In short, modern high-performance crucibles, such as those made from silicon carbide, are manufactured using a process called isostatic pressing. This method involves compacting the raw powdered material in a flexible mold by applying extreme, uniform pressure through a fluid. This technique is favored because it creates an exceptionally dense and uniform final product, which is critical for withstanding the intense thermal and chemical stress of metallurgical applications.
The specific manufacturing method isn't just a technical detail—it is the primary factor determining a crucible's reliability and performance. The goal of modern processes like isostatic pressing is to eliminate the microscopic inconsistencies that lead to catastrophic failure at high temperatures.

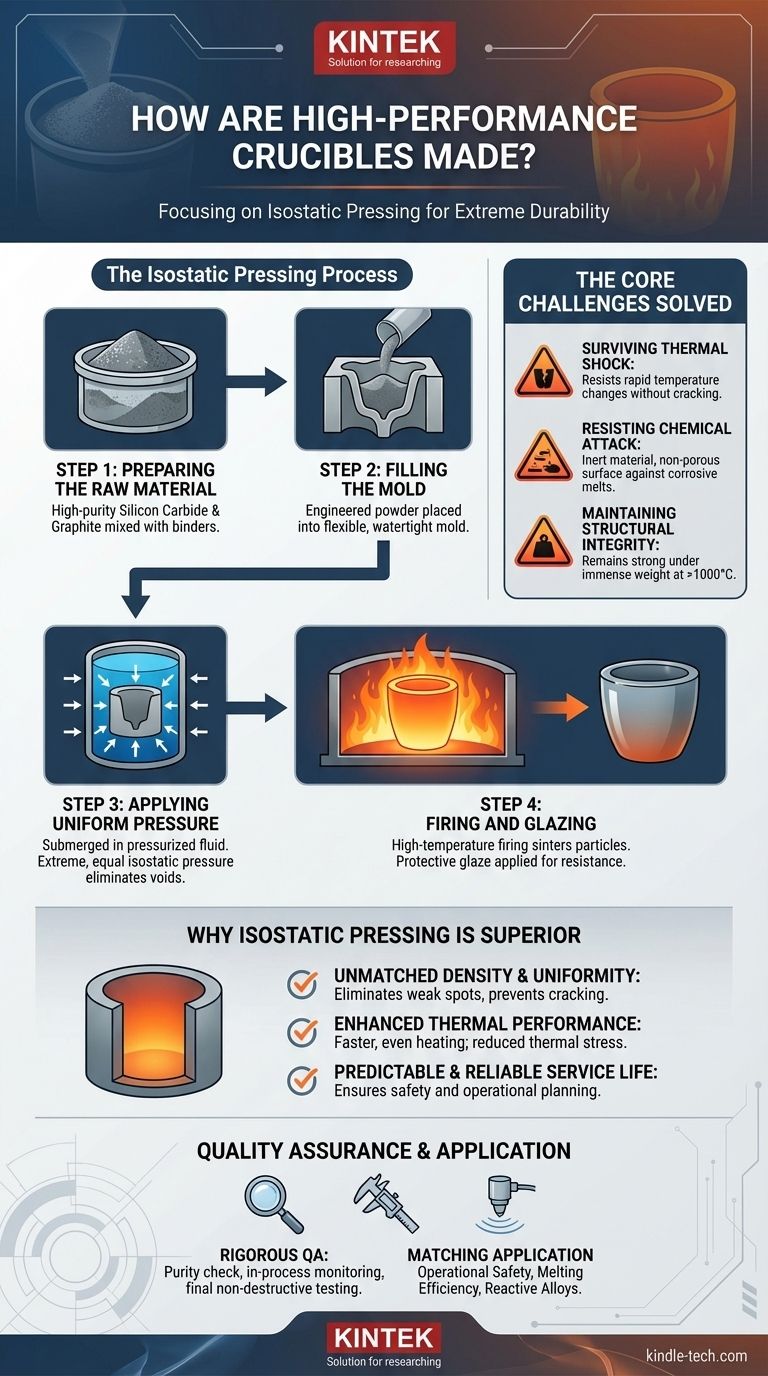
The Core Challenge: Resisting Extreme Conditions
Before detailing the manufacturing steps, it's essential to understand the problems the process is designed to solve. A crucible operates in one of the harshest environments imaginable.
Surviving Thermal Shock
A crucible must endure rapid and repeated temperature changes without cracking. Any internal inconsistencies or microscopic voids act as stress points where fractures can begin.
