At its core, a crucible furnace is a device that melts materials by heating them inside a high-temperature-resistant container, known as a crucible. The fundamental process involves placing a solid material (like metal) into the crucible, applying intense heat until it becomes liquid, and then pouring the molten material into a mold. The key differentiator between furnace types is how that heat is generated and transferred to the material.
The term "crucible furnace" describes a category, not a single technology. The most critical distinction is whether the crucible is heated externally by a flame or electric element, or if the material inside is heated directly using electromagnetic induction.
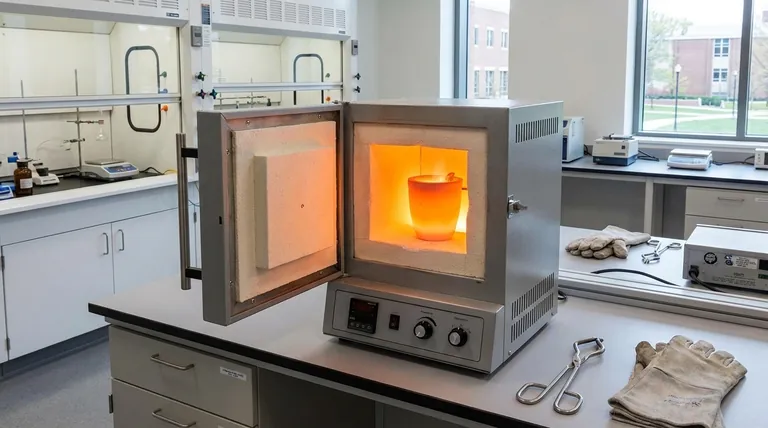

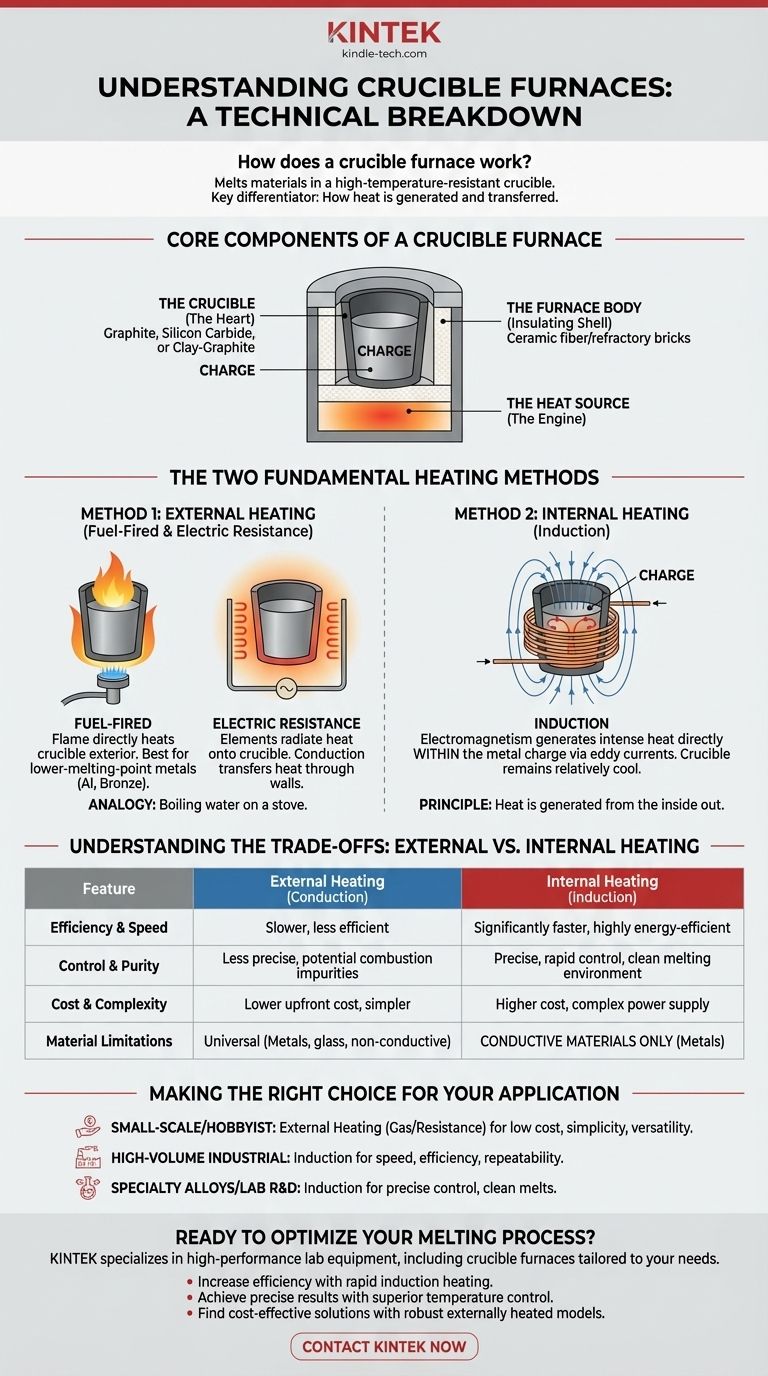
The Core Components of Any Crucible Furnace
Regardless of the heating method, all crucible furnaces share a similar set of fundamental parts that work together to contain heat and melt the target material.
