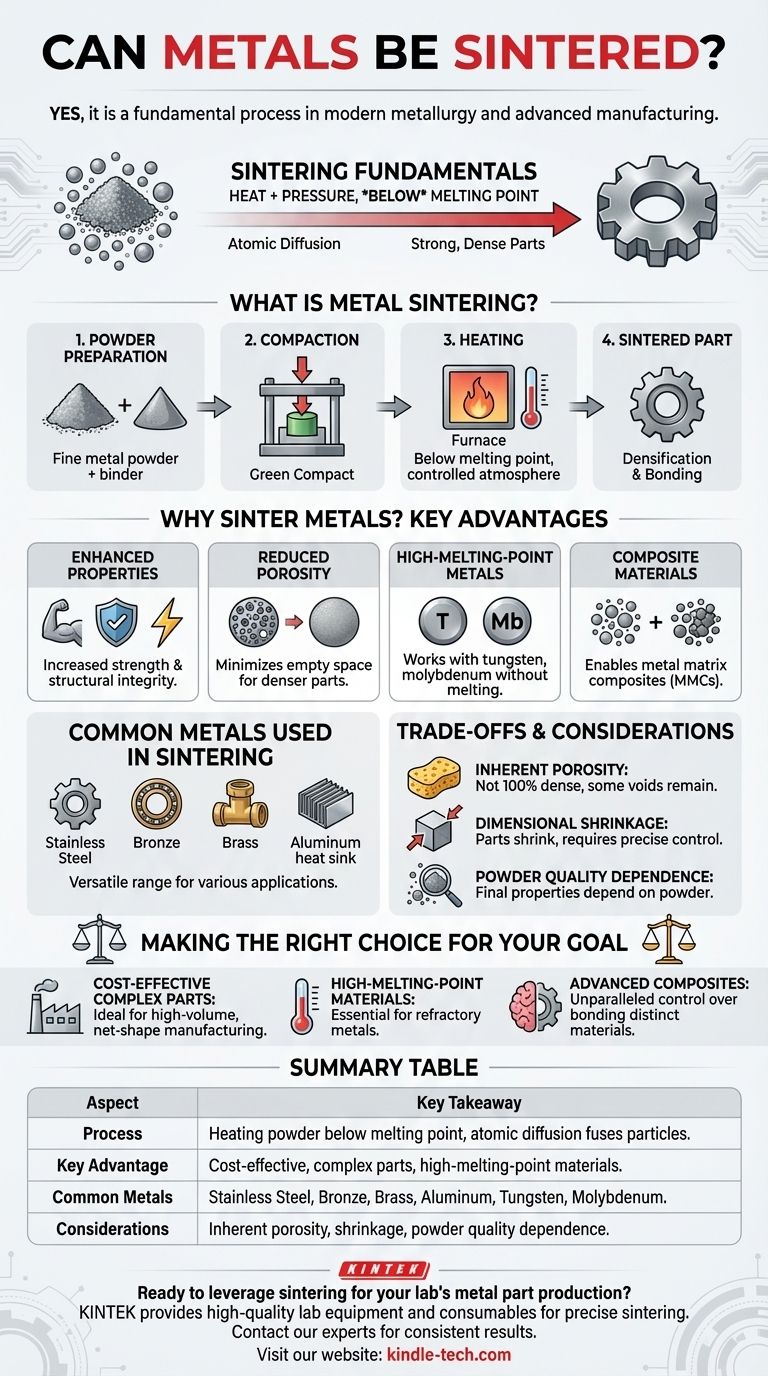
Yes, not only can metals be sintered, but it is a fundamental process in modern metallurgy and advanced manufacturing. Sintering is a thermal treatment applied to a powder compact to impart strength and integrity. The process heats the material in a controlled atmosphere to a temperature below its melting point, causing the individual metal particles to bond and form a solid, coherent mass.
Sintering is a powerful manufacturing method that fuses metal powders together below their melting point. The core principle is not melting, but using heat to drive atomic diffusion, creating strong, dense parts with highly controlled physical properties.

What is Metal Sintering? A Look at the Process
From Powder to Solid Part
The process begins with a fine metal powder, which may be mixed with a polymeric binder. This mixture is then compacted into a desired shape, often under high pressure, to create what is known as a "green compact."
The Role of Heat and Atomic Diffusion
This green compact is then heated in a furnace to a specific temperature below the metal's melting point. At this temperature, atoms from the metal particles migrate across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together and creating a solid piece.
Controlling the Atmosphere
This process must occur in a controlled environment, such as a vacuum or under a protective shielding gas. This prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions on the metal's surface, which would interfere with the atomic bonding between particles.
Why Sinter Metals? Key Advantages
Enhanced Physical Properties
Sintering significantly improves a material's strength, durability, and conductivity. By fusing the particles, the process creates a dense and robust structure.
Reducing Porosity
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce the empty space, or porosity, between the initial powder particles. This densification is directly responsible for the increase in the final part's structural integrity.
Manufacturing with High-Melting-Point Metals
Sintering is exceptionally valuable for metals with extremely high melting points, like tungsten or molybdenum. It allows for the creation of solid parts without having to achieve the massive energy inputs required for complete melting.
Creating Composite Materials
The process is vital for producing metal matrix composites (MMCs). It allows for the even distribution and bonding of reinforcement materials (like ceramic fibers or particles) within a metal matrix, creating materials with superior custom properties.
Common Metals Used in Sintering
Versatile and Widely Used Metals
A broad range of common metals and alloys are used in sintering due to the process's versatility.
Examples include stainless steel, bronze, brass, and aluminum. Each offers a different combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Inherent Porosity
While sintering dramatically reduces porosity, achieving 100% density is difficult. For applications requiring absolute maximum strength and zero voids, alternative methods like forging might be more suitable.
Dimensional Shrinkage
The part will shrink as the voids between particles are eliminated during the sintering process. This shrinkage must be precisely calculated and controlled to achieve the desired final dimensions.
Dependence on Powder Quality
The final properties of a sintered part are highly dependent on the quality, size, and shape of the initial metal powder. Inconsistency in the powder can lead to defects in the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a manufacturing process requires balancing material properties, complexity, and cost. Sintering is a powerful option when its specific strengths are aligned with your project's needs.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of complex parts: Sintering is an excellent choice for high-volume manufacturing, as it can produce net-shape or near-net-shape parts with minimal machining.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials: Sintering is often the most practical and sometimes the only viable method for creating solid components from materials like tungsten.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced composite materials: Sintering provides unparalleled control over bonding distinct materials together to achieve custom-engineered properties.
Ultimately, metal sintering is a versatile and precise manufacturing tool for creating robust components when its principles are correctly applied.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating metal powder below its melting point to fuse particles via atomic diffusion. |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective production of complex, high-strength parts; essential for high-melting-point metals. |
| Common Metals | Stainless steel, bronze, brass, aluminum, tungsten, molybdenum. |
| Considerations | Inherent porosity, dimensional shrinkage, high dependence on initial powder quality. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's metal part production? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for precise sintering processes. Whether you are working with common alloys or advanced high-melting-point metals, our solutions ensure consistent, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering and material science needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity and Performance
- What temperature does tungsten carbide sinter at? Master the 1350°C-1500°C Liquid-Phase Sintering Process
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics



















