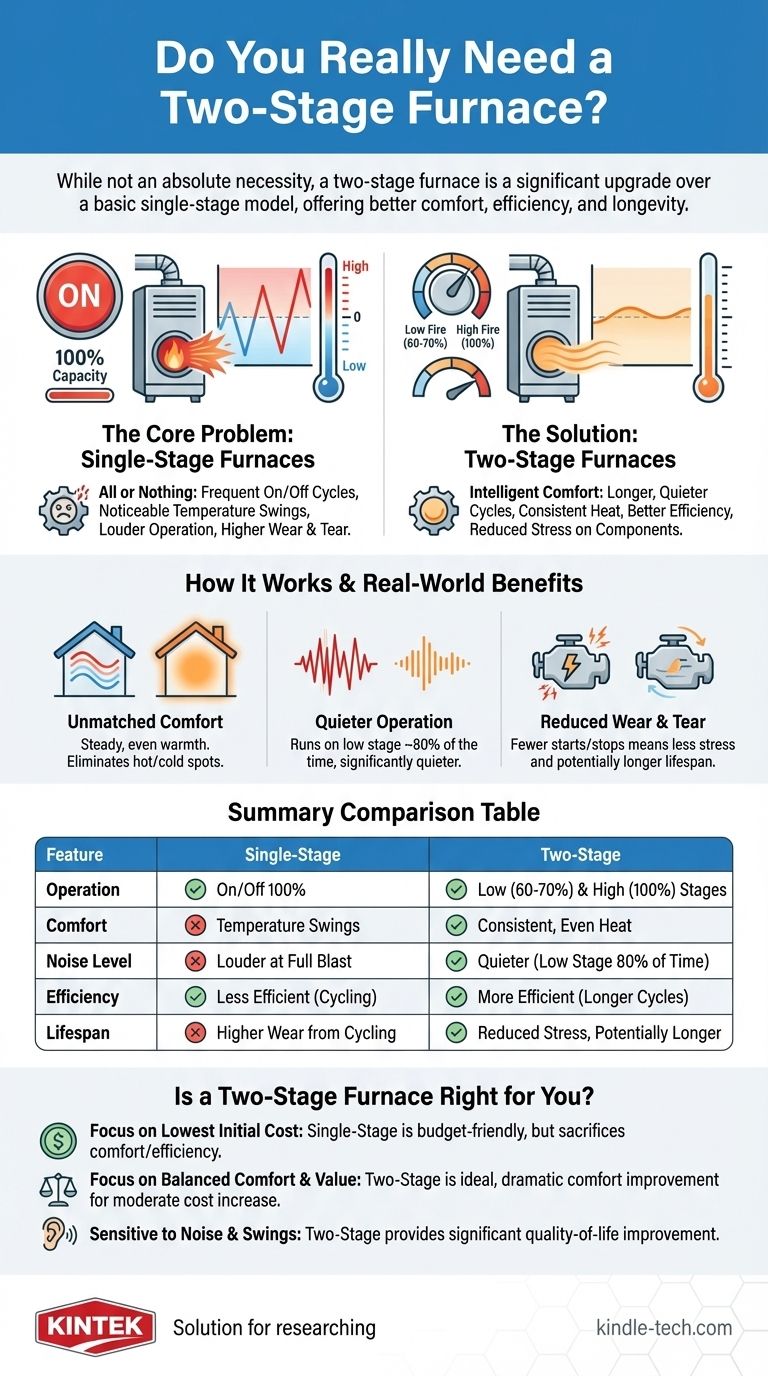
While not an absolute necessity, a two-stage furnace is a significant upgrade over a basic single-stage model for most homeowners. It operates on two levels: a lower-output setting for milder days and a higher-output setting for extreme cold. This dual-capacity approach provides more consistent heat, improves energy efficiency, and reduces wear on the system's components.
The core problem with traditional furnaces is that they are built for the coldest day of the year, meaning they are oversized and inefficient for most of the heating season. A two-stage furnace solves this by running longer on a lower, quieter, and more energy-efficient setting, delivering superior comfort and potential cost savings.

How a Two-Stage Furnace Actually Works
To understand the value of a two-stage system, you must first understand the limitations of the standard, single-stage furnace found in many homes.
The Problem with Single-Stage Furnaces
A single-stage furnace has only two states: on and off. When your thermostat calls for heat, the furnace ignites and runs at 100% capacity until the target temperature is reached, then shuts down completely.
