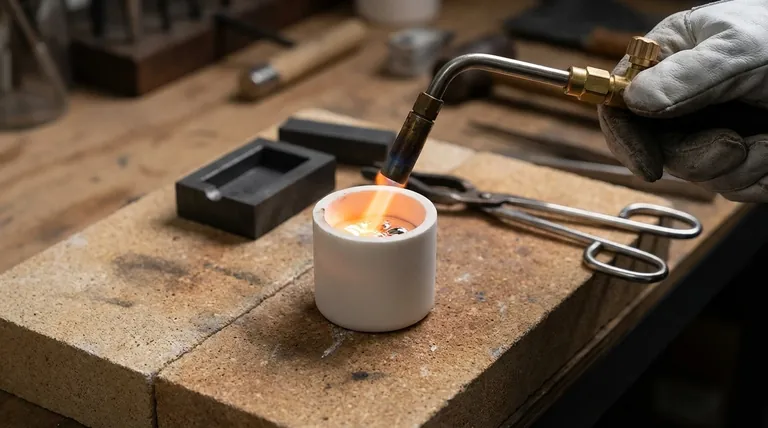
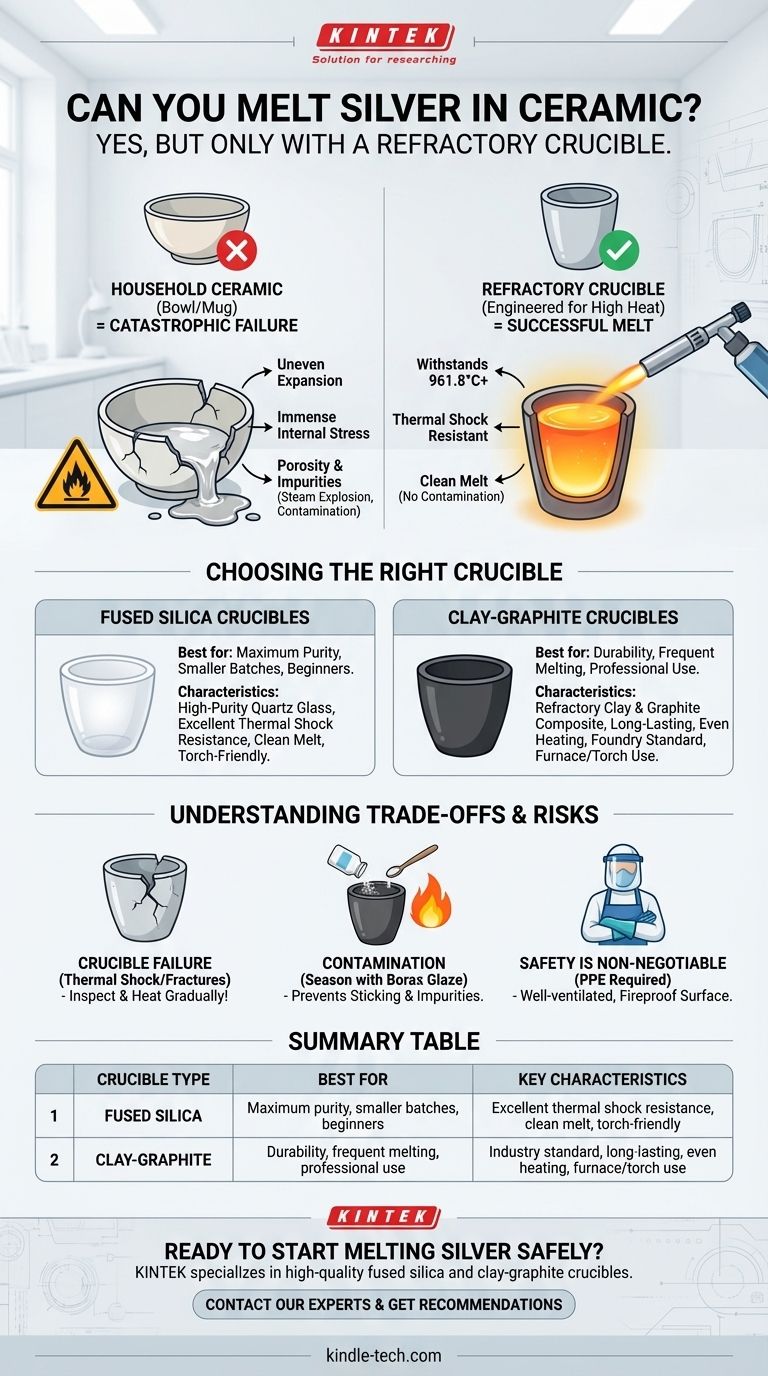
Yes, you can absolutely melt silver in ceramic, but only if you use a specific type of ceramic container known as a crucible. Using any standard ceramic item, like a bowl or mug, will result in catastrophic failure due to the extreme heat and thermal shock involved in the process.
