At its core, a power press is a machine tool designed to amplify force. It converts energy from a source like an electric motor into a controlled, linear motion to cut, shape, or form materials. While there are several designs, the two dominant types are mechanical presses, which use a flywheel and crankshaft, and hydraulic presses, which use fluid pressure.
The central purpose of any power press is force multiplication. Whether through the stored rotational energy of a mechanical flywheel or the incompressible nature of hydraulic fluid, the machine takes a relatively small input and converts it into a powerful, concentrated force to work on a material.
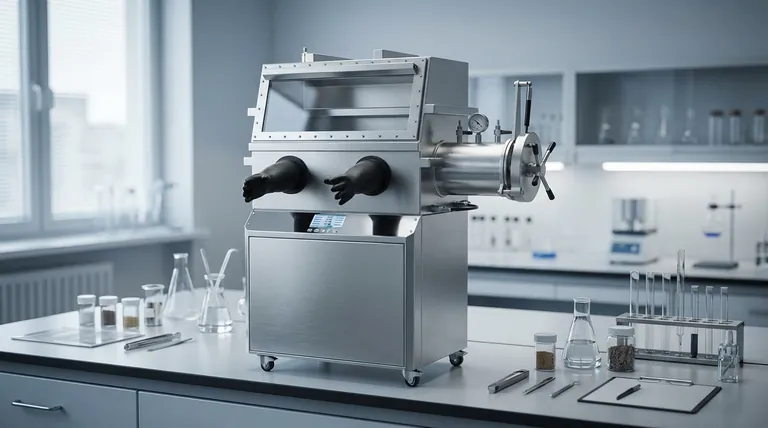

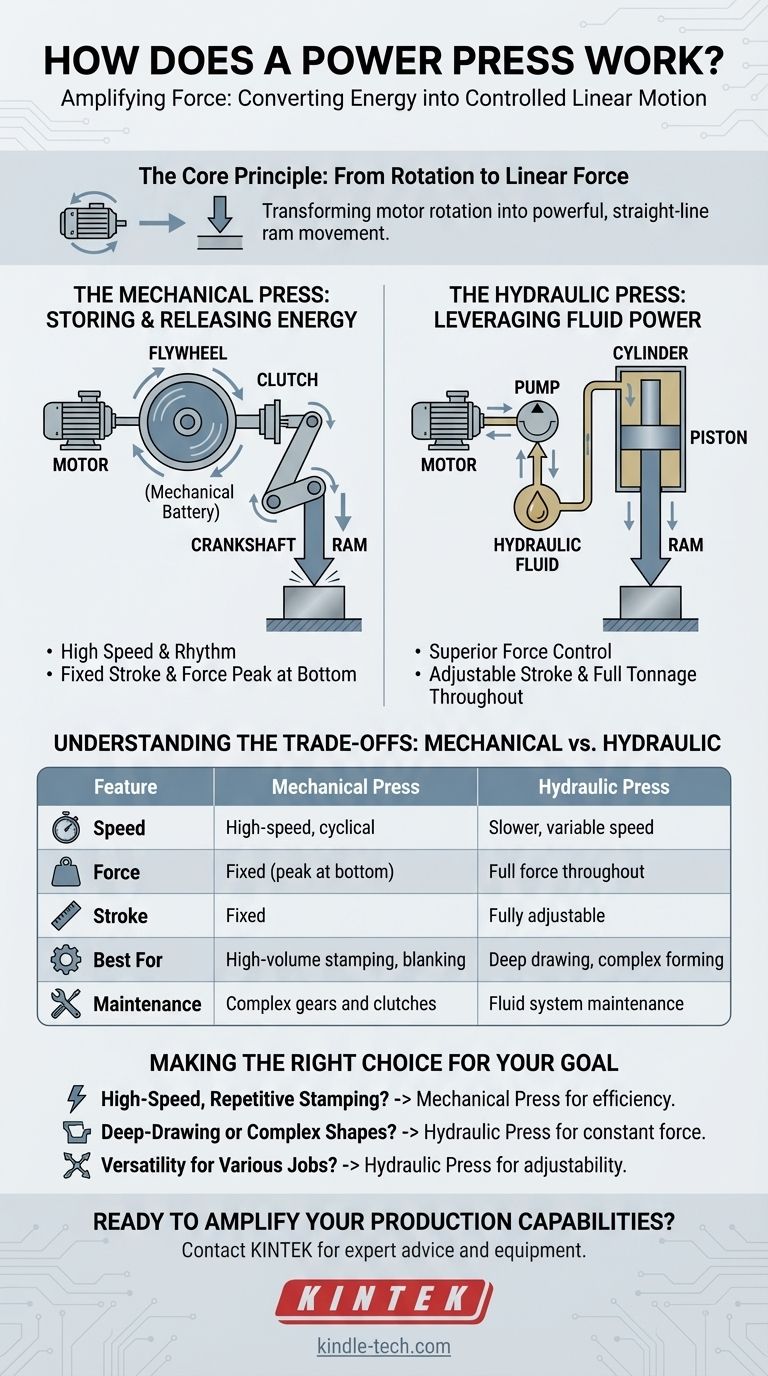
The Core Principle: From Rotation to Linear Force
The fundamental goal of a power press is to move a tool, known as a ram or slide, up and down in a straight line with tremendous force. The machine's entire design is built around achieving this conversion from the spinning of a motor to the powerful linear press of the ram.
