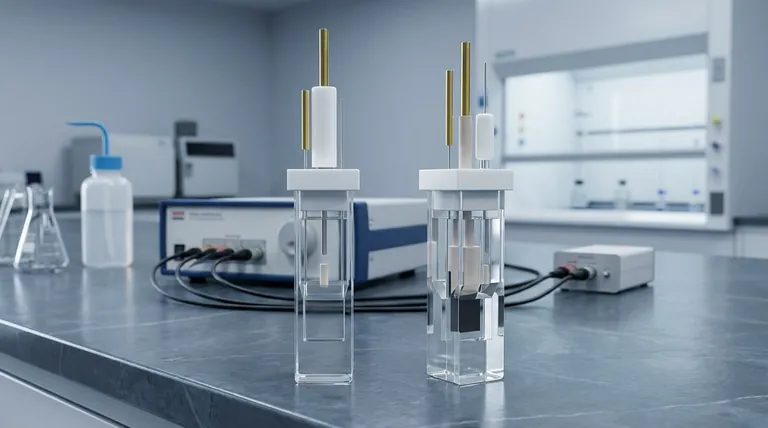
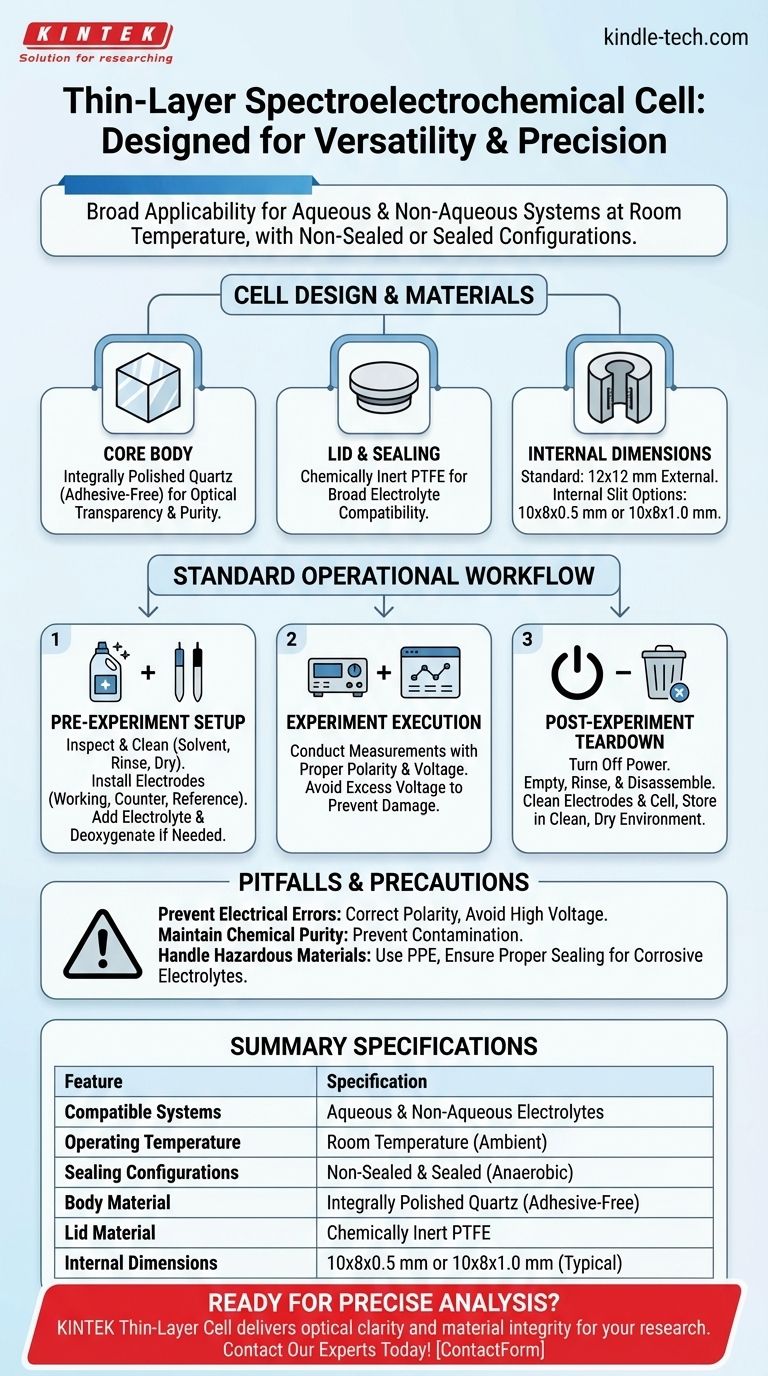
This thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell is designed for broad applicability. It is engineered for use with both aqueous and non-aqueous systems, operates specifically at room temperature, and is available in both non-sealed and sealed configurations to accommodate different experimental requirements.
