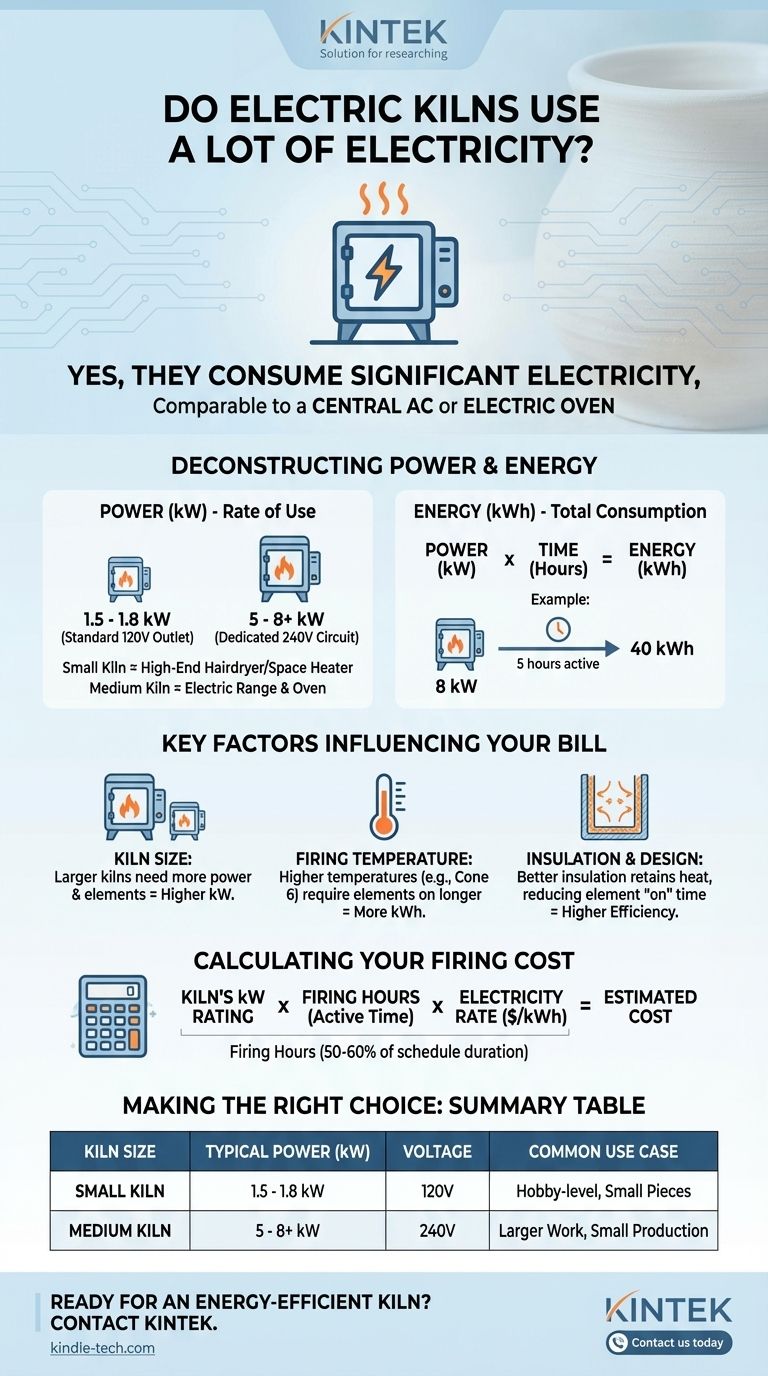
Yes, electric kilns use a significant amount of electricity, comparable to other major appliances like an electric oven or central air conditioning. A small kiln designed for a standard 120-volt household outlet typically consumes between 1.5 and 1.8 kilowatts (kW), while a medium-sized kiln can draw 5 kW to 8 kW or more.
The critical factor in determining your electricity cost isn't just the kiln's power rating, but the duration of the firing. Understanding how power (kW) and time (hours) combine to create energy usage (kWh) is the key to managing your expenses.

