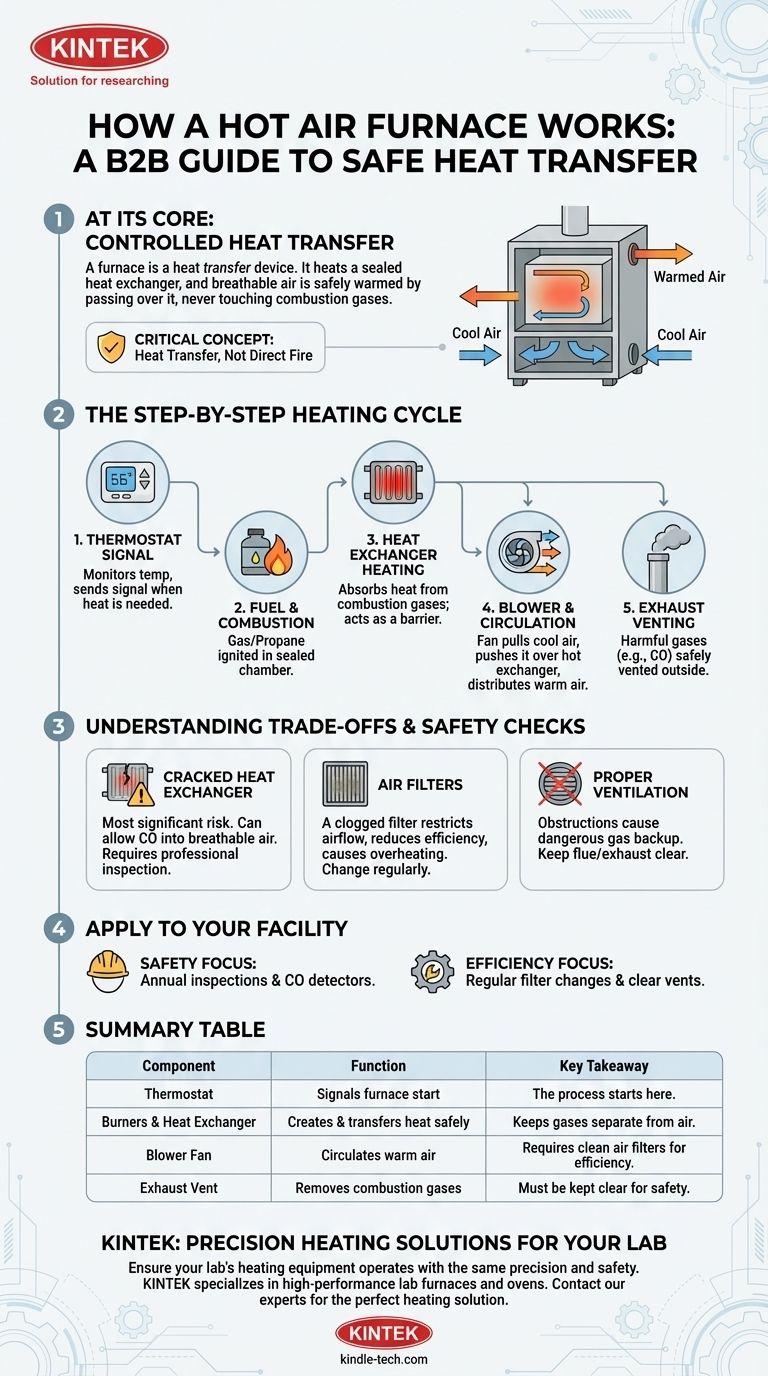
At its core, a hot air furnace works by creating heat in a controlled chamber and then using a fan to blow your home's air across the outside of that hot chamber. This process warms the air without ever letting it touch the dangerous combustion gases, which are then safely vented outside your home.
The most critical concept to understand is that a furnace is a heat transfer device. It doesn't heat your air with fire directly. Instead, it heats a sealed metal component—the heat exchanger—and your breathable air is safely warmed by passing over it.

The Step-by-Step Heating Cycle
To truly understand how a furnace operates, it’s best to follow the sequence of events from the moment you feel a chill to the warm air coming from your vents.
The Thermostat's Signal
The entire process begins with the thermostat. This device constantly monitors your home's temperature. When the temperature drops below your set point, it sends a low-voltage electrical signal to the furnace, initiating the call for heat.
Fuel, Burners, and Combustion
Once the signal is received, a valve opens to supply natural gas or propane to the furnace's burners. An ignitor—either an electronic spark or a hot surface element—lights this fuel, creating a controlled flame inside a sealed combustion chamber.
The Critical Role of the Heat Exchanger
The flames and hot gases produced by the burners heat a component called the heat exchanger. This is typically a series of metal tubes or chambers designed to absorb and hold a tremendous amount of heat. It acts as a crucial barrier, keeping the breathable air of your home separate from the toxic combustion byproducts.
The Blower and Air Circulation
After the heat exchanger reaches the proper operating temperature, the furnace's blower fan turns on. It pulls cooler air from your home through the return ducts, pushes it across the hot exterior surfaces of the heat exchanger, and then sends the newly warmed air into your home's supply ductwork to be distributed through the vents.
Safely Venting the Exhaust
While the blower distributes warm air, the harmful gases created during combustion—including carbon monoxide—are funneled out of the heat exchanger and into a flue pipe. This pipe safely vents all exhaust gases to the outside of your home.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Checks
A furnace is a reliable workhorse, but its safe operation depends on the integrity of its core components. Understanding the potential points of failure is key to maintaining a safe and efficient system.
The Danger of a Cracked Heat Exchanger
This is the most significant safety concern with any fuel-burning furnace. Over time, the constant expansion and contraction from heating and cooling can cause cracks in the heat exchanger's metal. A crack can allow dangerous combustion gases, including carbon monoxide, to mix with your home's breathable air. This is why regular professional inspections and functioning CO detectors are non-negotiable.
The Importance of Air Filters
The blower fan circulates all the air in your home, including dust, dander, and other debris. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, forcing the furnace to work harder and longer. This reduces efficiency, increases energy bills, and can cause the system to overheat, potentially shortening its lifespan.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
The furnace needs a clear and unobstructed flue or exhaust vent to operate safely. Any blockage from nests, debris, or snow and ice can cause exhaust gases to back up into your home, creating a hazardous situation.
How to Apply This to Your Home
Understanding this process empowers you to maintain your system effectively, ensuring it runs safely and efficiently for years to come.
- If your primary focus is safety: Prioritize annual professional inspections to check the heat exchanger's integrity and ensure you have working carbon monoxide detectors on every level of your home.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and longevity: Commit to changing your air filter every 1-3 months and clearing any debris from around the exterior intake and exhaust vents.
Knowing how your furnace safely separates combustion from circulation is the key to appreciating its simple yet critical role in your home's comfort.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Thermostat | Signals the furnace to start heating. | The process starts here. |
| Burners & Heat Exchanger | Creates heat and transfers it safely. | Keeps combustion gases separate from your air. |
| Blower Fan | Circulates warm air throughout the home. | Requires clean air filters for efficiency. |
| Exhaust Vent | Safely removes combustion gases (e.g., CO) outside. | Must be kept clear for safety. |
Ensure your lab's heating equipment operates with the same precision and safety. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, ovens, and related equipment, delivering the reliable temperature control and safety features essential for your research and processes. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- Why nitrogen is used in annealing furnace? To prevent oxidation and decarburization for superior metal quality
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















