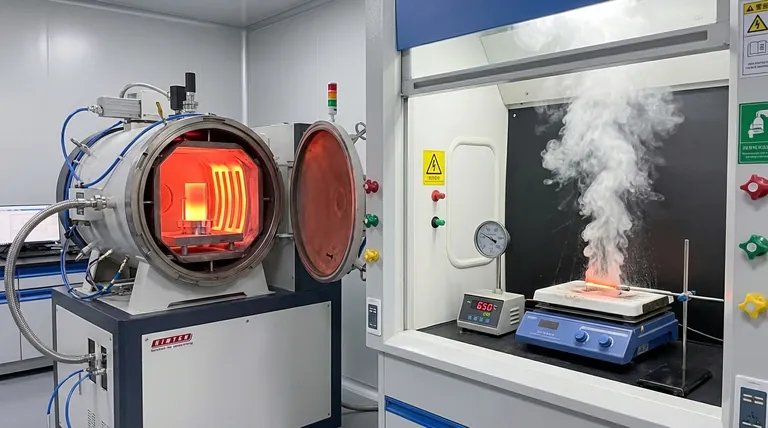
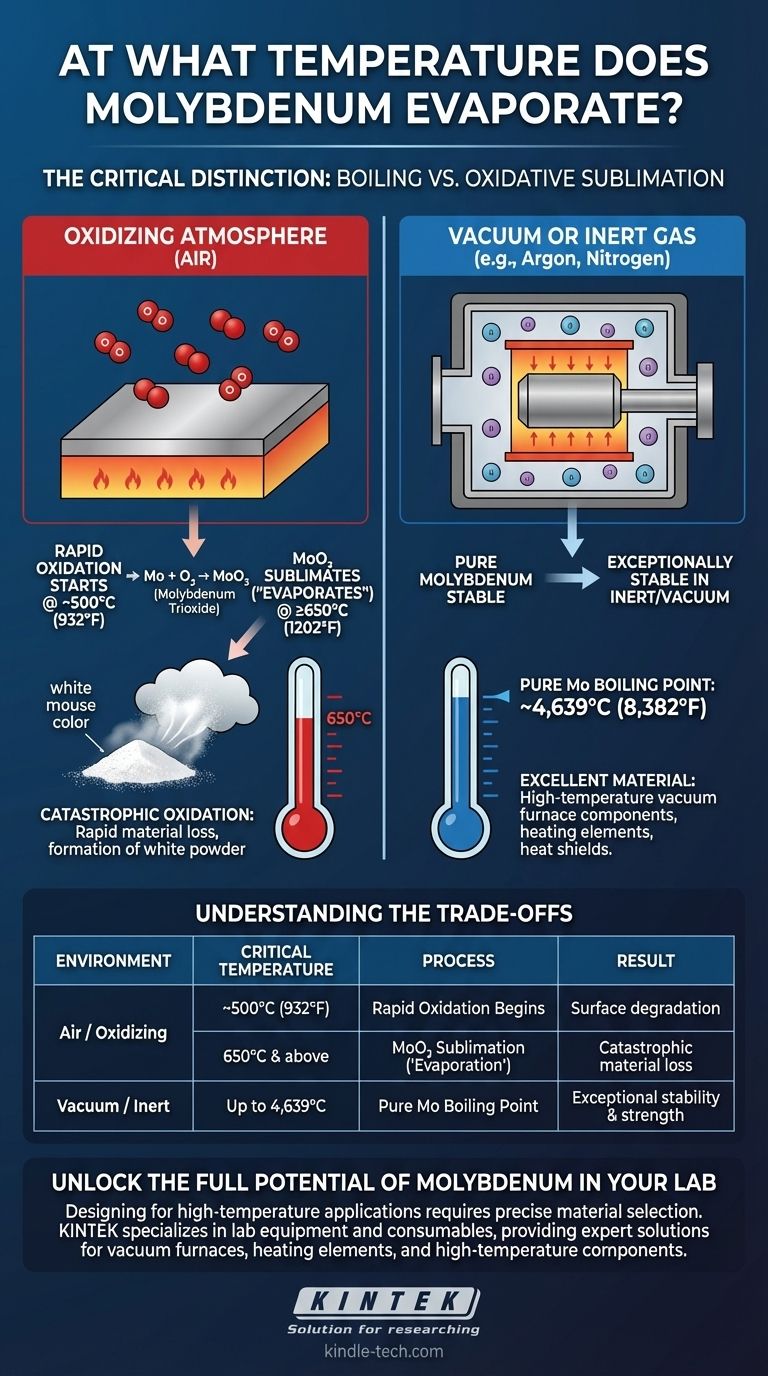
Under oxidizing conditions, molybdenum begins to form a volatile oxide that evaporates at temperatures of 650°C (1202°F) and higher. This phenomenon, often mistaken for the metal itself boiling, is a chemical reaction with oxygen that leads to rapid material loss and the formation of white molybdenum trioxide powder.
