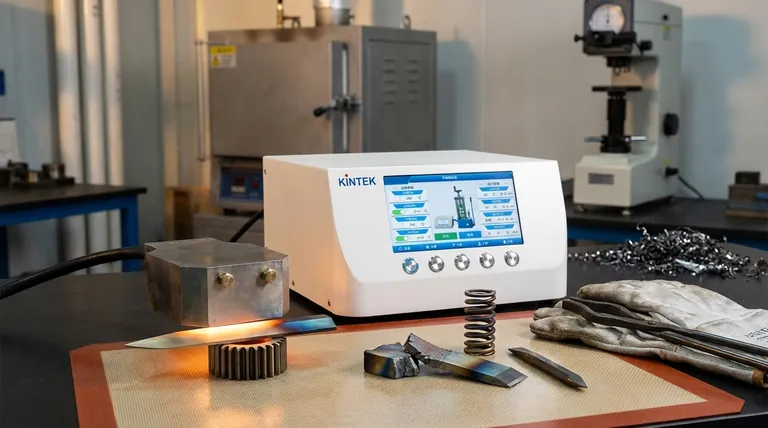
On the contrary, tempering steel does not increase its hardness. It is a critical heat-treatment process performed after hardening specifically to reduce hardness and relieve internal stress. This deliberate sacrifice of peak hardness is essential for gaining a far more valuable property for most applications: toughness.
Tempering is a trade-off. It strategically reduces the extreme, glass-like hardness of freshly quenched steel to prevent it from being dangerously brittle, thereby creating a tougher and more durable final product.

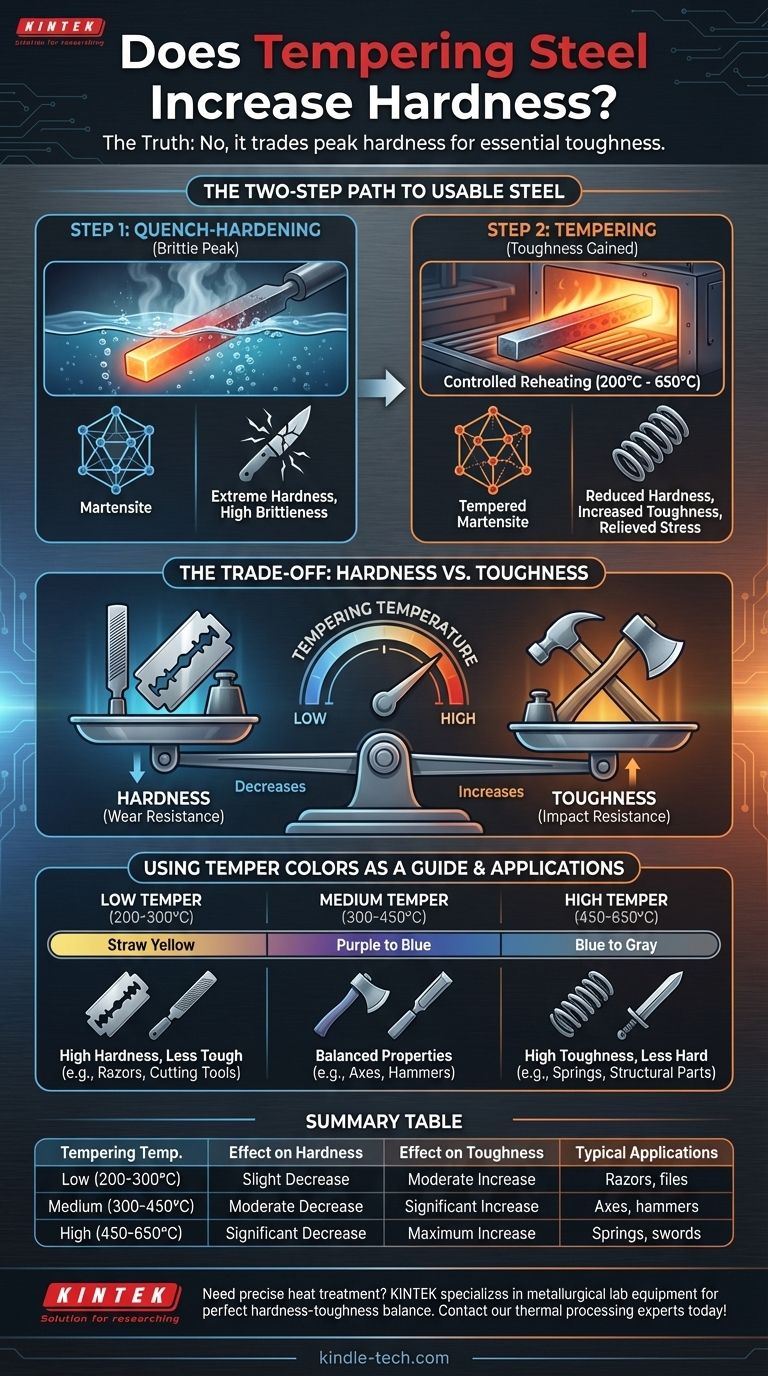
The Two-Step Path to Usable Steel
Achieving a useful balance of properties in steel is almost always a multi-stage process. Understanding the distinction between initial hardening and subsequent tempering is the key to understanding the material's final characteristics.