This "all or nothing" approach creates noticeable temperature swings. You feel a blast of hot air, followed by a period of cooling until the cycle repeats, often leaving some rooms too hot and others too cold.
The Two-Stage Solution: Low and High Fire
A two-stage furnace introduces a more intelligent intermediate step. The first stage typically runs at about 60-70% of the furnace's total capacity.
On cool fall days or mild winter days, the furnace will run exclusively in this lower, quieter, and more efficient first stage. Only when the outdoor temperature drops significantly will the system engage the second stage to deliver 100% of its heating power.
The Benefit of Longer, Slower Cycles
Because the first stage produces less intense heat, the furnace needs to run for longer periods to satisfy the thermostat. This is a significant advantage.
Longer, continuous run times allow the heated air to circulate more thoroughly throughout your home, eliminating hot and cold spots. This also improves air filtration and humidity control, as the air is constantly moving through your filter and humidifier (if you have one).
The Real-World Benefits: Comfort, Cost, and Longevity
The technical differences translate directly into tangible benefits for the homeowner, centered on creating a more comfortable and efficient living space.
Unmatched Temperature Consistency
The primary benefit of a two-stage furnace is comfort. By avoiding the jarring on/off cycles of a single-stage unit, it provides a steady, even warmth. The house maintains a consistent temperature with far fewer noticeable fluctuations.
Quieter Operation
Because the furnace operates in its lower stage an estimated 80% of the time, it is significantly quieter than a single-stage unit that always runs at full blast. The noise reduction is a commonly cited benefit that improves daily life.
Reduced Wear and Tear
The most stressful moments for any mechanical system are startup and shutdown. The frequent cycling of a single-stage furnace puts significant stress on components like the igniter, blower motor, and heat exchanger.
The longer, gentler cycles of a two-stage furnace mean fewer starts and stops, leading to less wear and tear and potentially a longer operational lifespan for the unit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a two-stage system offers clear advantages, it's critical to understand its limitations and associated costs to make an informed decision.
The Upfront Cost Investment
A two-stage furnace costs more than a comparable single-stage model. While it offers the potential for long-term energy savings, you must be prepared for a higher initial purchase and installation price.
The Importance of Proper Sizing
The benefits of a two-stage furnace are completely negated if the unit is improperly sized for your home. An oversized two-stage furnace will still heat the space too quickly, even on its low setting, and shut off. This short-cycling eliminates the comfort and efficiency gains you paid for.
Pairing with the Right Thermostat
To maximize the furnace's capabilities, you need a two-stage or multi-stage compatible thermostat. A basic thermostat may not be able to control both stages effectively, forcing the furnace to operate more like a single-stage unit.
Is a Two-Stage Furnace Right for You?
Your decision should be based on a clear assessment of your priorities, balancing upfront cost against long-term comfort and performance.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible initial cost: A properly sized single-stage furnace is the most budget-friendly choice, but you will sacrifice a degree of comfort and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is balanced comfort and long-term value: A two-stage furnace is the ideal choice, offering a dramatic improvement in comfort for a moderate increase in upfront cost.
- If you are sensitive to noise and temperature swings: The quiet operation and even heating of a two-stage system will provide a significant and immediate quality-of-life improvement.
By matching furnace technology to your home's needs, you are making an investment in consistent, quiet comfort for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single-Stage Furnace | Two-Stage Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | On/Off at 100% capacity | Low (60-70%) and High (100%) stages |
| Comfort | Noticeable temperature swings | Consistent, even heat |
| Noise Level | Louder at full blast | Quieter, runs on low stage 80% of the time |
| Efficiency | Less efficient due to frequent cycling | More efficient with longer, gentler cycles |
| Lifespan | Higher wear and tear from cycling | Reduced stress, potentially longer lifespan |
Upgrade your home's comfort and efficiency with the right furnace solution. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet your precise needs. Whether you're outfitting a research facility or a quality control lab, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for consistent performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a multi-position furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Flexible HVAC Installation
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is a three zone furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Uniformity
- Are multi-stage furnaces worth it? Maximize Comfort and Energy Savings
- What are the typical heating zone configurations and maximum temperature capabilities of tube furnaces? Find the Right Setup for Your Lab



















