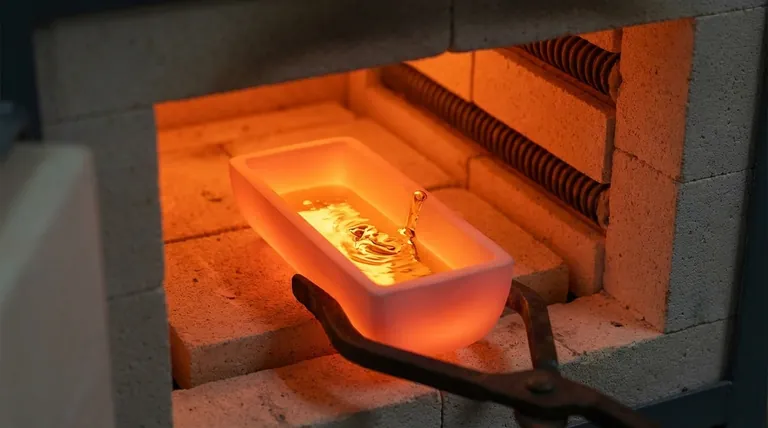
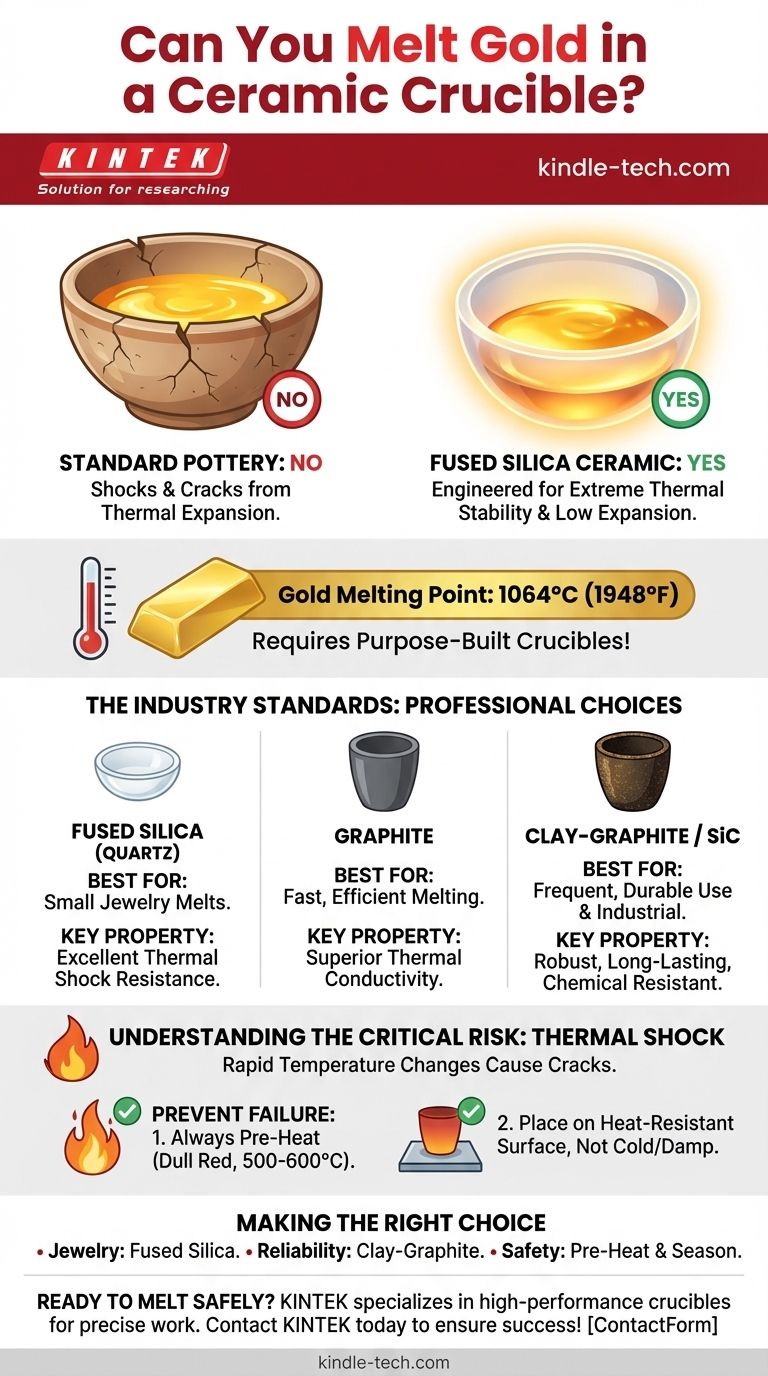
Yes, but only with a specific type of ceramic. While you cannot use a standard pottery bowl or generic ceramic dish, you can melt gold in a fused silica ceramic crucible. These are engineered to withstand the extreme temperature (1064°C / 1948°F) and, more importantly, to resist catastrophic failure from rapid temperature changes, a phenomenon known as thermal shock.
