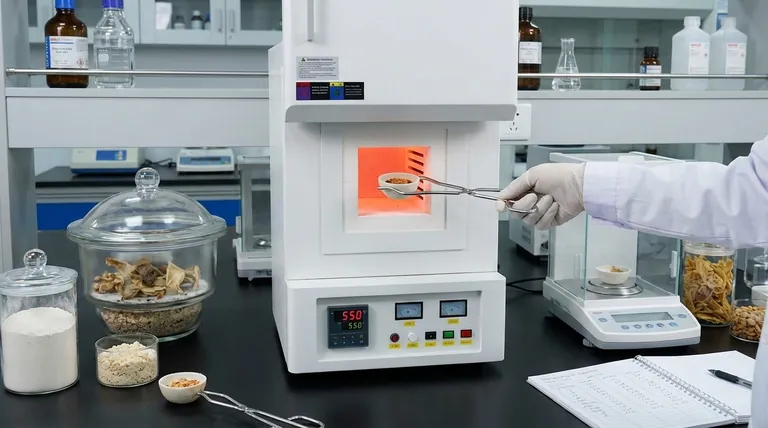
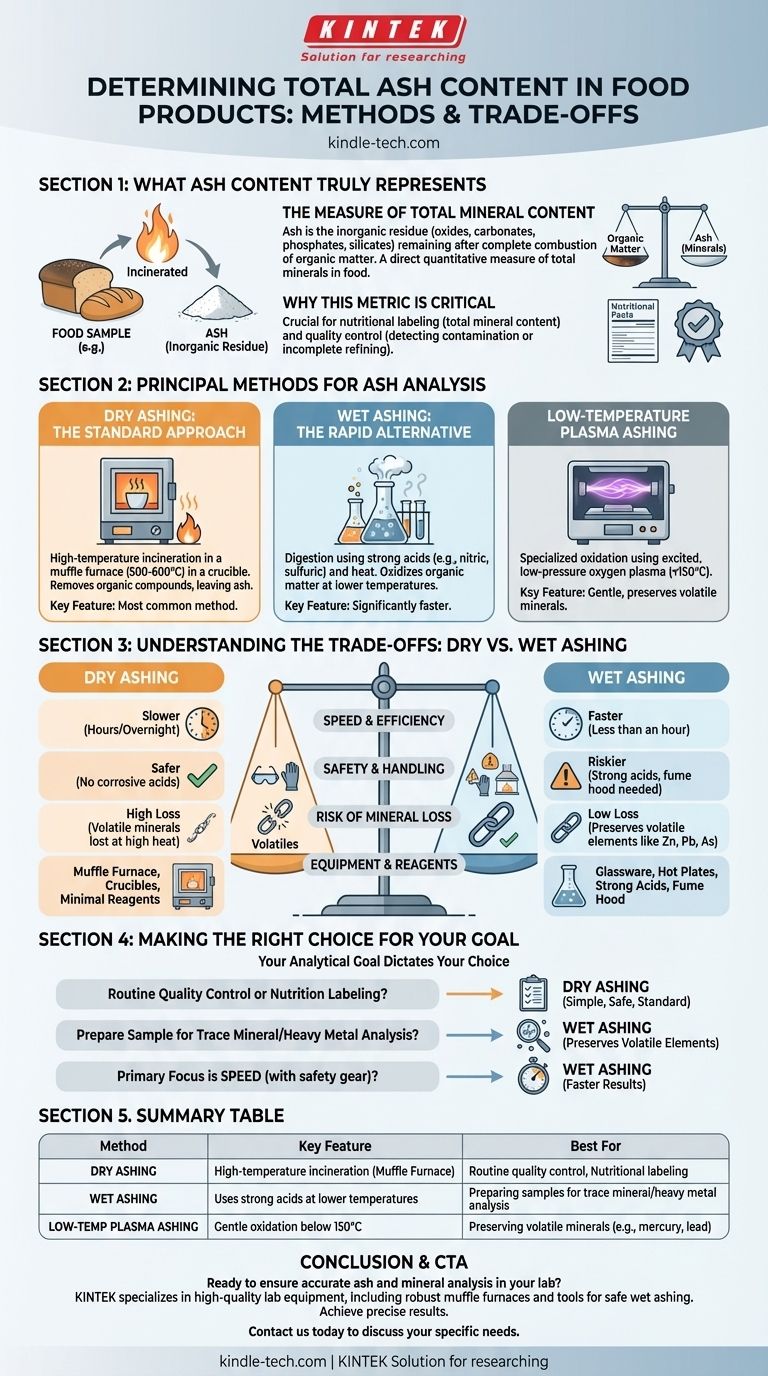
To determine the total ash content in a food product, the sample is incinerated at high temperatures to completely burn away all organic matter. The remaining inorganic, non-combustible material is weighed, and this residue is defined as the ash content. The principal methods for this analysis are dry ashing, wet ashing, and low-temperature plasma ashing.
