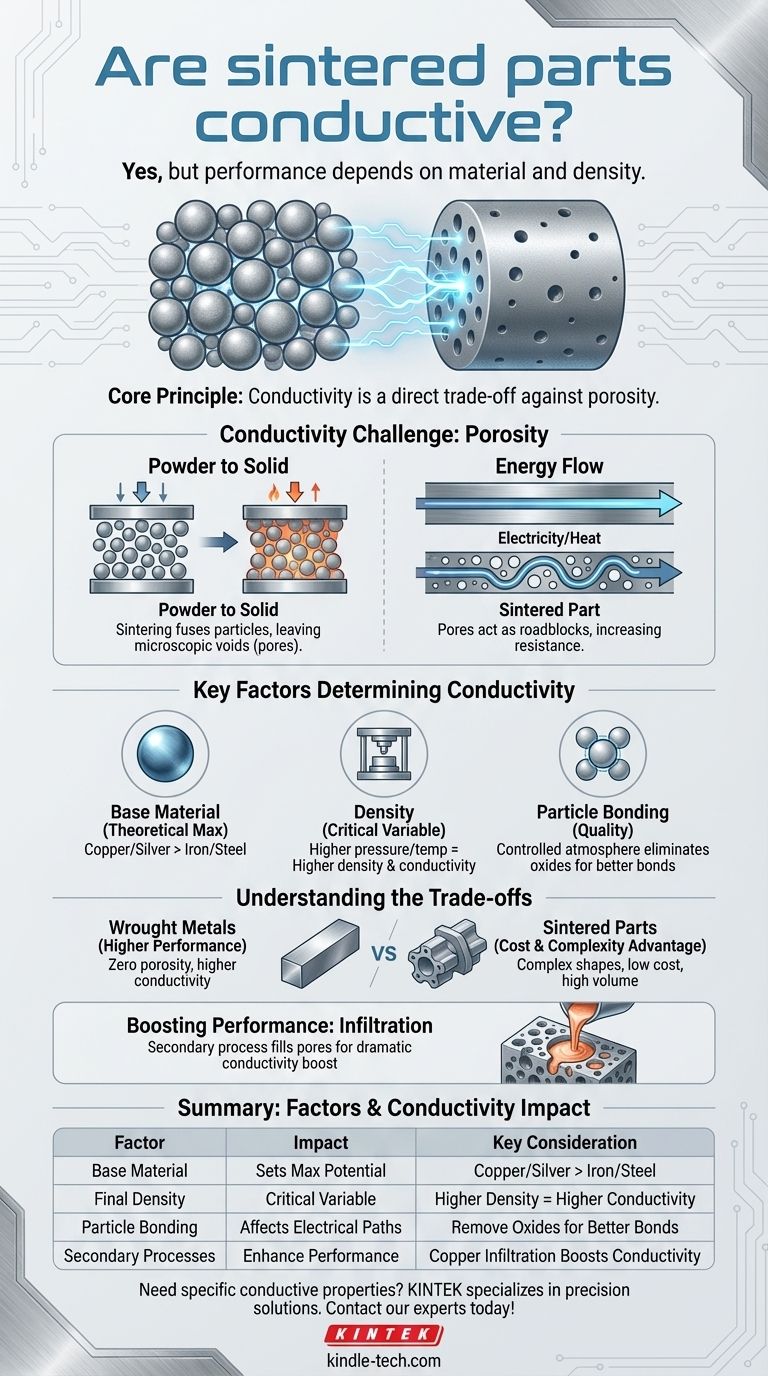
Yes, sintered parts can be highly conductive, but their performance depends entirely on the base material used and the final density of the part. Unlike a solid piece of metal, a sintered component is formed from pressed powder, which introduces porosity that can impede the flow of electrical and thermal energy.
The core principle is simple: conductivity in a sintered part is a direct trade-off against its porosity. While the base metal determines the maximum potential, the density achieved during the sintering process dictates the real-world performance.

Why Sintering Poses a Unique Conductivity Challenge
To understand the conductivity of a sintered part, you must first understand how it's made. The process inherently creates the primary obstacle that conductivity must overcome: voids.