Step 1: Quench-Hardening for Maximum Hardness
The journey begins by heating the steel to a very high temperature, a process called austenitizing. This changes its internal crystal structure.
The steel is then cooled with extreme rapidity, typically by plunging it into water or oil. This is known as quenching.
This rapid cooling traps carbon atoms within the steel's crystal lattice, forming a new structure called martensite. Martensite is incredibly hard but also extremely brittle, much like glass.
The Problem with Untempered Steel
While martensite provides the highest possible hardness, it is practically useless for tools, blades, or structural components.
The immense internal stresses created during quenching make the steel prone to cracking. A fully hardened, untempered steel file or knife edge would likely shatter upon its first significant impact.
Step 2: Tempering to Cultivate Toughness
Tempering is the solution to this brittleness. The hardened steel is reheated to a precise, much lower temperature (typically between 200°C and 650°C) and held there for a specific period.
This controlled reheating allows some of the trapped carbon atoms to precipitate out, forming carbides, and enables the crystal structure to relax slightly. This process relieves the internal stresses and transforms the brittle martensite into a more refined structure known as tempered martensite.
Why "Less Hard" is Often "More Useful"
The goal of heat treatment isn't simply to achieve the highest number on a hardness scale. The true goal is to optimize the material for a specific task, which almost always involves balancing competing properties.
The Inverse Relationship: Hardness vs. Toughness
It's crucial to distinguish between two key properties:
- Hardness is the ability of a material to resist scratching, abrasion, and indentation.
- Toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and deform without fracturing.
In steel, these two properties generally have an inverse relationship. As you increase toughness through tempering, you will decrease hardness.
Dialing In the Desired Properties
The temperature used during the tempering process is the primary control knob for the steel's final properties.
A lower tempering temperature results in a slight decrease in hardness but a significant increase in toughness. A higher tempering temperature results in a greater loss of hardness but an even more substantial gain in toughness and ductility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no "perfect" state for steel; there are only optimal states for a given application. Every choice in the heat-treatment process involves a calculated compromise.
The Inevitable Sacrifice
You cannot simultaneously have maximum hardness and maximum toughness in the same piece of steel. The purpose of tempering is to move away from the brittle peak-hardness state toward a more balanced and functional state.
Using Temper Colors as a Guide
For centuries, blacksmiths have used a visual cue to gauge the tempering process. As the steel is heated, a thin oxide layer forms on its surface, and its color changes predictably with temperature.
These temper colors, ranging from a light straw yellow (lower temperature, higher hardness) to blue or gray (higher temperature, higher toughness), serve as a practical indicator of the properties being achieved.
Matching the Properties to the Application
The correct level of temper is entirely dependent on the intended use of the steel component.
- If your primary focus is a keen edge and wear resistance (e.g., razors, files): A low-temperature temper is used to retain as much hardness as possible while relieving just enough stress to prevent chipping.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance (e.g., axes, hammers, cold chisels): A medium-temperature temper is required, sacrificing significant hardness for the high toughness needed to withstand repeated blows.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and springiness (e.g., springs, swords): A high-temperature temper is chosen to maximize toughness and ductility, making hardness a secondary consideration.
Ultimately, understanding that tempering refines raw hardness into functional toughness is the key to creating strong, reliable, and purpose-built steel tools.
Summary Table:
| Tempering Temperature | Effect on Hardness | Effect on Toughness | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (200-300°C) | Slight Decrease | Moderate Increase | Razors, files, cutting tools |
| Medium (300-450°C) | Moderate Decrease | Significant Increase | Axes, hammers, chisels |
| High (450-650°C) | Significant Decrease | Maximum Increase | Springs, swords, structural parts |
Need precise heat treatment for your steel components? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for metallurgical processes, serving laboratories and manufacturers who require reliable thermal processing solutions. Our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect balance of hardness and toughness for your specific applications. Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how we can support your material science needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of press machines? Choose the Right Heating Tech for Your Application
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- Why is it necessary to use high-precision temperature-controlled heating furnaces? Secure Natural Fiber Integrity.
- How is conventional heating different from induction heating? Direct vs. Indirect Heat Explained
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components



















