboratories:
Vacuum hot press furnaces are indispensable tools in research and development laboratories. They enable scientists and engineers to investigate the properties and behavior of advanced materials under controlled temperature and pressure conditions. Various materials, including novel ceramics, composites, and alloys, are processed using vacuum hot pressing to explore their potential applications.
Specific Applications:
Beyond the aforementioned industries, vacuum hot press furnaces are used in myriad other applications, including:
- Fabrication of high-temperature materials for aerospace and energy industries
- Production of cutting tools and wear-resistant components from materials like silicon nitride and boron carbide
- Sintering of transparent ceramics for optical and electronic applications
- Heat treatment of powders and compacts to improve their strength and properties
- Consolidation of nanomaterials and composites for advanced applications
Vacuum hot press furnaces offer exceptional capabilities for the precise manufacturing and processing of materials. Their ability to control temperature, pressure, and atmosphere enables the production of high-quality components with tailored properties for a wide range of industries.
Conclusion
Vacuum hot press furnaces are a revolutionary technology that has transformed material processing. These furnaces offer exceptional control over temperature and pressure, enabling the production of advanced materials with enhanced properties. Their ability to minimize contamination and achieve rapid cooling makes them ideal for industries demanding precision and quality. Vacuum hot press furnaces have revolutionized material processing, opening up new possibilities for innovation and technological advancements.
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
Related Articles
- Beyond Heat: Why Pressure is the Deciding Factor in Advanced Materials
- Comprehensive Guide to Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Application
- The Unseen Physics of Perfection: Mastering Heat, Pressure, and Time
- The War Against Voids: Mastering Material Density with Heat and Pressure
- The Physics of Perfection: Why a Vacuum Is the Material Scientist's Most Powerful Tool

















