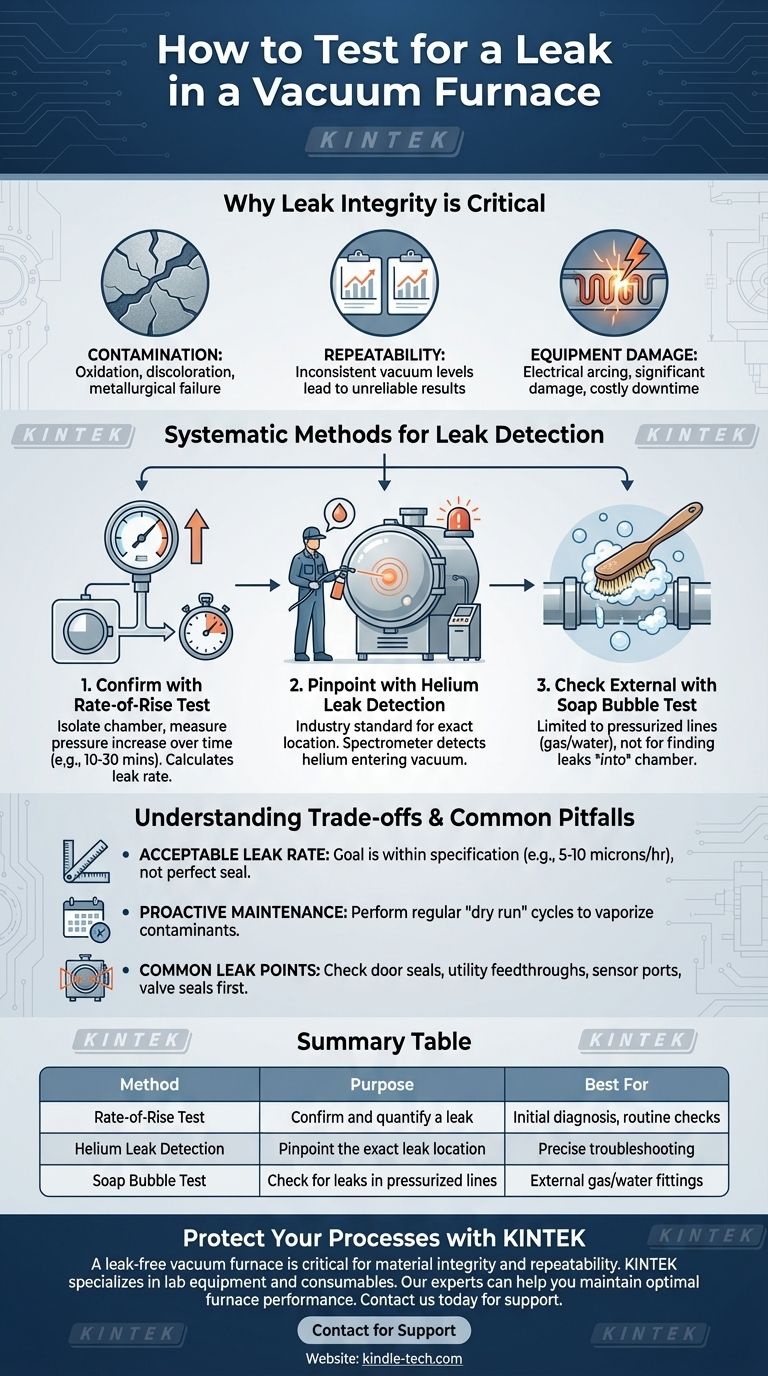
To test for a leak in a vacuum furnace, you must first confirm a leak exists with a "rate-of-rise" test by isolating the chamber and measuring the pressure increase over time. Once confirmed, the most effective method for pinpointing the source is to use a helium mass spectrometer leak detector, which can identify the precise location where gas is entering the vessel.
The goal of leak testing is not to achieve a perfect, impossible seal, but to ensure the furnace's "leak-up rate" is within the acceptable specification for your process. This prevents atmospheric contaminants from compromising the integrity of your materials and the consistency of your results.

Why Leak Integrity is Critical
A vacuum furnace's primary function is to create a tightly controlled, pure atmosphere. A leak, no matter how small, directly undermines this function.