The Crucible: The Heart of the Furnace
The crucible is the pot-like container that directly holds the material being melted, or "charge." It must be made from a refractory material capable of withstanding extreme thermal shock and high temperatures without reacting with the molten material. Common materials include graphite, silicon carbide, and clay-graphite mixtures.
The Furnace Body: The Insulating Shell
The furnace body, or casing, is the structure that surrounds the crucible. Its primary job is to insulate the system, containing the intense heat and directing it toward the crucible to maximize efficiency and ensure safety. It is typically lined with materials like ceramic fiber wool or refractory bricks.
The Heat Source: The Engine of the Process
This is the component that generates the heat and represents the main technological difference between furnace types. The method used to generate heat dictates the furnace's efficiency, speed, and suitability for different materials and applications.
The Two Fundamental Heating Methods
Understanding how heat is generated is the key to understanding how a crucible furnace truly works. The methods fall into two primary categories: external and internal heating.
Method 1: External Heating (Fuel-Fired & Electric Resistance)
This is the most traditional approach. An external heat source heats the outside surface of the crucible, and that heat is then transferred through the crucible walls to the material inside via conduction.
This is analogous to boiling water in a pot on a stove. The burner heats the pot, and the pot heats the water. The two primary types are:
- Fuel-Fired: A gas or oil burner generates a flame that directly envelops the crucible. This is a simple, robust, and common method, especially for lower-melting-point metals like aluminum and bronze.
- Electric Resistance: High-resistance heating elements, similar to those in an electric kiln, are positioned around the crucible. As electricity passes through them, they glow red-hot, radiating heat onto the crucible.
Method 2: Internal Heating (Induction)
An induction furnace is a more advanced type of crucible furnace that heats the material directly, from the inside out. It does not rely on an external flame or glowing heating element.
The process works on the principle of electromagnetism:
- A coil of hollow copper tubing is wrapped around the crucible.
- A powerful, high-frequency alternating current is passed through this coil.
- This creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field that passes through the crucible and into the conductive metal charge inside.
- The magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents (called eddy currents) directly within the metal itself.
- The metal's own electrical resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat, causing it to melt quickly.
In this system, the heat is generated within the charge material, not outside the crucible. The furnace body stays relatively cool, as it is not the primary source of heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs: External vs. Internal Heating
Choosing a heating method involves significant trade-offs in efficiency, cost, and capability.
Efficiency and Speed
Induction heating is significantly faster and more energy-efficient. Because heat is generated directly within the metal, very little energy is wasted heating the furnace body or the surrounding air. Externally heated furnaces are slower, as heat must first saturate the crucible before it can melt the charge.
Control and Purity
Induction offers extremely precise and rapid temperature control. Furthermore, because there is no combustion, it provides a much cleaner melting environment, which is critical for producing high-purity, specialized alloys.
Cost and Complexity
Externally heated furnaces, particularly simple propane-fired models, are mechanically simpler and have a much lower upfront cost. Induction furnaces require a sophisticated power supply and control system, making them more complex and expensive to purchase and install.
Material Limitations
The most significant limitation of induction is that it only works on electrically conductive materials, like metals. External heating methods are universal and can be used to melt anything from metals to glass and other non-conductive compounds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The best furnace design depends entirely on the goal of the user, balancing cost, performance, and material requirements.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting or hobbyist work: An externally heated furnace (gas or resistance) offers the best combination of low cost, simplicity, and versatility.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: An induction furnace provides the speed, efficiency, and repeatability required for a modern foundry.
- If your primary focus is creating specialty alloys or lab research: An induction furnace is superior for its precise temperature control and clean melting environment.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace comes down to understanding that the crucible holds the material, but the heating method defines the process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Heating Method | Key Advantages | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuel-Fired / Resistance | External (Conduction) | Lower cost, versatile, simple | Hobbyists, lower-melting-point metals (Al, Bronze) |
| Induction | Internal (Electromagnetic) | High speed, energy-efficient, precise control, clean melts | Industrial production, high-purity alloys, conductive metals only |
Ready to Optimize Your Melting Process?
Choosing the right furnace is critical for your project's success, whether you're in R&D or full-scale production. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including crucible furnaces tailored to your specific material and throughput requirements.
We can help you:
- Increase efficiency with rapid, energy-saving induction heating.
- Achieve precise results with superior temperature control for specialty alloys.
- Find a cost-effective solution with robust and versatile externally heated models.
Let our experts guide you to the perfect equipment for your laboratory or foundry. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and see how we can support your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















