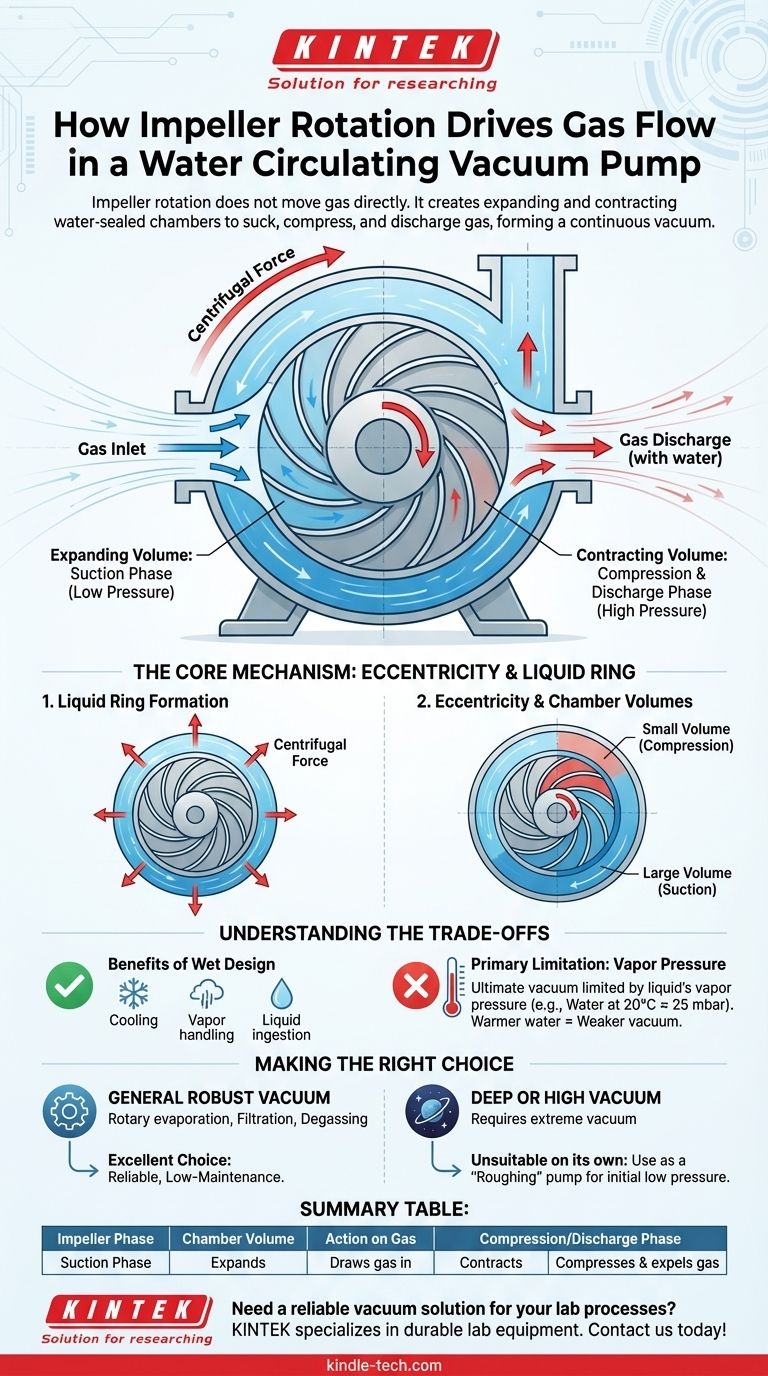
In a water circulating vacuum pump, the impeller's rotation does not move gas directly. Instead, its rotation creates a series of expanding and contracting water-sealed chambers. These chambers first expand to suck gas in from the inlet and then contract to compress and discharge that gas, creating a continuous vacuum effect.
The core principle is simple but brilliant: the impeller is mounted off-center within the pump casing. As it spins, it forces the water to form a ring against the outer wall, creating sealed chambers between the impeller blades that constantly change in volume, which is what drives the entire pumping action.

The Core Mechanism: From Rotation to Vacuum
To understand how the pump works, we must visualize the journey of a single pocket of gas as the impeller completes one rotation. The process relies on a synergy between the impeller, the casing, and the sealing liquid (typically water).
Forming the Liquid Ring
When the pump is turned on, the impeller spins at high speed. Centrifugal force throws the water outwards, forcing it to form a concentric liquid ring that follows the circular inner shape of the pump's casing. This liquid ring is the key sealing medium.
The Key is Eccentricity
The impeller's axis of rotation is deliberately offset from the geometric center of the casing. This eccentric mounting is the most critical design element.
Because of this offset, the space between the central hub of the impeller and the inner surface of the liquid ring is not constant. It's small on one side and large on the other.
The Suction Phase (Expanding Volume)
As a pair of impeller blades rotates through the area where the hub is moving away from the liquid ring, the volume of the chamber sealed between them increases.
This expansion creates a drop in pressure, turning the chamber into a low-pressure zone. This is the "suction" phase, where gas is drawn into the pump from the inlet port.
The Compression & Discharge Phase (Contracting Volume)
As the same blades continue to rotate to the opposite side, they move into the area where the impeller hub is moving toward the liquid ring.
Here, the volume of the chamber decreases, compressing the gas that was just drawn in. This pressure builds until it exceeds the pressure at the discharge port, forcing the compressed gas and a small amount of water out of the pump. This cycle repeats with every rotation for every chamber, creating a smooth and continuous vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Liquid ring vacuum pumps are valued for their robustness, but their design comes with inherent advantages and limitations that are important to recognize.
The Benefits of a Wet Design
The presence of the water ring provides several unique advantages. It constantly cools the pump, allows it to handle condensable vapors (like water vapor), and can even ingest small amounts of liquid or soft solids without damage, unlike many other vacuum pump designs.
The Primary Limitation: Vapor Pressure
The ultimate vacuum level a water ring pump can achieve is limited by the vapor pressure of the sealing liquid.
Water will begin to boil and turn to vapor at low pressures. For water at 20°C (68°F), this occurs around 25 mbar (18.75 Torr). The pump cannot create a vacuum deeper than the point at which its own sealing liquid starts boiling, as this would just fill the pump with more vapor. Warmer water has a higher vapor pressure, resulting in a weaker ultimate vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this operating principle helps you use the pump effectively and choose the right tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is robust, low-maintenance vacuum for general applications: This pump is an excellent choice for tasks like rotary evaporation, degassing, or vacuum filtration where extreme vacuum is not required.
- If your primary focus is achieving a deep or high vacuum: A liquid ring pump is unsuitable on its own. It is better used as a "roughing" pump to bring the system to an initial low pressure before a high-vacuum pump (like a turbomolecular or diffusion pump) takes over.
Grasping how rotation, eccentricity, and the liquid ring work together empowers you to operate and troubleshoot your vacuum system with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Impeller Rotation Phase | Effect on Chamber Volume | Action on Gas |
|---|---|---|
| Suction Phase | Expands | Draws gas in from the inlet |
| Compression/Discharge Phase | Contracts | Compresses and expels gas |
Need a reliable vacuum solution for your lab processes like rotary evaporation or filtration? KINTEK specializes in durable lab equipment, including water circulating vacuum pumps perfect for handling condensable vapors and offering robust, low-maintenance performance. Let our experts help you select the ideal pump for your application. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation



