The core distinction you must understand is between common pottery and refractory ceramics. To melt silver, which liquefies at 961.8°C (1763°F), you need a crucible made from a refractory material specifically engineered to withstand intense, rapid temperature changes without cracking or melting.

Why Household Ceramic Fails
The Impact of Thermal Shock
Standard ceramics, like those used for coffee mugs or dinner plates, are not designed for rapid heating. When you apply the intense, localized heat of a torch, different parts of the material expand at different rates.
This uneven expansion creates immense internal stress, causing the ceramic to crack, shatter, and spill molten metal, creating a significant safety hazard.
Porosity and Impurities
Most common ceramics are also porous. They can absorb moisture which, when heated rapidly, turns to steam and can cause the vessel to explode. Furthermore, their glazes and clay bodies are not pure and can release impurities that contaminate your silver.
Choosing the Right Crucible for Silver
A crucible is the correct tool for this job. It is a container made from a material with a very high melting point and, most importantly, excellent resistance to thermal shock. For melting silver, your primary choices are fused silica and clay-graphite.
Fused Silica Crucibles
These are often white or translucent and are made from high-purity quartz glass. They offer excellent thermal shock resistance and provide a very clean melt, meaning they won't contaminate your silver.
Fused silica is a fantastic choice for jewelers and hobbyists working with sterling or fine silver, especially when purity is a top priority. They are typically used with a torch.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
These are black or dark gray crucibles made from a composite of refractory clay and graphite. They are extremely durable, long-lasting, and the industry standard for foundries and frequent casting operations.
The graphite content improves thermal conductivity, allowing for more even heating, and enhances the crucible's overall strength. They are suitable for both torch and furnace melting.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing the right material is about managing risks and ensuring a clean result. Ignoring these factors can be dangerous and costly.
The Primary Risk: Crucible Failure
The single greatest risk is the crucible cracking during the melt. This is almost always caused by heating it too quickly (thermal shock) or using a vessel with a pre-existing fracture. Always inspect your crucible before use.
Contamination from Improper Use
A new crucible should be "seasoned" before its first use. This is done by heating the crucible and glazing the interior with a flux like borax.
This borax glaze creates a barrier that prevents the molten silver from sticking to the crucible walls and helps draw impurities out of the metal. Without it, you can lose small amounts of silver that become permanently embedded in the crucible surface.
Safety Is Non-Negotiable
Melting metal involves serious hazards. Always work in a well-ventilated area on a fireproof surface. You must use personal protective equipment (PPE), including a full face shield, leather apron, and heat-resistant gloves designed for foundry work.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of crucible depends on your specific application, budget, and the scale of your work.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and smaller batches: A fused silica crucible is your best choice for its clean-melting properties.
- If your primary focus is durability and frequent melting: A clay-graphite crucible is the professional-grade workhorse that will last longer.
- If you are a beginner learning the process: Start with a fused silica crucible, as they are very forgiving to the thermal shock from a torch.
Ultimately, selecting the correct crucible is the foundational step for any safe and successful metal-melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Type | Best For | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Fused Silica | Maximum purity, smaller batches, beginners | Excellent thermal shock resistance, clean melt, torch-friendly |
| Clay-Graphite | Durability, frequent melting, professional use | Industry standard, long-lasting, even heating, furnace/torch use |
Ready to start melting silver safely and efficiently?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for protecting your materials and ensuring a successful melt. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including durable fused silica and clay-graphite crucibles designed specifically for precious metals like silver.
Our experts can help you select the perfect crucible for your project, whether you're a jeweler focused on purity or a hobbyist needing a durable workhorse.
Contact our technical team today to discuss your silver melting needs and get personalized product recommendations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- Why are alumina crucibles selected for wood-plastic composite tests? Ensure Precision at 1000°C
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- Why use high-purity alumina crucibles for RPPO calcination? Ensure Stoichiometric Purity at 1150°C
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy



















