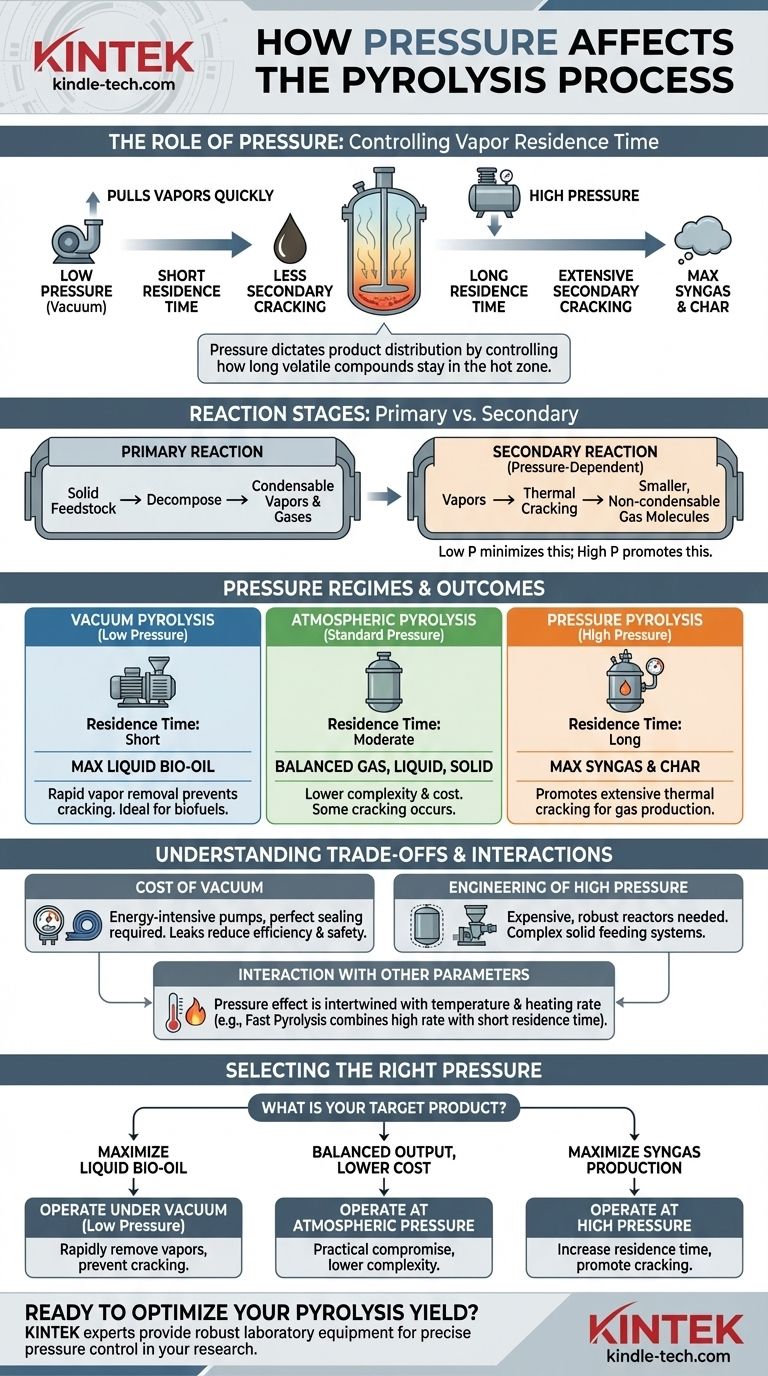
In the context of pyrolysis, pressure is a critical control parameter that directly dictates the final product distribution between gas, liquid, and solid. While many basic pyrolysis systems operate at atmospheric pressure, intentionally modifying the pressure—either by creating a vacuum or applying positive pressure—is a key technique used to optimize the process for a specific desired output.
The fundamental role of pressure in pyrolysis is to control the residence time of volatile compounds within the reactor. Low pressure removes these vapors quickly to preserve them as liquids (bio-oil), while high pressure traps them, forcing further breakdown into gas (syngas) and char.

The Role of Pressure in Pyrolysis Reactions
To understand the effect of pressure, you must first distinguish between the two stages of reaction that occur inside a pyrolysis reactor.
