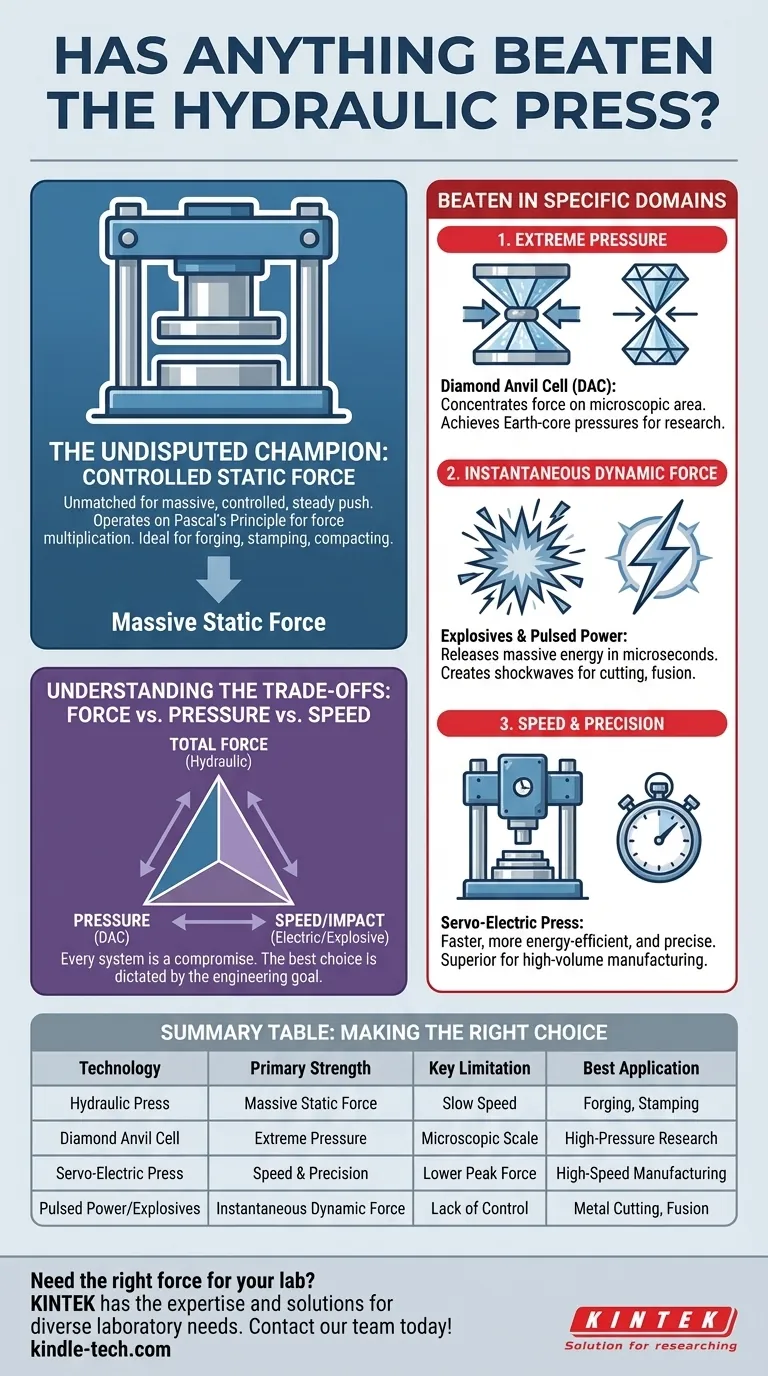
In terms of generating immense, controlled, static force, nothing has truly "beaten" the hydraulic press. It remains the undisputed champion for a vast range of industrial applications due to its straightforward design and incredible force multiplication. However, if the question is about generating the highest pressure or applying force in different ways, then several other technologies have surpassed it in specific domains.
The hydraulic press is the pinnacle of generating massive, controlled static force. Yet, it is surpassed by other technologies when the goal shifts to achieving the highest pressures, instantaneous dynamic force, or greater speed and efficiency.

The Foundational Power of Hydraulics
The enduring dominance of the hydraulic press comes from a simple, powerful principle of physics that allows it to achieve incredible feats of strength.