Resisting Chemical Attack
At high temperatures, molten metals and fluxes can be extremely corrosive. The crucible material must be chemically inert and its surface must be non-porous to prevent degradation from the inside out.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
A crucible must remain strong and rigid even when holding the immense weight of molten metal at temperatures exceeding 1000°C. Any weakness in its structure can lead to deformation or failure.
The Isostatic Pressing Process Explained
Isostatic pressing is the solution to creating a crucible that can overcome these challenges. It ensures every part of the crucible has the same density and strength.
Step 1: Preparing the Raw Material
The process begins by carefully mixing high-purity raw materials, such as silicon carbide and graphite, with specialized binders. This homogenous mixture is the foundation for the crucible's final properties.
Step 2: Filling the Mold
This precisely engineered powder is then placed into a flexible, watertight mold, often made of polyurethane or rubber. The mold is shaped like the final crucible.
Step 3: Applying Uniform Pressure
The sealed mold is submerged in a chamber of hydraulic fluid. This fluid is then pressurized to extremely high levels, exerting equal force on every point of the mold's surface—the defining characteristic of isostatic pressure.
This uniform compaction squeezes out air pockets and ensures the powdered material achieves a consistently high density throughout the crucible's walls and base.
Step 4: Firing and Glazing
After being removed from the mold, the compacted "green" crucible is carefully dried. It is then fired in a kiln at very high temperatures. This step burns away the binders and sinters the ceramic particles together, creating a strong, monolithic structure. A final protective glaze is often applied to enhance oxidation and chemical resistance.
Why This Method is Superior
Older methods could introduce weak points, but isostatic pressing is designed to eliminate them. The benefits are directly tied to the physics of the process.
Unmatched Density and Uniformity
Unlike methods where pressure is applied from one or two directions, isostatic pressing eliminates density gradients. The resulting crucible has no inherent weak spots, making it far more resistant to cracking under stress.
Enhanced Thermal Performance
A uniformly dense body conducts heat far more evenly and efficiently. This means faster melt times for the user and, more importantly, a reduction in thermal stresses that could otherwise build up and cause a fracture.
Predictable and Reliable Service Life
Because the process removes the variables that lead to premature failure, crucibles made this way offer a more predictable and reliable service life. This is a critical factor for safety and operational planning in any foundry or lab.
The Critical Role of Quality Assurance
The manufacturing process is only as good as the controls that govern it. Strict quality assurance is not an afterthought but an integral part of production.
Material Purity Inspection
It begins with testing the purity and particle size of all incoming raw materials. Any impurity can compromise the final product's integrity at high temperatures.
In-Process Monitoring
During and after pressing, the crucibles are checked for dimensional accuracy and density. Any piece that falls outside of strict tolerances is rejected.
Final Non-Destructive Testing
After firing, every crucible undergoes final inspection. This often includes visual and sometimes ultrasonic testing to detect any hidden internal flaws or surface cracks that could lead to failure in service.
Matching the Crucible to Your Application
Understanding the manufacturing process empowers you to select the right tool for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is operational safety: Demand crucibles made via isostatic pressing. This method directly minimizes the internal defects that are the primary cause of catastrophic failure.
- If your primary focus is melting efficiency: An isostatically pressed crucible provides superior thermal conductivity, ensuring faster, more consistent heating and reducing energy costs.
- If you are working with reactive alloys: The high density and low porosity achieved through this process result in a more chemically inert crucible, protecting your melt from contamination.
Ultimately, a crucible's manufacturing journey from powder to a finished product is a direct indicator of its strength and trustworthiness.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Step | Key Benefit | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Isostatic Pressing | Uniform density throughout | Eliminates weak spots, prevents cracking |
| High-Purity Materials | Chemical inertness | Resists corrosion, prevents contamination |
| High-Temperature Firing | Strong, monolithic structure | Maintains integrity under extreme heat and load |
| Rigorous Quality Assurance | Predictable service life | Ensures safety and operational reliability |
Ready to enhance your lab's safety and efficiency? The right crucible is critical for reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including crucibles manufactured to the highest standards for superior thermal and chemical resistance. Contact our experts today to find the perfect crucible for your specific application and experience the KINTEK difference in quality and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- What temperature is cold isostatic pressing? A Guide to Room-Temperature Powder Compaction
- What advantages does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) offer for solid-state batteries? Superior Density & Uniformity
- What role does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) play in aluminum matrix composites? Achieve 90% Density for Better Hot Pressing
- What advantages does Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) offer for nickel-alumina composites? Enhance Density & Strength
- What is cold isostatic pressing of metal powder? Achieve Uniform Density in Complex Metal Parts



