Deconstructing Kiln Power Consumption
To accurately assess the electrical impact of a kiln, you need to look beyond the simple power rating and consider how that power is used over time.
The Kilowatt (kW) Rating
A kilowatt is a measure of power, or the rate at which electricity is used. A kiln's kW rating tells you how much power it draws when the heating elements are actively on.
To put this in context, a small 1.8 kW kiln uses about the same amount of power as a high-end hairdryer or a powerful portable space heater. A medium 8 kW kiln draws as much power as an electric range with multiple burners and the oven running simultaneously.
From Power (kW) to Energy (kWh)
Your utility company doesn't bill you for power (kW); it bills you for energy, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This is the crucial distinction.
One kWh is the energy consumed by using one kilowatt of power for one full hour. If your 8 kW kiln runs with its elements on for a total of 5 hours during a 10-hour firing schedule, it has consumed 40 kWh of energy.
Key Factors Influencing Your Bill
The final cost of a firing depends on several variables that determine the total kWh consumed.
- Kiln Size: As the references state, larger kilns have more space to heat and require more powerful elements, leading to a higher kW rating and greater energy consumption.
- Firing Temperature: Reaching higher temperatures (e.g., a cone 6 glaze firing) requires the heating elements to stay on longer than a lower temperature bisque firing, thus using more kWh.
- Insulation and Design: A kiln with thicker, higher-quality insulation will retain heat more effectively. This reduces the amount of time the elements need to be on to maintain and increase the temperature, leading to higher overall efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Real-World Costs
While the raw numbers can seem high, it's important to view them in the context of efficiency and predictable costs.
The Principle of Efficiency
Electric heating elements are exceptionally efficient at their core task: converting electrical energy directly into heat. Unlike fuel-based kilns where significant heat is lost through a chimney flue, an electric kiln contains most of this energy.
However, the overall system efficiency depends entirely on the kiln's design. A well-made, well-insulated kiln will have minimal heat loss, making the firing process more energy-efficient and cost-effective.
Calculating Your Firing Cost
You can estimate the cost of a single firing with a simple formula. You'll need to find your electricity rate on your utility bill, expressed in cents or dollars per kWh.
Kiln's kW Rating x Firing Hours x Your Electricity Rate ($/kWh) = Estimated Firing Cost
Note that the "Firing Hours" in this formula refers to the time the elements are actually drawing power, which is typically 50-60% of the total firing schedule duration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding these factors, you can align your kiln choice and usage with your specific needs and budget.
- If your primary focus is hobby-level use with minimal cost: A smaller kiln that plugs into a standard 120-volt outlet is the most accessible and least expensive option to operate for small pieces.
- If your primary focus is creating larger work or small-scale production: A medium-sized 240-volt kiln is a necessary investment, and its higher running cost should be factored into the pricing of your finished artwork.
- If your primary focus is maximizing efficiency: Choose a kiln from a reputable brand known for excellent insulation and modern digital controllers, which optimize the firing cycle to save energy.
Ultimately, knowing how a kiln consumes electricity empowers you to control your costs and focus on creating your work.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Size | Typical Power Rating (kW) | Voltage Requirement | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Kiln | 1.5 - 1.8 kW | 120V (Standard Outlet) | Hobby-level use, small pieces |
| Medium Kiln | 5 - 8+ kW | 240V (Dedicated Circuit) | Larger work, small-scale production |
Ready to find the perfect, energy-efficient kiln for your studio?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including electric kilns designed with superior insulation and modern controllers to maximize efficiency and minimize your electricity costs. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, our experts can help you select the right kiln for your specific needs and budget.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK power your creativity efficiently!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- What are the principles of a rotary kiln? Master the Mechanics of High-Temperature Processing
- What temperature is needed for porcelain? A Guide to Cone 6 and Cone 10 Firing
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C



















