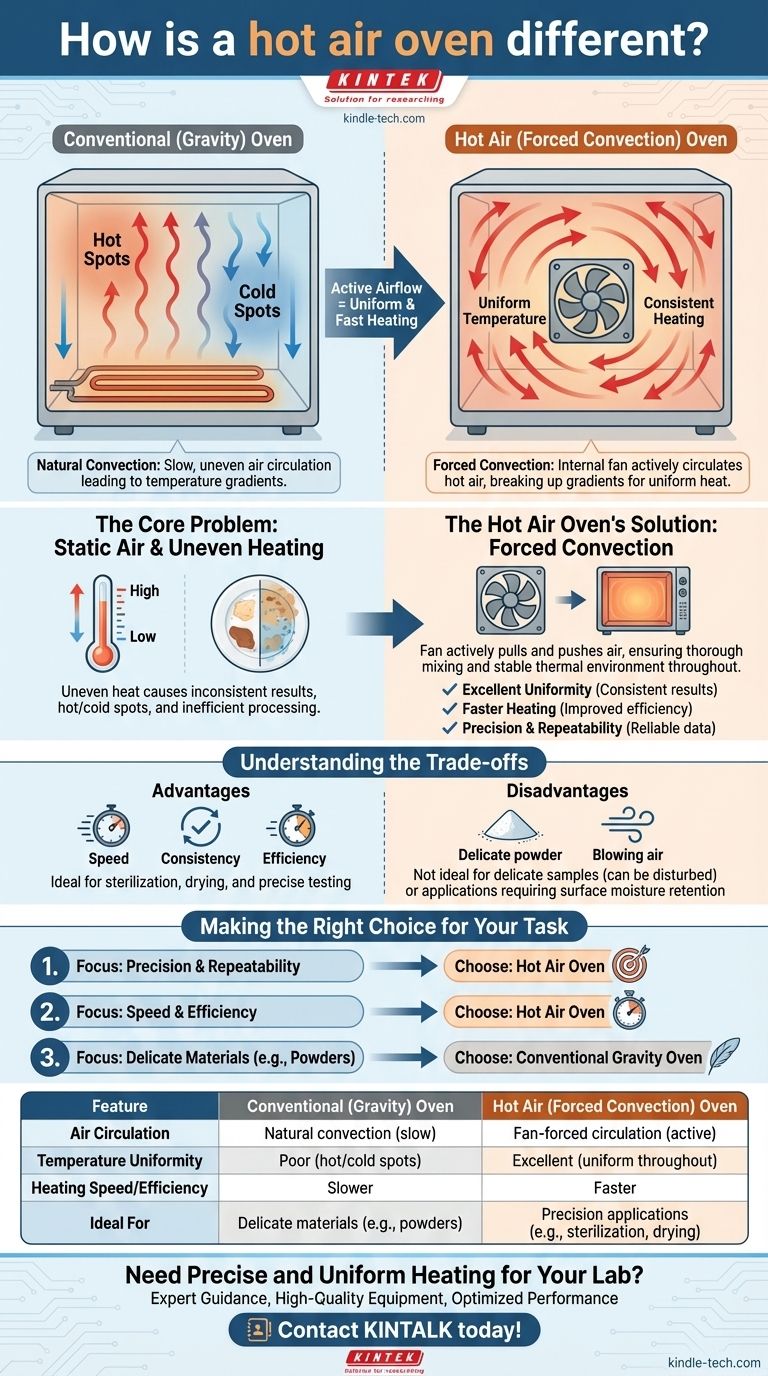
At its core, a hot air oven is different because it includes a fan. While a conventional oven relies on natural heat radiation and convection, a hot air oven (also known as a forced air or mechanical convection oven) uses an internal fan to actively circulate hot air. This single design change creates a fundamentally more uniform and efficient heating environment.
The critical difference is not the presence of a fan, but the outcome it produces: a consistent, uniform temperature throughout the entire chamber. This eliminates the "hot and cold spots" that are unavoidable in ovens relying on natural heat circulation.