At its core, this cell is a versatile tool for standard spectroelectrochemical analysis. Its design prioritizes optical clarity and material inertness for a wide range of common solvents under ambient, room-temperature conditions.

Understanding the Cell's Design and Materials
The physical construction of the cell is fundamental to its function, ensuring optical transparency and chemical resistance for reliable data collection.
Core Body Construction
The cell body is constructed from integrally polished quartz. This material choice is critical, as it is transparent on all four sides, allowing for unobstructed spectroscopic measurements.
Importantly, the quartz components are assembled without any adhesives, which eliminates potential sources of contamination from glue or epoxy that could interfere with sensitive electrochemical reactions.
Lid and Sealing
The lid is made of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a material well-known for its excellent chemical resistance and inertness. This makes it suitable for a wide variety of electrolyte systems.
Internal Dimensions
The cell features a standard square shape with external dimensions of 12x12 mm. You can acquire it with different internal slit dimensions, typically 10x8x0.5 mm or 10x8x1.0 mm, which defines the volume and path length for your experiment.
Standard Operational Procedures
Proper handling before and after each experiment is essential for maintaining the cell's integrity and ensuring the accuracy of your results.
Pre-Experiment Setup
Before beginning, always inspect all components for damage. The setup process involves thoroughly cleaning the cell with an appropriate solvent, rinsing with distilled water, and allowing it to dry completely.
Next, correctly install the working, counter, and reference electrodes, ensuring they are positioned properly for good electrical contact. Finally, prepare and add the required electrolyte, performing pre-treatments like deoxygenation if necessary for your system.
Post-Experiment Teardown
Safety is paramount. Always turn off the power source before disconnecting the cell to prevent electrical arcing.
Immediately empty the used electrolyte and rinse the cell multiple times with distilled water to remove all residues. Carefully disassemble, clean, and dry the electrodes and cell body before storing them in a clean, dry environment away from dust and moisture.
Common Pitfalls and Precautions
While versatile, this cell requires careful handling to avoid common issues that can compromise your experiment or damage the equipment.
Preventing Electrical Errors
Always ensure the correct polarity for the anode and cathode connections. Reversing the polarity can lead to incorrect results or damage to your sample and electrodes.
Avoid applying excessively high voltage. This can cause the electrolyte to decompose or permanently damage the electrode surfaces.
Maintaining Chemical Purity
Prevent environmental contaminants like dust from entering the cell, as even small impurities can significantly affect electrochemical measurements.
Handling Hazardous Materials
When using corrosive electrolytes, you must use appropriate personal protective gear to prevent contact with skin and eyes. Ensure the cell is properly sealed to prevent leaks and maintain a safe lab environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
This cell is an excellent tool when used within its designed operational window. Its suitability depends entirely on your specific experimental goals.
- If your primary focus is on standard aqueous or organic solvent systems: This cell is ideal due to its quartz and PTFE construction, offering high chemical compatibility.
- If your experiment requires anaerobic (oxygen-free) conditions: Choose the sealed configuration to maintain an inert atmosphere after deoxygenation.
- If you are working with high-temperature or high-pressure systems: This cell is not suitable, as it is explicitly designed for ambient, room-temperature operation.
Ultimately, this cell provides a reliable and clear optical window for a wide range of common spectroelectrochemical experiments.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Compatible Systems | Aqueous and non-aqueous electrolytes |
| Operating Temperature | Room temperature (ambient) |
| Sealing Configurations | Non-sealed and sealed (for anaerobic conditions) |
| Body Material | Integrally polished quartz (adhesive-free) |
| Lid Material | Chemically inert PTFE |
| Internal Dimensions | 10x8x0.5 mm or 10x8x1.0 mm (typical) |
Ready to achieve precise spectroelectrochemical analysis with optimal optical clarity?
The thin-layer cell from KINTEK is engineered for reliability in your lab. Whether you're working with standard solvents requiring a non-sealed configuration or sensitive reactions needing a sealed, anaerobic environment, our cell delivers the material inertness and design integrity critical for accurate results.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving researchers who demand precision. Let us provide the right tool for your experimental needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how this cell can enhance your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
- PTFE Electrolytic Cell Electrochemical Cell Corrosion-Resistant Sealed and Non-Sealed
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
People Also Ask
- What types and sizes of electrodes are typically configured with a thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell? Standard Setup for Accurate Analysis
- What are the dimensions for thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cells? Optimize Your Lab's Optical Path Length
- What are the physical dimensions of the thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell body and its slit? Key Specs for Your Lab
- What are the necessary preparation steps before using a thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell? A Guide to Reliable Results
- What is the correct post-experiment procedure for a thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cell? A Step-by-Step Guide for Lab Safety and Accuracy



