Protecting Product from Contamination
The most immediate consequence of a leak is contamination. Atmospheric air, composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen, enters the chamber and can react with the materials being processed, leading to oxidation, discoloration, and failure to meet metallurgical specifications.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
For scientific and industrial applications, consistency is key. A furnace with a fluctuating leak rate will produce inconsistent vacuum levels from one cycle to the next, leading to unreliable and non-repeatable results.
Preventing Equipment Damage
In some systems, a poor vacuum can lead to more than just contamination. It can cause electrical arcing between heating elements or other internal components, potentially causing significant damage and costly downtime.
Systematic Methods for Leak Detection
Finding a leak should be a systematic process, moving from general confirmation to specific identification.
The Initial Indicator: The Rate-of-Rise Test
Before you can find a leak, you must confirm one exists. A rate-of-rise (or leak-up) test is the standard method for quantifying the leak rate.
The process is simple:
- Pump the furnace down to its normal operating vacuum level.
- Close the main valve to isolate the chamber from the vacuum pumps.
- Record the pressure at the start and monitor its increase over a set period (e.g., 10-30 minutes).
A significant pressure increase confirms a leak is present and its rate can be calculated (e.g., in microns per hour).
Pinpointing the Source: Helium Leak Detection
This is the industry-standard method for finding the exact location of a leak. A helium mass spectrometer is attached to the furnace's vacuum system.
With the furnace under vacuum, a fine stream of helium gas is sprayed over suspected leak points on the outside of the chamber. If helium enters the chamber through a leak, the spectrometer will detect it instantly, alerting the operator.
A Low-Tech Check for External Components
The classic "soap bubble" test has a limited but important role. It is not effective for finding a leak into a vacuum chamber.
However, it is useful for checking pressurized components connected to the furnace, such as inert gas supply lines or water-cooling fittings. By pressurizing the line and spraying it with a soap solution, any bubbles that form will indicate a leak out of that component.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Effective leak management requires understanding nuance and knowing where to look first.
Defining an "Acceptable" Leak Rate
No furnace is perfectly hermetic. All have a baseline, acceptable leak-up rate defined by the manufacturer. The goal is to ensure your furnace stays within this specified tolerance, which is typically very low (e.g., 5-10 microns per hour).
The Role of Proactive Maintenance
Preventing contamination is as important as finding leaks. Regularly performing "dry run" or "burn-out" cycles at high temperature and high vacuum helps vaporize and pump away contaminants that have accumulated inside the furnace. This should be done at least weekly.
Common Leak Points to Check First
When using a helium leak detector, start with the most common failure points to save time:
- Door Seals: The largest seal on the furnace and subject to the most wear.
- Utility Feedthroughs: Points where power, water, or gas lines enter the chamber.
- Sensor Ports: Connections for thermocouples and vacuum gauges.
- Valve Seals: Seals on the main valve, roughing valve, and gas inlet valves.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this framework to guide your maintenance and troubleshooting efforts.
- If you suspect a leak but don't know its severity: Perform a rate-of-rise test to quantify the problem and determine if it exceeds the manufacturer's specification.
- If you need to find the precise location of a known leak: The helium mass spectrometer leak detector is the definitive tool for the job.
- If you are performing routine preventative maintenance: Regularly perform dry run cycles and check external, pressurized gas and water fittings for leaks.
Adopting this systematic approach to leak detection and prevention will ensure the reliability, consistency, and longevity of your vacuum furnace operations.
Summary Table:
| Method | Purpose | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Rate-of-Rise Test | Confirm and quantify a leak | Initial diagnosis, routine checks |
| Helium Leak Detection | Pinpoint the exact leak location | Precise troubleshooting |
| Soap Bubble Test | Check for leaks in pressurized lines | External gas/water fittings |
Protect your processes and ensure consistent results. A leak-free vacuum furnace is critical for material integrity and repeatability. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you maintain optimal furnace performance. Contact us today for support with leak detection, maintenance, or to find the right equipment for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Filter Testing Machine FPV for Dispersion Properties of Polymers and Pigments
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is the role of the hydraulic system in hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Density and Strength
- What is a magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How mechanical properties are affected by sintering? Master the Trade-offs for Stronger Materials



