From Powder to a Solid Part
Sintering is a manufacturing process that uses pressure and heat to bond metallic or ceramic powders into a solid, near-net-shape component. Crucially, the material is heated below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together at their contact points.
The Inevitable Reality of Porosity
This particle-fusing process almost always leaves microscopic voids, or pores, between the original powder grains. The total volume of these pores relative to the total volume of the part is known as its porosity.
How Pores Disrupt the Flow of Energy
Think of electricity or heat flowing through a solid metal bar as traffic on a multi-lane highway. Pores act like roadblocks or detours.
Electrons and heat must travel a longer, more convoluted path to navigate around these voids. This increases electrical resistance and reduces thermal conductivity compared to a fully dense, non-porous material made by casting or forging.
Key Factors That Determine Conductivity
Several variables allow engineers to control the final conductive properties of a sintered component. Understanding these is key to specifying a part that meets your needs.
The Base Material: The Theoretical Maximum
The single most important factor is the material itself. A part made from sintered copper or silver powder will always have a higher potential for conductivity than one made from sintered iron or steel powder. The base material sets the upper limit.
Density: The Most Critical Process Variable
For any given material, density is the dominant factor. A part sintered to 95% of its theoretical maximum density will be significantly more conductive than a part sintered to only 85% density. Higher pressures and temperatures during the process reduce porosity and increase density.
Particle Bonding and Surface Condition
The quality of the metallurgical bonds between particles is critical. If powder particles are coated in oxides, these insulating layers can prevent strong, conductive bonds from forming, even in a high-density part. Sintering in a controlled, reducing atmosphere (like hydrogen) is often used to eliminate these oxides and promote superior bonding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintered components are rarely chosen when absolute maximum conductivity is the sole objective. Their value comes from balancing performance with significant manufacturing advantages.
Performance Gap vs. Wrought Metals
A fully dense, wrought metal bar (one that has been forged or drawn) will almost always have higher electrical and thermal conductivity than a sintered part of the same alloy. This is simply because it has virtually zero porosity.
The Cost and Complexity Advantage
Sintering excels at producing complex, net-shape parts at a very low cost and high volume. It eliminates the need for expensive and wasteful machining operations, which is a major trade-off for a small reduction in conductivity in many applications.
Boosting Performance with Infiltration
For applications needing both a complex shape and higher conductivity, a secondary process called infiltration is used. The porous sintered part (typically iron) is heated with a lower-melting-point metal (typically copper), which wicks into the pores via capillary action, dramatically increasing density and conductivity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use a sintered part depends on the specific requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum conductivity: A wrought or cast component is often the most direct path, especially for simple geometries.
- If your primary focus is a complex shape at a low unit cost: Sintering is an exceptional choice, but you must specify the required density to ensure adequate conductive performance.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost, complex geometry, and good conductivity: A high-density sintered part or a copper-infiltrated component is likely the ideal solution.
- If your primary focus is specific magnetic properties: Sintering is a dominant technology for soft magnetic components, as porosity can be controlled to tune performance.
By understanding the relationship between material, density, and performance, you can confidently leverage the unique advantages of the sintering process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Conductivity | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Sets the theoretical maximum | Copper/silver offer higher potential than iron/steel |
| Final Density | Most critical process variable | Higher density (e.g., 95% vs. 85%) reduces porosity, increases conductivity |
| Particle Bonding | Affects quality of electrical paths | Controlled atmosphere sintering removes oxides for better bonds |
| Secondary Processes | Can enhance performance | Copper infiltration fills pores to boost conductivity significantly |
Need a sintered part with specific conductive properties? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for material testing and production. Our expertise ensures you get the right balance of conductivity, complex geometry, and cost-effectiveness for your laboratory or manufacturing needs. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how we can enhance your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum furnace environment influence sintered Ruthenium powder? Achieve High Purity and Theoretical Density
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury
- How much psi can a hydraulic press make? From 2,000 PSI to over 50,000 PSI Explained
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production



















