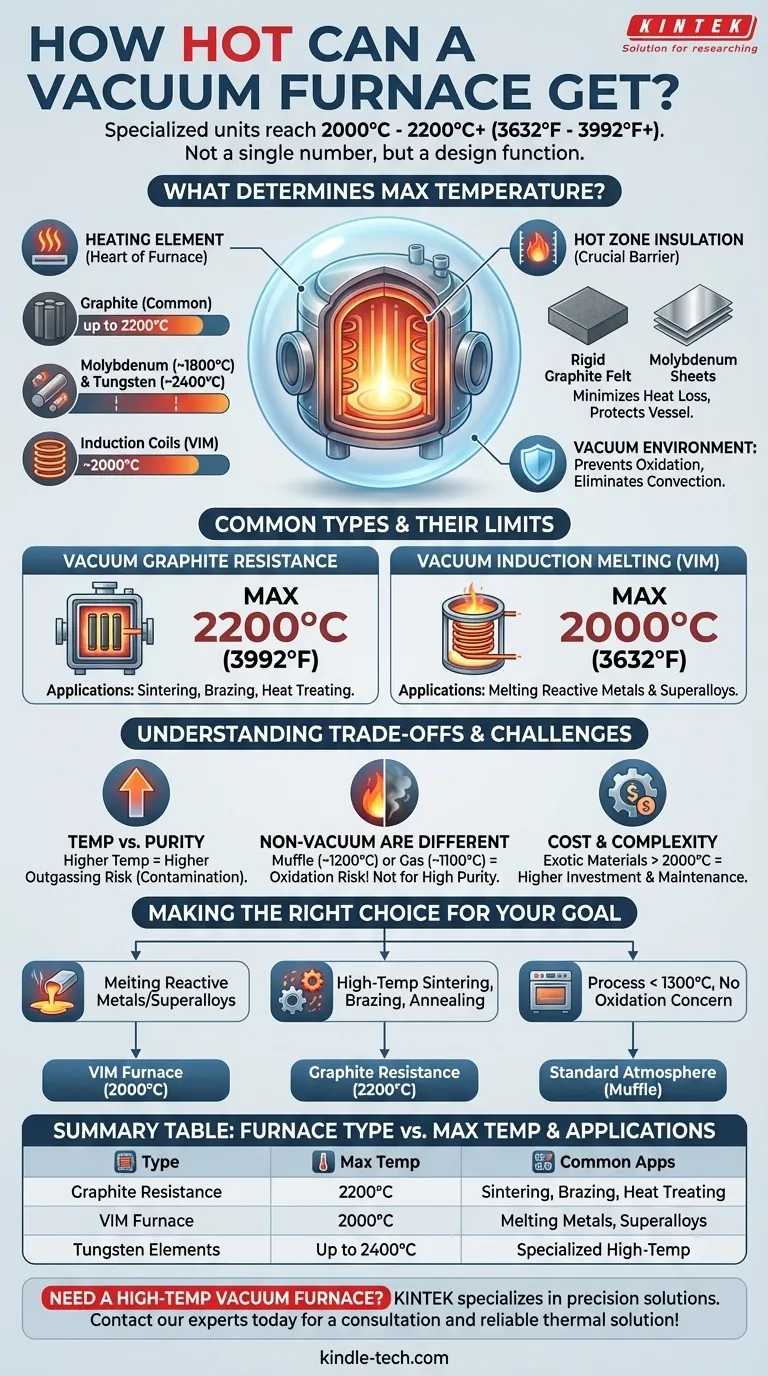
At a minimum, specialized vacuum furnaces can reach temperatures between 2000°C (3632°F) and 2200°C (3992°F). The exact maximum temperature is not a single number, but rather a function of the furnace's specific design, particularly its heating elements and insulation materials.
The ultimate temperature a vacuum furnace can achieve is defined by the physical limits of its internal components. While many furnaces operate in the 1300°C range, specialized designs using graphite or refractory metals are required to push beyond 2000°C in a controlled, non-oxidizing environment.

