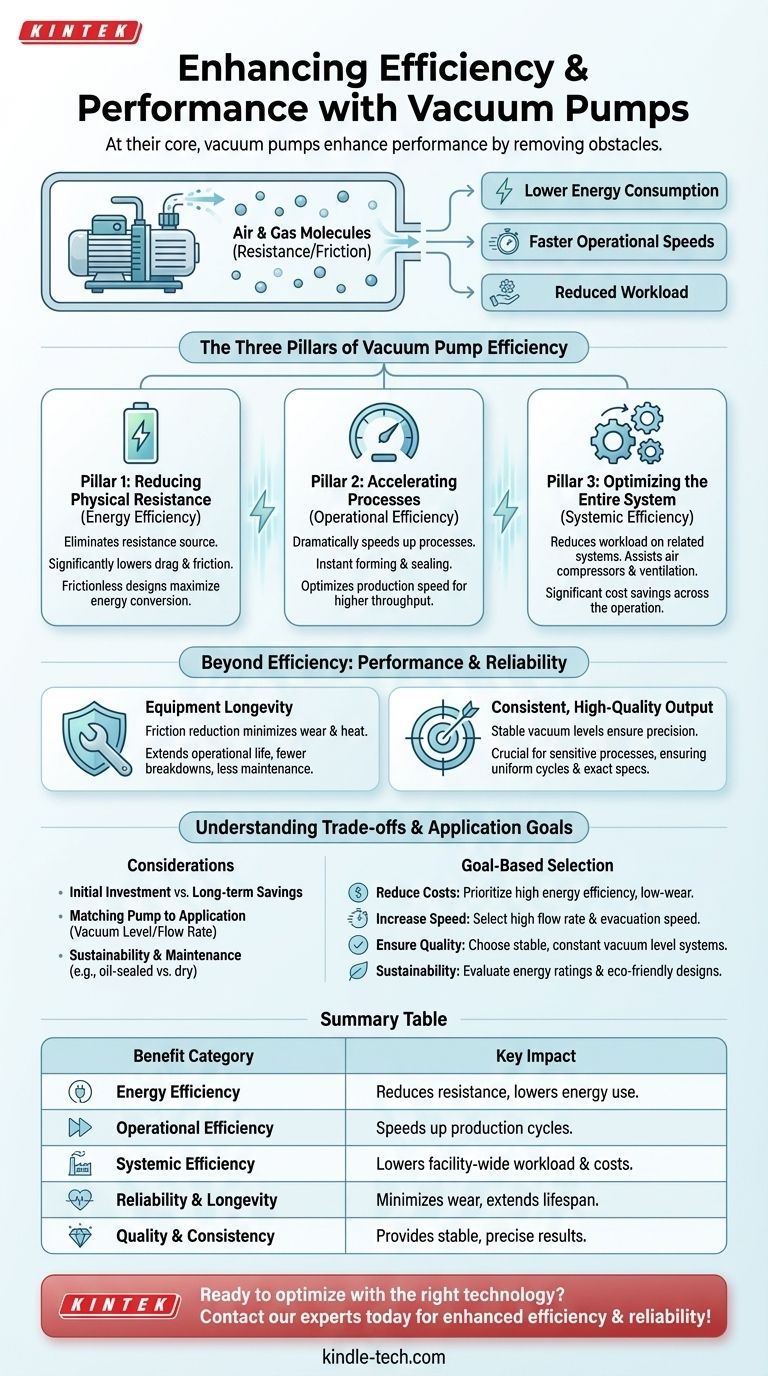
At their core, vacuum pumps enhance performance by removing obstacles. By systematically removing air and other gas molecules from a sealed space, they reduce physical resistance and friction. This fundamental action translates directly into lower energy consumption, faster operational speeds, and a reduced workload on other equipment, creating a cascade of efficiency gains throughout a system.
The true value of a vacuum pump is not merely the creation of empty space. It is the optimization of an entire process by eliminating the parasitic drag of air, which cuts energy waste, accelerates production cycles, and improves the overall reliability and lifespan of the equipment involved.
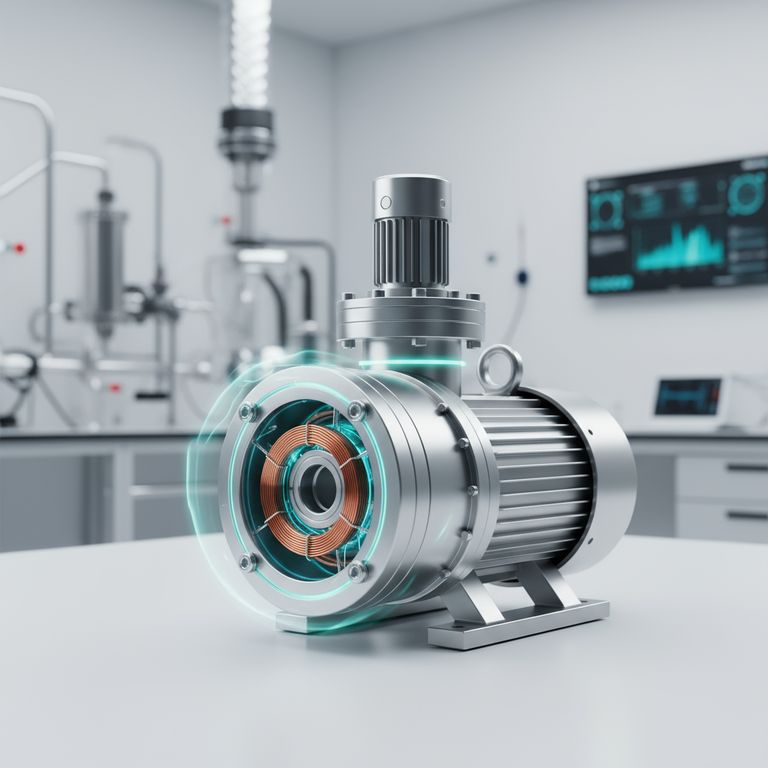

The Three Pillars of Vacuum Pump Efficiency
To understand how vacuum pumps deliver these benefits, it's useful to break down their impact into three distinct categories: energy, operations, and the surrounding system.
