Excessive heat is the single most destructive force in a hydraulic system. It silently undermines performance before causing catastrophic failure. The primary effect of heat is a drastic reduction in the hydraulic fluid's viscosity, causing it to become too thin to properly lubricate, seal, and transmit power, which in turn accelerates wear on every component in the system.
Heat in a hydraulic system is not just a problem; it's a symptom of wasted energy. Left unmanaged, it systematically breaks down every component, from the fluid itself to the seals that contain it, leading to reduced performance, shorter service life, and costly downtime.

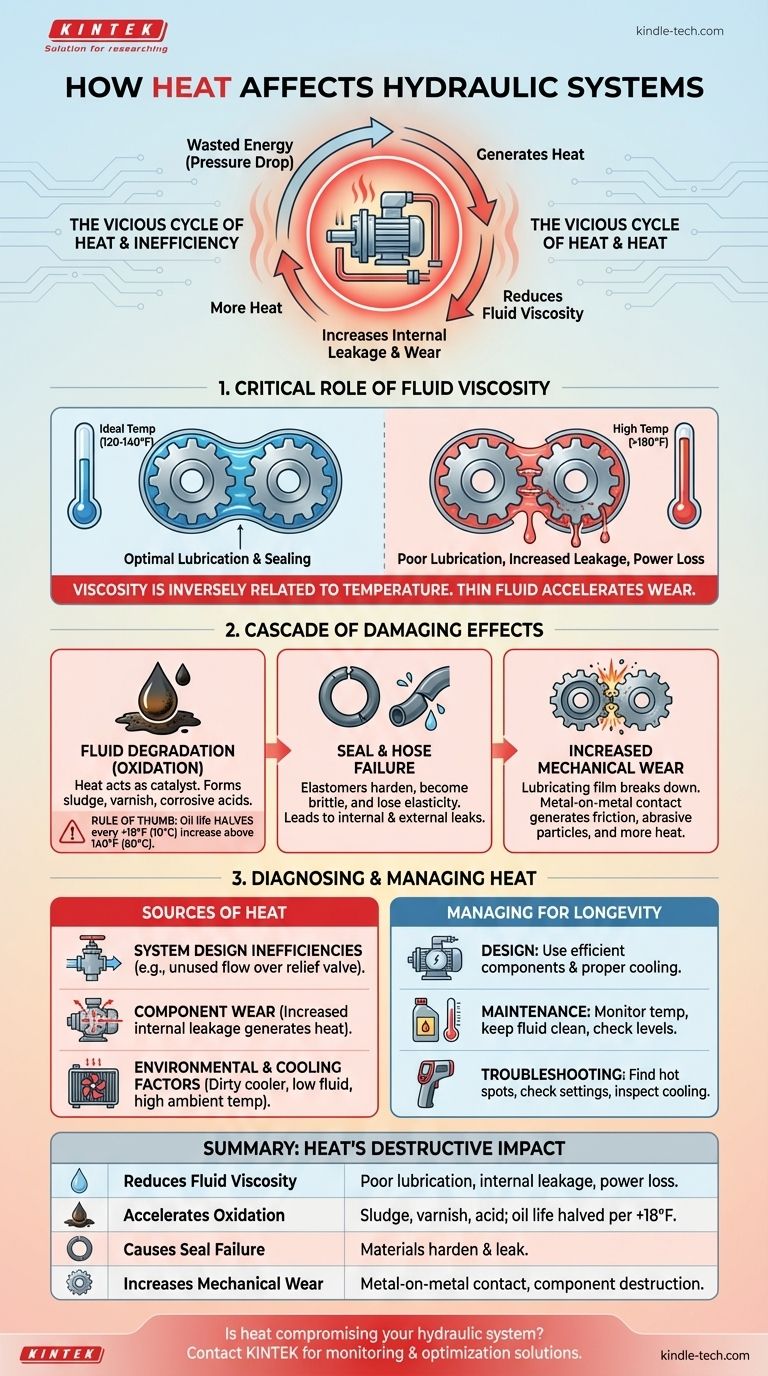
The Vicious Cycle of Heat and Inefficiency
To understand the danger of heat, you must first understand that it represents energy that is not being converted into useful work. Every hydraulic system has inherent inefficiencies, and this lost energy is converted directly into heat.
Heat is Wasted Energy
A hydraulic system is an energy conversion device. The electrical or mechanical energy powering the pump is converted into hydraulic energy (flow and pressure).
Any pressure drop in the system that does not result in work (like moving a cylinder) is converted to heat. This includes fluid flowing across a relief valve, through flow controls, or even from friction in hoses and pipes.