The success of melting gold hinges not on whether the crucible is "ceramic," but on whether the specific material is engineered for metallurgical work. While fused silica ceramic is a viable option, professionals often prefer graphite or clay-graphite crucibles for their superior durability and thermal properties.

Why Not All Crucibles Are Created Equal
The term "ceramic" covers a vast range of materials with vastly different properties. Understanding this distinction is the first step toward a safe and successful melt.
The Problem with Standard Ceramics
A common ceramic bowl or piece of pottery is not vitrified in a way that can handle the stress of molten metal. When heated rapidly to over 1000°C, the material will expand unevenly, build up internal stress, and crack or shatter. This failure is a result of high thermal expansion.
Technical Ceramics: The Fused Silica Exception
Fused silica (also called fused quartz) is a high-purity glass ceramic designed for extreme thermal stability. Its key property is an incredibly low coefficient of thermal expansion.
This means it expands and contracts very little when heated or cooled, making it highly resistant to thermal shock. Small, dish-like fused silica crucibles are very common among jewelers for melting small quantities of gold and silver.
The Challenge of Gold's Melting Point
Gold melts at 1064°C (1948°F). This temperature is far beyond the limits of household materials and many industrial ones. A proper crucible must not only contain this heat but also remain chemically inert, meaning it won't react with or contaminate the molten gold.
The Industry Standards: Graphite and Silicon Carbide
While fused silica works well, most professionals and serious hobbyists rely on crucibles made from graphite-based materials for their superior performance and longevity.
Graphite Crucibles: The Professional's Choice
Pure graphite crucibles offer excellent thermal conductivity. This allows for fast, even heating of the metal, which reduces melting time and energy use. Graphite is also self-lubricating, making it easier to pour the molten gold without it sticking.
Clay-Graphite and Silicon Carbide: The Workhorses
Clay-graphite crucibles are a durable and cost-effective mixture that combines the heat resistance of graphite with the structural integrity of clay. They are thicker, heavier, and can withstand more physical abuse than pure graphite or silica.
Silicon carbide is another extremely durable material that offers excellent longevity and resistance to chemical erosion, making it a top choice for industrial-scale operations.
Understanding the Critical Risk: Thermal Shock
The single greatest risk to your crucible, regardless of material, is thermal shock. This is the primary cause of crucible failure.
What Is Thermal Shock?
Thermal shock occurs when a material experiences a rapid change in temperature, causing different parts of it to expand or contract at different rates. This creates immense internal stress that can lead to cracking. Think of a hot glass dish shattering when placed in cold water.
How to Prevent Crucible Failure
The most important practice is to always pre-heat your crucible. Before introducing metal, gently heat the empty crucible until it glows with a dull red color (around 500-600°C). This drives out any moisture and minimizes the temperature difference when you begin the main melt, dramatically reducing the risk of a crack.
Equally important, never place a red-hot crucible on a cold or damp surface. Always place it on a designated heat-resistant brick or stand.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Your goal determines the best tool for the job. There is no single "best" crucible, only the one that is most appropriate for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is small, occasional melts for jewelry: A fused silica melting dish is an excellent, clean-working, and widely available choice.
- If your primary focus is reliability and frequent use: A clay-graphite or pure graphite crucible offers superior durability and a longer service life.
- If your primary focus is safety and preventing failure: Always pre-heat your crucible before every melt and ensure it is properly seasoned according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Ultimately, selecting the correct, purpose-built crucible is the foundation for a safe and successful melt.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Best For | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Fused Silica | Small, occasional jewelry melts | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Graphite | Fast, efficient melting | Superior thermal conductivity |
| Clay-Graphite | Frequent, durable use | Cost-effective and robust |
| Silicon Carbide | Industrial-scale operations | Extreme durability and chemical resistance |
Ready to Start Melting Gold Safely and Efficiently?
Choosing the right crucible is just the first step. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles designed for precise metallurgical work. Whether you're a jeweler, a researcher, or a hobbyist, we have the durable, reliable tools you need for successful melting.
Let our experts help you select the perfect crucible for your specific application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your needs and ensure your next melt is a success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- How much heat can a graphite crucible handle? Practical limits from 500°C to 3,600°C explained
- Why is the use of high-quality crucibles and ceramic consumables essential for the thermal analysis of polymer materials?
- What are crucible furnaces where are they preferred and why? Unmatched Flexibility for Small-Batch Melting
- Why is graphite used in making refractory crucibles? For Superior High-Temperature Melting Performance
- Why is it necessary to use a zirconia crucible for LLZO sintering? Ensure High-Purity Solid-State Battery Materials
- What is the importance of high-purity ceramic crucibles? Ensure Accuracy in Subcritical Crack Growth Studies
- Why are zirconia crucibles utilized for LSTH solid electrolytes? Ensure Pure-Phase Synthesis at 1450°C
- What are the advantages of using graphite crucibles in 3000°C experiments? Achieve Superior Purity and Performance



