Primary vs. Secondary Reactions
Pyrolysis is not a single event. First, the solid feedstock (like biomass or plastic) decomposes into a mix of condensable vapors and non-condensable gases. This is the primary reaction.
These initial vapors can then undergo further reactions if they remain in the hot zone of the reactor. They can break down, or "crack," into smaller, non-condensable gas molecules. These are secondary reactions.
How Pressure Controls Vapor Residence Time
Pressure directly influences how long the initial pyrolysis vapors stay in the hot reaction zone.
At low pressure (vacuum), there is a strong driving force pulling the vapors out of the reactor almost as soon as they are formed. This shortens their residence time, minimizing the chance for secondary reactions to occur.
At high pressure, the vapors are more compressed and move more slowly. Their residence time in the hot zone is significantly increased, which promotes extensive secondary cracking.
Comparing Pyrolysis Pressure Regimes
The choice of operating pressure is a deliberate decision made to target a specific product. Each regime has a distinct outcome.
Vacuum Pyrolysis (Low Pressure)
By operating under a vacuum, the system maximizes the yield of liquid bio-oil.
The rapid removal of vapors prevents them from cracking into smaller gas molecules. The vapors are quickly transported to a cooler condensation unit, where they are collected as a liquid. This method is ideal for producing liquid biofuels or chemical feedstocks.
Atmospheric Pyrolysis (Standard Pressure)
This is the most common and often simplest configuration, operating at or near ambient atmospheric pressure.
It offers a balanced distribution of solid, liquid, and gas products. Some secondary cracking occurs, but it is less extensive than in a high-pressure system. This approach is often chosen for its lower complexity and cost.
Pressure Pyrolysis (High Pressure)
Operating at pressures significantly above atmospheric shifts the product distribution toward syngas and bio-char.
The long residence time of vapors ensures they undergo extensive thermal cracking, converting valuable liquid precursors into permanent gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This process is sometimes used to maximize gas production for energy generation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While pressure is a powerful tool, modifying it introduces engineering and economic challenges that must be considered.
The Cost of Vacuum
Creating and maintaining a vacuum requires energy-intensive pumps and a perfectly sealed reactor system. Any leaks degrade the vacuum, reducing efficiency and potentially creating safety hazards by allowing air to enter the hot system.
The Engineering Challenges of High Pressure
High-pressure reactors are significantly more expensive to build, as they must be robust enough to operate safely. The systems required to feed solid material into a pressurized vessel are also far more complex and costly than those for atmospheric systems.
Balancing Pressure with Other Parameters
Pressure does not act in isolation. Its effect is intertwined with temperature and heating rate. For example, "fast pyrolysis" combines a high heating rate with a short vapor residence time (often achieved at near-atmospheric pressure with high gas flow) to maximize bio-oil yield. The most effective process design always considers how these key parameters interact.
Selecting the Right Pressure for Your Goal
Your choice of operating pressure should be dictated entirely by your target product and operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil yield: Operate under a vacuum (low pressure) to rapidly remove pyrolysis vapors and prevent secondary cracking.
- If your primary focus is maximizing syngas production: Operate at high pressure to increase vapor residence time and promote the thermal cracking of vapors into non-condensable gases.
- If your primary focus is a balanced output with lower capital cost: Operate at or near atmospheric pressure, as it provides a practical compromise between product yields and system complexity.
Ultimately, manipulating pressure provides a powerful lever to steer the pyrolysis process toward your desired chemical products and economic outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Pressure Regime | Vapor Residence Time | Primary Product Outcome | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum (Low) | Short | Maximizes Liquid Bio-oil | Rapid vapor removal prevents cracking |
| Atmospheric | Moderate | Balanced Gas, Liquid, Solid | Lower complexity and cost |
| High Pressure | Long | Maximizes Syngas & Char | Promotes extensive secondary cracking |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum yield? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your pyrolysis research and development needs. Whether you're targeting bio-oil, syngas, or char production, our solutions can help you achieve precise control over pressure and other critical parameters.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success with the right equipment for your specific pyrolysis goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth
- Why are sealed laboratory reaction vessels necessary in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Ensure Purity and Yield
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research



