Pillar 1: Reducing Physical Resistance (Energy Efficiency)
The primary function of removing air is to eliminate a source of resistance. In any mechanical system, moving through air requires energy.
By creating a vacuum, the pump significantly lowers the number of air molecules that moving parts must push against. This directly reduces drag and friction.
Modern designs, such as those with frictionless membrane movement, take this further. They minimize internal mechanical wear and heat generation, maximizing the amount of electrical energy that is converted into vacuum generation.
Pillar 2: Accelerating Processes (Operational Efficiency)
In many industrial applications, speed is paramount. A vacuum can dramatically accelerate processes that would otherwise be slowed by air pressure.
Consider manufacturing and packaging. A vacuum can instantly form a plastic sheet around a mold or quickly seal a food container. Without it, you would be fighting against ambient air pressure, slowing the entire production line.
This ability to optimize production speed while maintaining quality is a key driver of performance, allowing for higher throughput and greater output.
Pillar 3: Optimizing the Entire System (Systemic Efficiency)
A vacuum pump rarely works in isolation. Its benefits often extend to a facility's other core equipment.
By creating negative pressure, a vacuum pump can reduce the workload on related systems like air compressors or large-scale ventilation. Instead of a compressor working hard to create high pressure, a vacuum pump can assist by creating low pressure on the other side.
This systemic support role leads to significant energy cost savings across the entire operation, not just at the pump itself.
Beyond Efficiency: Enhancing Performance and Reliability
The benefits of a vacuum extend past immediate efficiency gains and contribute to the long-term health and quality of an operation.
The Impact on Equipment Longevity
Friction is the enemy of mechanical systems. It causes wear, generates heat, and leads to eventual failure.
By reducing the physical resistance on moving parts and employing frictionless internal designs, vacuum pumps not only operate more efficiently but also extend their own operational life and that of connected machinery.
This translates to fewer breakdowns, less maintenance, and a higher return on the initial equipment investment.
Ensuring Consistent, High-Quality Output
In sensitive scientific or manufacturing processes, consistency is just as important as speed. Uncontrolled variables can ruin product quality.
Certain designs, like a water circulating vacuum pump, do more than just create a vacuum. They can also provide cooling and maintain a constant, stable vacuum level and temperature.
This stability is critical for applications where precision is non-negotiable, ensuring that every cycle is identical and the final product meets exact specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum pumps are not a universal solution. Their effectiveness depends on proper selection and implementation.
The Initial Investment
A high-quality, efficient vacuum pump is a capital expense. The upfront cost must be weighed against the projected long-term savings in energy, maintenance, and increased productivity.
Matching the Pump to the Application
There is no "one-size-fits-all" vacuum pump. A pump designed for rough vacuum in packaging is fundamentally different from one creating an ultra-high vacuum for a laboratory.
Choosing the wrong type of pump for your required vacuum level or flow rate can be highly inefficient and fail to deliver the desired performance benefits.
Sustainability and Environmental Factors
Energy-efficient operation inherently lowers a facility's carbon footprint. Many modern pumps are also designed to minimize the release of harmful gases.
However, some pump types, such as oil-sealed pumps, require careful maintenance to prevent oil vapor from contaminating the process or the environment. This maintenance overhead is a critical consideration.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
To select the right vacuum technology, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational costs: Prioritize pumps with documented high energy efficiency and low-wear designs to maximize your return on investment through power and maintenance savings.
- If your primary focus is increasing production speed: Select a pump with the flow rate and evacuation speed calibrated to accelerate your specific process, such as packaging, lifting, or forming.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process quality: Choose a system نائب that provides a stable, constant vacuum level, and consider integrated models that also control for variables like temperature.
- If your primary focus is sustainability: Evaluate pumps on their energy ratings to lower your carbon footprint and on designs that prevent the release of lubricants or process gases.
Integrating the correct vacuum technology is a strategic decision to make your entire operation more robust, efficient, and cost-effective.
Summary Table:
| Benefit Category | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces physical resistance, lowering energy consumption and drag. |
| Operational Efficiency | Speeds up production cycles like packaging and forming. |
| Systemic Efficiency | Lowers workload on connected equipment, saving costs across the facility. |
| Reliability & Longevity | Minimizes wear and heat, extending equipment lifespan. |
| Quality & Consistency | Provides stable vacuum levels for precise, repeatable results. |
Ready to optimize your lab or industrial process with the right vacuum technology? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including vacuum pumps tailored to your specific needs—whether your goal is cutting energy costs, accelerating production, or ensuring precision. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for enhanced efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Vertical Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation



