The Principle of Force Multiplication
A hydraulic system operates on Pascal's Principle. This states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
By using two pistons of different sizes, a small force applied to the smaller piston generates a much larger force on the larger piston. This ability to multiply force is why even a relatively small hydraulic press can crush cars or forge steel.
Why It Excels at Static Force
The "strength" of a hydraulic press lies in its ability to generate and hold an enormous static force—a slow, steady, and controllable push. For applications like stamping, forging, or compacting materials, this is the ideal type of force.
Redefining "Beaten": Contenders in Other Arenas
While supreme in static force, the hydraulic press is "beaten" when we change the rules of the contest. Different technologies are superior for generating extreme pressure, speed, or dynamic impact.
For Sheer Pressure: The Diamond Anvil Cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a scientific device that can generate pressures exceeding those at the center of the Earth. It does this not by generating more total force than a press, but by concentrating that force onto an infinitesimally small point.
Two flawless diamonds are pushed together, squeezing a sample between their tips. While the total force might be applied by a simple screw, the resulting pressure (force per unit area) is trillions of times higher than a hydraulic press can achieve.
For Dynamic Force: Explosives and Pulsed Power
When the goal is to apply a massive amount of force in an instant, a hydraulic press is far too slow. This is the realm of dynamic force.
Technologies like shaped explosive charges or massive capacitor banks (like the Z Pulsed Power Facility) can release incredible energy in microseconds. This generates a shockwave with pressures and forces that far exceed what a static press can do, allowing for specialized metal cutting or nuclear fusion research.
For Speed and Precision: The Servo-Electric Press
In modern high-speed manufacturing, the hydraulic press is often being replaced by servo-electric presses. These use high-torque electric motors and ball screws to move the ram.
While they may not reach the peak force of the largest hydraulic systems, they are significantly faster, more energy-efficient, and offer vastly superior precision and repeatability. For producing thousands of identical parts per hour, they have decisively "beaten" their hydraulic counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Force vs. Pressure vs. Speed
Choosing the "strongest" technology is impossible without defining the engineering goal. Each system is built around a fundamental compromise.
The Domain of Hydraulics: Raw Compressive Force
Hydraulic presses trade speed for power. The incompressibility of fluid makes them ideal for applications requiring a slow, deliberate, and overwhelmingly powerful squeeze.
The Domain of Diamond Anvils: Extreme Pressure
Diamond anvil cells trade total force and scale for pressure. They are designed for one purpose: to concentrate a modest force onto a microscopic area to create unimaginable pressures for scientific study.
The Domain of Electrics and Explosives: Speed and Impact
Servo-electric presses trade some peak force for superior speed, efficiency, and control. Explosives and pulsed power systems trade control for an unparalleled release of dynamic, instantaneous force.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The concept of a single "best" technology is a misconception. The superior choice is always dictated by the specific problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is maximum controlled static force for heavy industry: The hydraulic press remains the unparalleled and most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating the highest possible pressures for scientific research: A diamond anvil cell is the required instrument.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, precise, and repeatable manufacturing: A servo-electric press offers superior performance and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is applying an extreme, instantaneous force: Technologies involving pulsed power or explosives are the only options.
Ultimately, understanding the specific type of force required—static, dynamic, or highly concentrated—is the key to identifying the truly superior technology for the task.
Summary Table:
| Technology | Primary Strength | Key Limitation | Best Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Press | Massive Static Force | Slow Speed | Forging, Stamping, Compacting |
| Diamond Anvil Cell | Extreme Pressure | Microscopic Scale | High-Pressure Scientific Research |
| Servo-Electric Press | Speed & Precision | Lower Peak Force | High-Speed, Precision Manufacturing |
| Pulsed Power/Explosives | Instantaneous Dynamic Force | Lack of Control | Metal Cutting, Fusion Research |
Need to apply the right force for your project? Whether your lab requires the controlled pressure of a hydraulic press, the precision of a servo-electric system, or specialized equipment for high-pressure research, KINTEK has the expertise and solutions. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Let our experts help you select the perfect technology to achieve your goals. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
















