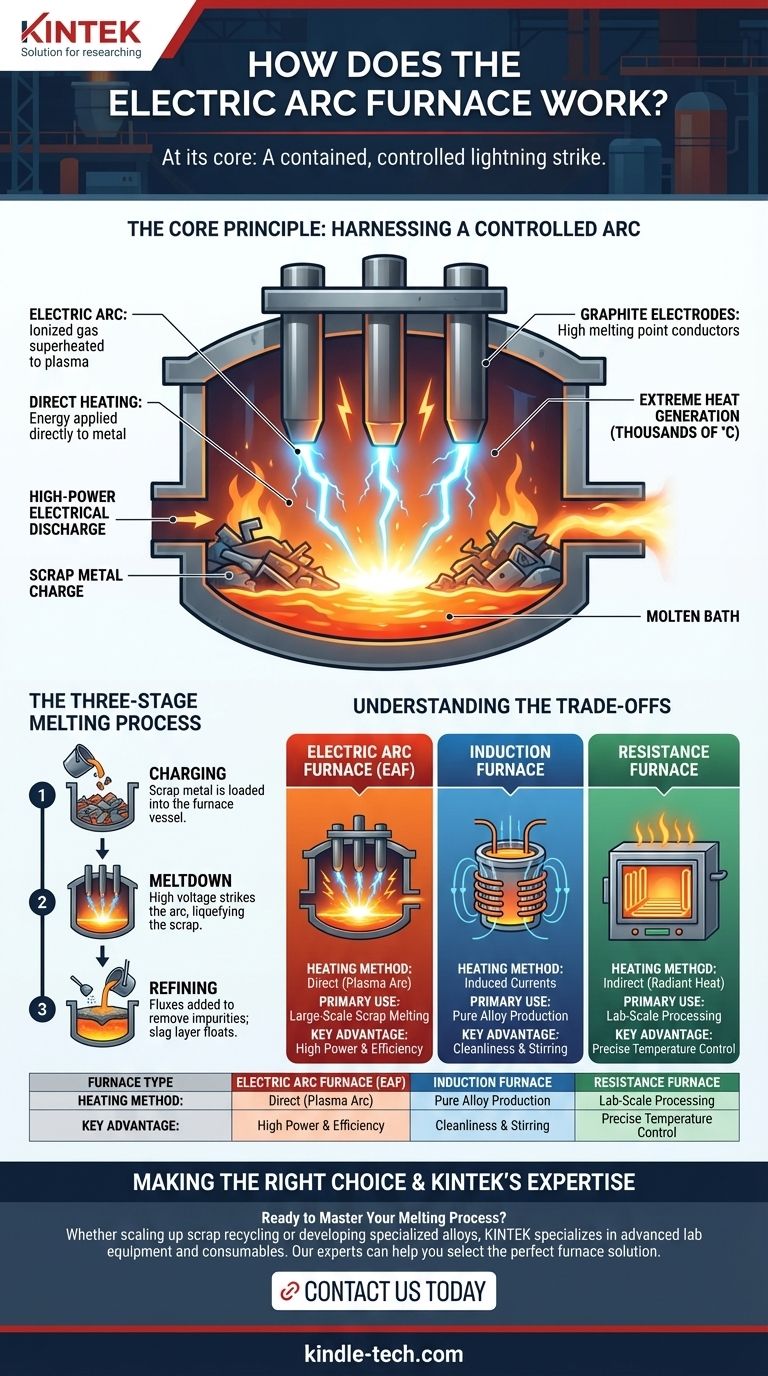
At its core, an electric arc furnace (EAF) operates like a contained, controlled lightning strike. It uses massive graphite electrodes to pass an enormous electric current through a metal charge (typically scrap steel), creating an electric arc. This arc generates incredibly intense heat, reaching thousands of degrees Celsius, which rapidly melts the metal.
The crucial distinction of an arc furnace is its use of direct heating via a plasma arc. Unlike other furnaces that heat the surrounding environment or a container, the EAF applies its energy directly to the metal, making it an exceptionally powerful and efficient tool for melting large quantities of scrap material.

The Core Principle: Harnessing a Controlled Arc
An electric arc furnace's power comes from a simple but powerful phenomenon. It transforms electrical energy into thermal energy with brutal efficiency.
What is an Electric Arc?
An electric arc is a high-power electrical discharge that occurs when electricity jumps a gap between two conductors—in this case, between the electrodes and the metal scrap. This discharge ionizes the gas in the gap, creating a channel of superheated plasma.
