In essence, molds are manufactured using either traditional subtractive methods like CNC machining and EDM, or modern additive methods like 3D printing. The traditional approaches carve molds from metal blocks, offering extreme durability for mass production, while 3D printing builds molds layer-by-layer for rapid, low-cost prototyping.
The method used to manufacture a mold is dictated entirely by its intended purpose. The core decision is a trade-off between the high upfront cost and long lead time of a durable steel mold for mass production versus the speed and low cost of a 3D printed mold for prototyping and low-volume runs.

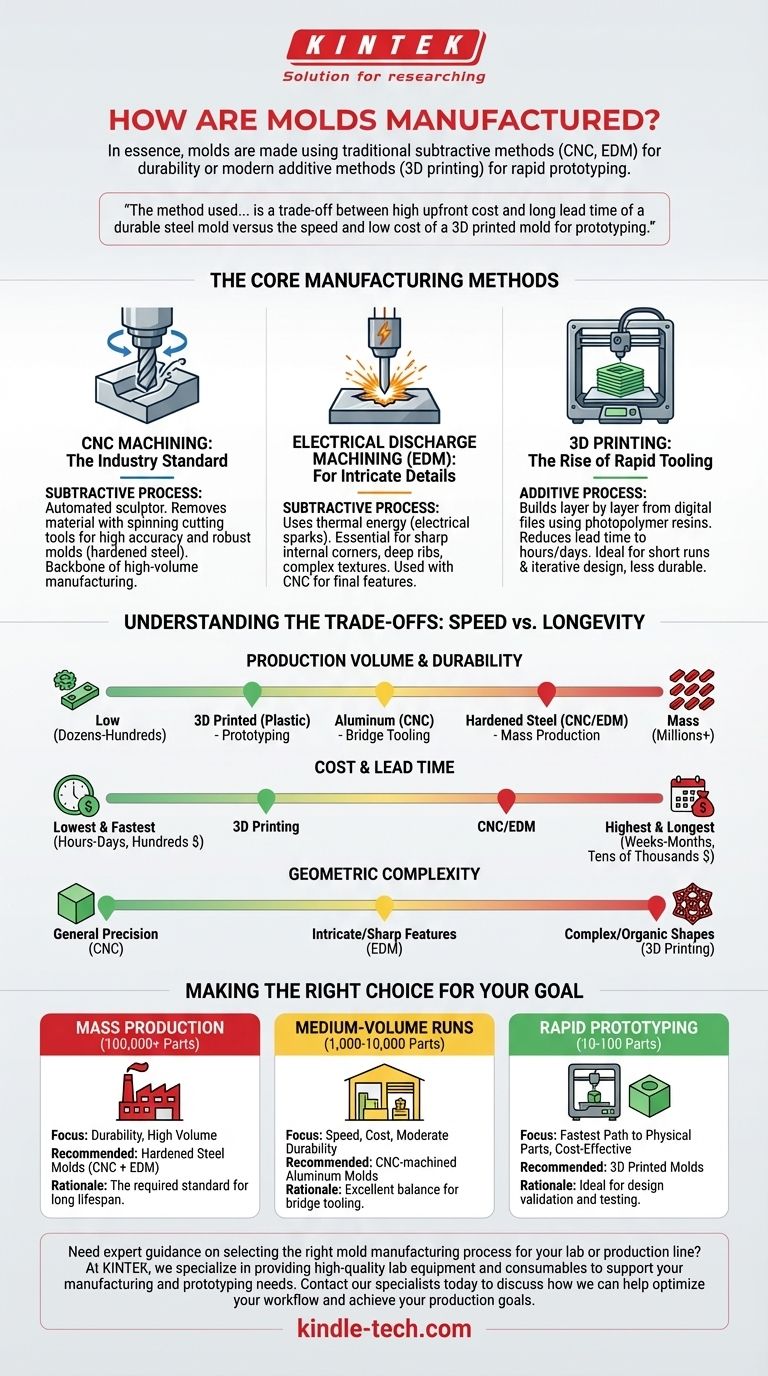
The Core Manufacturing Methods
Understanding how a mold is made is to understand the fundamental difference between carving something out of a solid block versus building it from the ground up. Each approach has a distinct role in modern manufacturing.