The core issue is not the evaporation of pure molybdenum, which has an extremely high boiling point. The practical temperature limit in air is dictated by its reaction with oxygen to form molybdenum trioxide (MoO₃), which then sublimates at a much lower temperature.

The Critical Distinction: Boiling vs. Oxidative Sublimation
To effectively use molybdenum, you must understand the difference between its intrinsic properties in a vacuum and its behavior when exposed to air at high temperatures.
The Boiling Point of Pure Molybdenum
In an inert or vacuum environment, pure molybdenum is exceptionally stable. Its actual boiling point is approximately 4,639°C (8,382°F).
This makes it an excellent material for high-temperature vacuum furnace components, evaporation boats, and other applications shielded from oxygen.
The Role of Oxygen
When heated in the presence of oxygen, a two-stage degradation process begins. The reference indicates that rapid oxidation starts at temperatures of 500°C (932°F) or higher.
During this stage, oxygen from the atmosphere reacts with the surface of the metal, forming a layer of molybdenum trioxide (MoO₃).
Evaporation of Molybdenum Trioxide (MoO₃)
This newly formed oxide is the true source of the "evaporation." Molybdenum trioxide is a volatile substance that begins to sublimate (turn from a solid directly to a gas) at temperatures around 650°C (1202°F).
This process is often called "catastrophic oxidation" because it quickly removes material from the component, which appears to simply vanish into a cloud of white powder, described as a "white mouse color."
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Limits
The environmental conditions completely define the operational limits and viability of using molybdenum for a high-temperature application.
The Weakness in Oxidizing Atmospheres
The primary limitation of molybdenum is its poor resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Using an unprotected molybdenum component in air above 500°C is not advisable for any long-term application.
Significant material loss will begin, accelerating as the temperature approaches and exceeds 650°C. This leads to component failure.
The Strength in Vacuum or Inert Gas
Conversely, in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen), molybdenum retains its strength and structural integrity to very high temperatures, making it a premier refractory metal.
This is why molybdenum is a standard material for heating elements, heat shields, and structural parts inside vacuum furnaces.
The Role of Alloying
Alloying molybdenum, such as by doping it with lanthanum oxide (ML) or yttrium oxide (MY), primarily enhances other properties.
These additions improve ductility, corrosion resistance at lower temperatures, and mechanical workability. However, they do not fundamentally prevent the high-temperature oxidation process.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your operating environment is the single most important factor when designing with molybdenum.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature use in a vacuum or inert gas: Molybdenum is an outstanding choice, remaining stable far beyond the temperatures seen in most industrial processes.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature use in air or an oxidizing environment: You must either keep the service temperature below 500°C or specify a protective coating to prevent catastrophic oxidation.
Ultimately, understanding your environment is the key to harnessing the remarkable high-temperature strength of molybdenum.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Critical Temperature | Process | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air / Oxidizing | ~500°C (932°F) | Rapid Oxidation Begins | Surface degradation |
| Air / Oxidizing | 650°C (1202°F) & above | MoO₃ Sublimation ('Evaporation') | Catastrophic material loss |
| Vacuum / Inert Gas | Up to 4,639°C (8,382°F) | Pure Molybdenum Boiling Point | Exceptional stability and strength |
Unlock the full potential of molybdenum in your lab.
Designing for high-temperature applications requires precise material selection. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for vacuum furnaces, heating elements, and high-temperature components. We help you select the right materials and configurations to ensure performance and longevity, whether you're working in oxidizing or inert environments.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your project's success.
Get in touch with our experts →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