How the Arc Generates Intense Heat
The plasma arc is the heart of the furnace's operation. It radiates immense thermal energy, rapidly transferring heat to the solid metal. This process is far more direct and intense than the indirect heating used in many other furnace types.
The Role of Graphite Electrodes
The furnace uses large graphite electrodes for two key reasons. First, graphite is an excellent electrical conductor. Second, and more importantly, it has an extremely high melting point and can withstand the incredible temperatures generated by the arc without being consumed too quickly.
The Three-Stage Melting Process
The operation of an EAF is not just about melting; it's a refined, multi-stage process designed to produce steel of a specific quality.
Stage 1: Charging
The process begins by loading, or charging, the furnace. A large bucket drops scrap metal into the furnace vessel. This charge is often preheated to improve energy efficiency.
Stage 2: Meltdown
Once charged, the furnace roof is closed, and the graphite electrodes are lowered toward the metal. A high voltage is applied, striking the arc between the electrodes and the charge. The intense heat begins the meltdown period, liquefying the scrap into a molten bath.
Stage 3: Refining
Melting the metal is only half the battle. During the refining stage, fluxes like burnt lime are added to the molten bath. These materials combine with impurities in the steel to form a liquid layer called slag, which floats on top of the molten metal and can be easily removed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Arc vs. Other Furnaces
To truly understand the EAF, it's helpful to compare it to other common industrial furnaces. The primary difference lies in the method of heat transfer.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
An EAF uses direct heating; the energy source (the arc) is in direct contact with the material being heated. Most other furnaces, like chamber or tube furnaces, use indirect heating. They rely on heating elements or flames to heat the furnace interior, which then heats the material through radiation and convection. This is generally slower and less powerful.
Arc Furnace vs. Induction Furnace
An induction furnace also uses electricity but in a completely different way. It generates a powerful magnetic field, which induces eddy currents within the metal itself. These currents generate heat through resistance. This method is excellent for creating very pure alloys and provides natural stirring of the melt, but it lacks the raw melting power of an EAF for large-scale scrap processing.
Arc Furnace vs. Resistance Furnaces
Lab-scale chamber or tube furnaces use resistive heating elements (metal or ceramic coils) that glow hot when electricity passes through them. They heat the air or a work tube, which then slowly heats the sample. This allows for excellent temperature control and uniformity but is not suitable for melting tons of steel.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on the material, the scale of the operation, and the desired final product.
- If your primary focus is melting large volumes of scrap steel efficiently: The Electric Arc Furnace is the industry standard due to its unmatched power and direct, intense heating capability.
- If your primary focus is creating highly pure, specialized alloys in a controlled vacuum: An Induction Furnace (especially a Vacuum Induction Melter) is superior for its cleanliness and electromagnetic stirring.
- If your primary focus is precise heat treatment or lab-scale sample processing: A chamber or tube furnace using resistance elements offers the best temperature uniformity and control.
Ultimately, mastering industrial heating is about selecting the right tool for the specific metallurgical job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Induction Furnace | Resistance Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct (Plasma Arc) | Induced Currents | Indirect (Radiant Heat) |
| Primary Use | Large-Scale Scrap Melting | Pure Alloy Production | Lab-Scale Processing |
| Key Advantage | High Power & Efficiency | Cleanliness & Stirring | Precise Temperature Control |
Ready to Master Your Melting Process?
Whether you're scaling up scrap metal recycling or developing specialized alloys, choosing the right furnace technology is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and industrial facilities.
Our experts can help you select the perfect furnace solution to enhance efficiency, purity, and control in your operations.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can power your innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Can gold be induction heated? Yes, and it's the superior method for high-purity melting.
- What are the hazards of molten metals? Beyond Burns to Explosions and Toxic Fumes
- What are the disadvantages of induction heating? High Cost & Geometric Limits Explained
- What is the structure of an induction furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components and Design
- What is the difference between arc melting and induction melting? Power vs. Precision for Your Metal Melting Needs
- What is the main application of indirect arc furnace is to melt? Master Non-Ferrous Alloy Melting with Precision
- What are the disadvantages of direct core type induction furnace? High Standby Costs and Inflexibility
- What are the advantages of vacuum induction melting? Achieve Ultimate Purity & Precision for High-Performance Alloys



