Ash analysis is fundamentally a measure of the total mineral content within a food product. The choice between the two primary methods, dry and wet ashing, hinges on a critical trade-off between safety, speed, and whether you need to preserve volatile minerals for further analysis.

What Ash Content Truly Represents
The Measure of Total Mineral Content
Ash is the inorganic residue that remains after the complete combustion of organic matter.
This residue consists of the oxides, carbonates, phosphates, and silicates of the elements present in the original sample. Essentially, ash content serves as a direct quantitative measure of the total amount of minerals in a food.
Why This Metric is Critical
Ash analysis is a crucial parameter in food science and quality control.
It is used for nutritional labeling to declare total mineral content. It also serves as an indicator of quality; for instance, high ash content in flour can indicate contamination with bran, while in sugar it can signify incomplete refining.
Principal Methods for Ash Analysis
Dry Ashing: The Standard Approach
Dry ashing is the most common method used for determining total ash content.
The process involves placing a precisely weighed sample in a heat-resistant crucible and heating it in a muffle furnace at very high temperatures, typically between 500 and 600°C. The high heat incinerates all organic compounds, leaving only the inorganic ash behind.
Wet Ashing: The Rapid Alternative
Wet ashing, or wet digestion, uses a combination of strong acids (like nitric and sulfuric acid) and heat to oxidize and break down the organic matter.
This method operates at much lower temperatures than dry ashing and is significantly faster. It is often the preferred method when the sample needs to be prepared for subsequent elemental analysis.
Low-Temperature Plasma Ashing
This is a more specialized method where a sample is oxidized in a chamber using excited, low-pressure oxygen gas (plasma).
It is a very gentle method that operates at temperatures below 150°C. This makes it ideal for analyzing samples where the loss of volatile trace minerals (like mercury or lead) at high temperatures is a major concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Dry vs. Wet Ashing
Speed and Efficiency
Wet ashing is generally much faster, often taking less than an hour for digestion, whereas dry ashing can require several hours or even run overnight to ensure complete combustion.
Safety and Handling
Dry ashing is inherently safer because it avoids the use of hazardous and highly corrosive acids. Wet ashing demands a well-ventilated fume hood and careful handling of dangerous chemicals, posing a greater risk to the operator.
Risk of Mineral Loss
The high temperatures of dry ashing can cause some volatile mineral elements (such as zinc, lead, and arsenic) to be lost. Wet ashing's lower temperatures minimize this loss, making it the superior choice if you plan to analyze for specific trace elements afterward.
Equipment and Reagents
Dry ashing primarily requires a muffle furnace and crucibles with minimal chemical reagents. Wet ashing requires specialized glassware, hot plates, and strong acids, along with mandatory safety infrastructure like a fume hood.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct method is critical for obtaining accurate and relevant data. Your analytical goal should dictate your choice.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control or nutrition labeling: Dry ashing is the simple, safe, and universally accepted standard for determining total ash.
- If your primary focus is preparing a sample for trace mineral or heavy metal analysis: Wet ashing is the superior method because its lower temperature prevents the loss of volatile elements.
- If your primary focus is speed and you have the necessary safety equipment: Wet ashing provides much faster results than the conventional dry ashing procedure.
Understanding these core principles allows you to select the precise analytical method that aligns with your specific food science objectives.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Ashing | High-temperature incineration in a muffle furnace | Routine quality control, nutritional labeling |
| Wet Ashing | Uses strong acids at lower temperatures | Preparing samples for trace mineral/heavy metal analysis |
| Low-Temperature Plasma Ashing | Gentle oxidation below 150°C | Preserving volatile minerals (e.g., mercury, lead) |
Ready to ensure accurate ash and mineral analysis in your lab?
Choosing the right equipment is essential for reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including robust muffle furnaces for dry ashing and the necessary tools for safe wet ashing procedures. Our solutions are designed to meet the rigorous demands of food science laboratories, helping you achieve precise quality control and nutritional labeling.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your specific needs and let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your ash analysis workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of heat treatment? It Depends on Your Metal and Desired Properties
- What is the introduction of muffle furnace? A Guide to High-Temperature, Contamination-Free Heating
- Is a muffle furnace an oven? A Guide to High-Temperature vs. Low-Temperature Heating
- What is the heat capacity of a muffle furnace? Understanding Thermal Mass for Optimal Performance
- What is the use of muffle furnace in chemistry laboratory? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Material Processing



