What Determines a Vacuum Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The ability of a vacuum furnace to reach and sustain extreme temperatures is not arbitrary. It is a direct result of two critical internal systems working together within the vacuum environment.
The Role of the Heating Element
The heart of the furnace is its heating element, which converts electrical energy into heat. The material used for this element is the primary limiting factor for temperature.
- Graphite: Common in high-temperature furnaces, graphite elements can reliably operate at temperatures up to 2200°C. They offer excellent thermal stability and are relatively cost-effective.
- Refractory Metals: For even higher temperatures or specific chemical environments, metals like Molybdenum (up to ~1800°C) and Tungsten (up to ~2400°C) are used.
- Induction Coils: In a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace, a copper coil generates an electromagnetic field. This field directly heats the conductive material inside the crucible, with maximum temperatures typically around 2000°C.
The Importance of the "Hot Zone" Insulation
The heating elements are enclosed within an insulated chamber called the "hot zone." This insulation is crucial for minimizing heat loss and protecting the outer furnace vessel.
Like heating elements, these insulation packs are made from materials that can withstand the target temperatures, such as rigid graphite felt or layered sheets of reflective metals like molybdenum.
Why the Vacuum is Essential
The vacuum environment is what makes these high temperatures practical. By removing air and other gases, the vacuum prevents oxidation of the heating elements, insulation, and the workload itself. It also eliminates heat transfer through convection, improving thermal efficiency.
Common Types and Their Temperature Limits
Different industrial processes require different types of vacuum furnaces. The name often tells you about its heating method and intended use.
Vacuum Graphite Resistance Furnaces
These are among the most common high-temperature designs. They use graphite heating elements and can achieve maximum temperatures of 2200°C (3992°F), making them ideal for sintering, brazing, and heat treating.
Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) Furnaces
VIM furnaces are designed specifically for melting and purifying metals and alloys. The induction heating method is highly efficient and allows these systems to reach 2000°C (3632°F) to melt reactive metals and superalloys in a clean environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Simply reaching a high temperature is not the only goal. The furnace must provide a stable and clean environment, and higher temperatures introduce significant challenges.
Temperature vs. Atmosphere Purity
As temperatures increase, the risk of outgassing rises. This is where atoms can escape from the furnace's own internal materials (like insulation or fixtures), which can compromise the purity of the vacuum and potentially contaminate the workpiece.
Non-Vacuum Furnaces Are Different
It is critical to distinguish vacuum furnaces from others. Furnaces like a muffle furnace (up to ~1200°C) or a natural gas furnace (up to ~1100°C) operate in air. They cannot protect materials from oxidation and are therefore unsuitable for the high-purity processes performed in a vacuum.
Cost and Complexity
Achieving temperatures above 2000°C requires exotic and expensive materials for heating elements and insulation. These components have a finite life and are more costly to maintain and replace, making ultra-high-temperature furnaces a significant investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your process requirements for both temperature and atmospheric purity.
- If your primary focus is melting reactive metals or superalloys: A Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace designed for operation up to 2000°C is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sintering, brazing, or annealing: A vacuum resistance furnace with graphite elements, capable of reaching 2200°C, provides the necessary control.
- If your process is below 1300°C and oxidation is not a primary concern: A standard atmosphere furnace, like a muffle furnace, may be a far more cost-effective solution.
Understanding these distinctions ensures you select a furnace that meets not just your temperature needs, but the critical atmospheric requirements of your process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Heating Method | Typical Maximum Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Graphite Resistance Furnace | Graphite Elements | 2200°C (3992°F) | Sintering, Brazing, Heat Treating |
| Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) Furnace | Induction Coil | 2000°C (3632°F) | Melting Reactive Metals & Superalloys |
| Furnace with Tungsten Elements | Metal Resistance | Up to 2400°C | Specialized High-Temp Applications |
Need a high-temperature vacuum furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision vacuum furnaces for sintering, melting, and heat treatment. Our experts will help you select the right system to achieve the precise temperature and atmospheric control your process demands. Contact us today for a consultation and let us provide the reliable thermal solution your research deserves!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision



