The Mechanical Press: Storing and Releasing Energy
The most common type of power press operates mechanically, using a system analogous to the internal combustion engine in your car.
A motor turns a large, heavy flywheel, which acts like a mechanical battery, storing kinetic energy from the motor's continuous rotation.
When the operator engages the press, a clutch connects the spinning flywheel to a crankshaft.
The crankshaft, through its eccentric design, converts the flywheel's rotational motion into the powerful up-and-down linear motion of the ram, which holds the die or tool.
The Hydraulic Press: Leveraging Fluid Power
The hydraulic press works on a completely different principle, leveraging Pascal's Law, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
An electric motor drives a pump, which forces hydraulic fluid (typically oil) into a cylinder.
This pressurized fluid pushes against a large piston inside the cylinder. Because the piston has a large surface area, the fluid pressure creates a massive downward force.
This piston is connected directly to the ram, driving it down with consistent force throughout its entire stroke. Reversing the flow of the fluid with control valves retracts the ram.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Mechanical vs. Hydraulic
Choosing between a mechanical and a hydraulic press depends entirely on the job. Neither is universally superior; they are simply different tools for different tasks.
Speed and Rhythm
Mechanical presses are significantly faster. Their fixed, cyclical motion makes them ideal for high-volume, repetitive operations like stamping, blanking, or coining where thousands of identical parts are needed quickly.
Force Control and Consistency
Hydraulic presses offer superior force control. They can deliver their full rated tonnage at any point in the stroke, not just at the bottom like a mechanical press. This makes them ideal for deep drawing or forming complex parts that require sustained pressure.
Stroke Length and Flexibility
The stroke length on a mechanical press is fixed by the geometry of the crankshaft. In contrast, the stroke on a hydraulic press is fully adjustable, offering greater versatility for jobs with varying depths.
Initial Cost and Maintenance
Mechanical presses tend to have a lower upfront cost for smaller tonnages. However, their complex systems of clutches, brakes, and gears can require specialized maintenance. Hydraulic systems are simpler in principle but are susceptible to fluid leaks and contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific needs will determine which type of power press is the appropriate tool.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive stamping: A mechanical press is the clear choice for its efficiency and rhythm.
- If your primary focus is deep-drawing or forming complex shapes: A hydraulic press provides the necessary constant force throughout the stroke.
- If your primary focus is versatility for a variety of jobs: A hydraulic press's adjustable stroke and tonnage offer greater operational flexibility.
By understanding these fundamental operating principles, you can select the right tool to apply immense force with precision and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mechanical Press | Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | High-speed, cyclical | Slower, variable speed |
| Force Control | Fixed (peak at bottom of stroke) | Full force throughout the stroke |
| Stroke Length | Fixed | Fully adjustable |
| Best For | High-volume stamping, blanking | Deep drawing, complex forming |
| Maintenance | Complex gears and clutches | Fluid system maintenance |
Ready to Amplify Your Production Capabilities?
Understanding the right press for your application is key to maximizing efficiency and precision. Whether you need the high-speed rhythm of a mechanical press for stamping or the versatile, sustained force of a hydraulic press for deep drawing, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory and industrial needs.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can power your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the hydraulic forging process? Master the Art of High-Strength Metal Forming
- What is an example of a hydraulic press? Discover the Power of Laboratory Sample Preparation
- What core conditions does a laboratory hydraulic press provide for solid-state electrolyte pellets? Enhance Density!
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press contribute to the preparation of green pellets for nanostructured eutectic steel?
- What is the purpose of a laboratory hydraulic press for LATP electrolyte pellets? Achieve Optimal Density & Conductivity



