CNC Machining: The Industry Standard
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a subtractive process. Think of it as a highly precise, automated sculptor carving a block of metal.
A computer sends digital design instructions to the machine, which uses spinning cutting tools to systematically remove material from a solid block of aluminum or steel until the final mold cavity is formed.
This method is prized for its high accuracy and ability to produce robust molds from hardened tool steel, making it the backbone of high-volume manufacturing.
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): For Intricate Details
EDM is another subtractive process, but it uses thermal energy instead of mechanical force. It removes material by generating a series of rapid, controlled electrical sparks between an electrode and the metal workpiece.
This technique is essential for creating features that are difficult or impossible for standard cutting tools to produce, such as sharp internal corners, deep ribs, or complex textures.
EDM is not a standalone process; it is almost always used in conjunction with CNC machining to create the final, highly-detailed features of a steel mold.
3D Printing: The Rise of Rapid Tooling
3D printing is an additive process. Instead of removing material, it builds the mold layer by layer from a digital file, typically using photopolymer resins that are cured by UV light.
This approach dramatically reduces lead time from weeks or months down to just hours or days, enabling engineers to create and test physical prototypes with unprecedented speed.
While these plastic molds are not as durable as metal ones, they are more than sufficient for short production runs and iterative design validation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Longevity
Choosing a mold manufacturing method is a strategic decision that balances cost, speed, and the required production volume. There is no single "best" method; there is only the right method for the job.
Production Volume and Durability
A mold's lifespan is directly tied to the material it's made from.
- Hardened Steel Molds (CNC/EDM): Built for millions of injection cycles. This is the only option for true mass production.
- Aluminum Molds (CNC): A "bridge tooling" solution. They are faster and cheaper to machine than steel but wear out much faster, typically lasting for thousands to tens of thousands of cycles.
- 3D Printed Molds (Plastic): Designed for prototyping. They can withstand dozens to hundreds of cycles, which is ideal for design verification but unsuitable for production.
Cost and Lead Time
The financial and time investment varies dramatically between methods.
- CNC/EDM: Highest cost and longest lead time. A complex steel mold can cost tens of thousands of dollars and take 4-12 weeks or more to produce.
- 3D Printing: Lowest cost and fastest lead time. A prototype mold can be printed in-house for a few hundred dollars in under 24 hours.
Geometric Complexity
Each method has unique strengths when it comes to the part's geometry.
CNC machining is excellent for general precision, but EDM is required for sharp internal features. 3D printing, however, can create incredibly complex and organic shapes with internal cooling channels that would be impossible to machine traditionally.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your production goal is the single most important factor in determining the right mold manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is mass production (100,000+ parts): Hardened steel molds created with a combination of CNC machining and EDM are the required standard for durability.
- If your primary focus is medium-volume runs (1,000-10,000 parts): CNC-machined aluminum molds provide an excellent balance of speed, cost, and moderate durability.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping and design validation (10-100 parts): 3D printed molds offer the fastest and most cost-effective path to get physical parts in hand for testing.
Ultimately, selecting the correct mold manufacturing process is about aligning the tool's capabilities with your specific project timeline and production volume.
Summary Table:
| Manufacturing Method | Process Type | Best For | Typical Material | Lead Time | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Subtractive | Mass Production | Steel, Aluminum | 4-12 weeks | High Accuracy & Durability |
| EDM | Subtractive | Intricate Details | Steel | Used with CNC | Sharp Corners & Complex Features |
| 3D Printing | Additive | Prototyping & Low-Volume | Photopolymer Resin | Hours to Days | Rapid Turnaround & Low Cost |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right mold manufacturing process for your lab or production line?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your manufacturing and prototyping needs. Whether you're engaged in mass production requiring durable steel molds or rapid prototyping with 3D printing, our solutions ensure precision and efficiency.
Contact our specialists today to discuss how we can help optimize your workflow and achieve your production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
People Also Ask
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What are the primary functions of graphite dies in sintering? Optimize Nano-AlN Sintering Efficiency
- What are the primary functions of high-density graphite molds in FAST/SPS? Optimizing Thermal and Mechanical Performance
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What is the role of high-strength graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing Beryllium? Enhance Densification & Precision



