The Critical Role of Fluid Viscosity
Viscosity is the most important property of a hydraulic fluid. It is a measure of the fluid's resistance to flow and its ability to maintain a lubricating film between moving parts.
Crucially, viscosity is inversely related to temperature. As the fluid gets hotter, its viscosity drops—it becomes thinner. Most hydraulic systems are designed to operate with fluid in a specific viscosity range, typically around 120-140°F (50-60°C).
How Low Viscosity Degrades Performance
When the fluid becomes too thin, it can no longer perform its core functions effectively. This leads to increased internal leakage in pumps, motors, and valves.
The pump must then work harder to produce the same output, generating even more heat. This creates a destructive feedback loop where heat causes inefficiency, and that inefficiency generates more heat.
How Excessive Heat Systematically Destroys Components
Operating a hydraulic system above the recommended temperature—especially above 180°F (82°C)—initiates a cascade of damaging chemical and physical reactions.
Accelerated Fluid Degradation (Oxidation)
Heat acts as a catalyst for oxidation, a chemical reaction between the oil and oxygen. This process permanently degrades the fluid, forming sludge, varnish, and corrosive acids.
As a general rule, for every 18°F (10°C) increase in fluid temperature above 140°F (60°C), the service life of the oil is cut in half. Varnish coats internal surfaces, causing valves to stick and blocking small orifices.
Seal and Hose Failure
Seals, O-rings, and hoses are made from specific elastomer compounds designed to operate within a certain temperature range.
Excessive heat causes these materials to harden, become brittle, and lose their elasticity. This leads to leaks, both internal and external, which can result in fluid loss, contamination, and component failure.
Increased Mechanical Wear
The lubricating film created by the hydraulic fluid is what prevents metal-on-metal contact in pumps, motors, and actuators.
When heat thins the fluid, this film can break down. The resulting increase in friction and wear generates more heat and introduces metal particles into the system, which act as an abrasive to accelerate the destruction of other components.
Diagnosing the Source of Heat
Controlling heat isn't just about adding a bigger cooler; it's about identifying and fixing the underlying inefficiency. High temperatures are a symptom, and you must diagnose the cause.
System Design Inefficiencies
The most common source of heat is a system design that constantly forces fluid over a relief valve. A fixed-displacement pump running at full flow when no work is being done is a prime example. All that unused flow goes over the relief valve, converting 100% of its energy into heat.
Component Wear
As pumps and motors wear out, the clearances between their internal parts increase. This allows more high-pressure fluid to leak back to the low-pressure side internally. This leakage generates no work and is converted entirely to heat.
Environmental Factors and Cooling
The system's ability to dissipate heat is critical. A dirty or clogged heat exchanger (cooler), low fluid level in the reservoir, or high ambient temperatures can all prevent the system from shedding the heat it naturally generates, causing it to build up to dangerous levels.
Managing Heat for System Longevity
Your approach to managing heat depends on whether you are designing, maintaining, or troubleshooting a system.
- If your primary focus is designing a new system: Prioritize efficiency from the start by using pressure-compensated pumps, correctly sizing the reservoir for passive cooling, and incorporating an adequately sized heat exchanger.
- If your primary focus is maintaining an existing system: Regularly monitor operating temperatures, keep the fluid clean, ensure the heat exchanger is free of debris, and verify proper fluid levels in the reservoir.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting an overheating system: Use an infrared thermometer to find hot spots, check relief valve settings and operation, and inspect the cooling circuit for blockages or malfunction.
Ultimately, controlling temperature is about controlling efficiency and ensuring the long-term reliability of your entire hydraulic system.
Summary Table:
| Heat Effect | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Reduces Fluid Viscosity | Poor lubrication, increased internal leakage, loss of power |
| Accelerates Fluid Oxidation | Sludge, varnish, and acid formation; oil life is halved every 18°F (10°C) above 140°F |
| Causes Seal & Hose Failure | Materials harden and crack, leading to leaks |
| Increases Mechanical Wear | Metal-on-metal contact, abrasive contamination, and component destruction |
Is heat compromising your hydraulic system's efficiency and lifespan? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the precise laboratory equipment and consumables needed to monitor, maintain, and optimize your systems. From fluid analysis tools to temperature monitoring solutions, we support the reliability and performance of your operations. Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss how we can help you combat heat and extend the life of your critical equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Manual Lab Heat Press
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation
- What is the role of a hydraulic press with heating plates in copper welding tests? Analyze Stress & Thermal Cycles



