The Core Problem: Static Air and Uneven Heating
To understand why a hot air oven is necessary, we must first look at the limitations of a conventional oven, often called a gravity convection oven.
How Conventional Ovens Work
A conventional oven uses a heating element, typically at the bottom, to heat the air inside. As the air heats up, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler, denser air sinks to take its place.
This natural process, known as gravity convection, creates a continuous but slow circulation of air.
The "Hot Spot" Phenomenon
This natural circulation is imperfect. It leads to significant temperature variations, or gradients, within the oven chamber.
The area near the top is often much hotter than the bottom, and items placed closer to the heating element will receive more intense, direct heat. This results in uneven heating, where one sample dries faster than another or one side of a product bakes before the other.
The Hot Air Oven's Solution: Forced Convection
A hot air oven directly solves the problem of uneven heating by taking control of the air circulation.
Introducing the Fan
The internal fan actively pulls air across the heating element and forces it to circulate throughout the entire chamber. This mechanical or forced convection overrides the slow, natural currents.
This process breaks up the layers of hot and cool air, ensuring the temperature is mixed thoroughly and distributed evenly to every corner of the oven.
The Benefit of Uniformity
The result is a highly uniform and stable thermal environment. An object placed in the top left corner will experience virtually the same temperature as an object in the bottom right corner.
This consistency is critical for applications like laboratory testing, sterilization, and materials drying, where repeatable and precise results are non-negotiable.
Faster, More Efficient Heating
Moving air transfers heat more effectively than static air. The constant airflow in a hot air oven means items inside reach the target temperature more quickly and are heated more consistently.
This can significantly reduce drying or sterilization times, leading to greater efficiency and throughput.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While superior for most applications requiring precision, the forced air design is not universally perfect.
Not Ideal for Delicate Samples
The active airflow can be a disadvantage for certain delicate materials. Lightweight powders or fine samples can be disturbed or blown around by the fan.
For these specific cases, a gentler gravity convection oven may be the more appropriate tool.
Drying Out Surfaces
The constant movement of hot air can also lead to faster surface drying. While often desirable, this can be detrimental for applications where retaining some surface moisture is important.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Ultimately, the choice between a hot air oven and a conventional one depends entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is precision and repeatability: A hot air oven is essential for ensuring every sample is exposed to the same thermal conditions.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency: A hot air oven will deliver faster heat-up and processing times due to more effective heat transfer.
- If your primary focus is on delicate materials like powders: A conventional gravity oven is the safer choice to prevent samples from being disturbed by airflow.
Understanding this core difference empowers you to select the right tool for achieving consistent and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional (Gravity) Oven | Hot Air (Forced Convection) Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Air Circulation | Natural convection (slow) | Fan-forced circulation (active) |
| Temperature Uniformity | Poor (hot/cold spots) | Excellent (uniform throughout) |
| Heating Speed/Efficiency | Slower | Faster |
| Ideal For | Delicate materials (e.g., powders) | Precision applications (e.g., sterilization, drying) |
Need Precise and Uniform Heating for Your Lab?
Choosing the right oven is critical for consistent, reliable results. The KINTEK team understands the nuances of thermal processing. Whether your application requires the gentle heat of a gravity oven or the precision and speed of a forced air oven, we have the solution.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Help you select the perfect oven for your specific materials and processes.
- High-Quality Equipment: Durable and reliable hot air ovens and gravity ovens built for laboratory demands.
- Optimized Performance: Ensure your drying, sterilization, and testing protocols are repeatable and efficient.
Let's find the ideal oven for your lab's needs. Contact KINTALK today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Bottom Discharge Graphitization Furnace for Carbon Materials
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- Why is a laboratory-grade forced air drying oven required for alloy chip moisture analysis? Ensure Data Precision



















