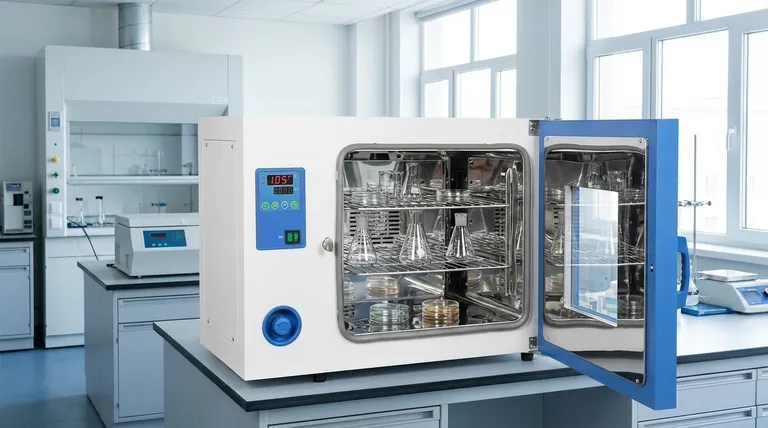
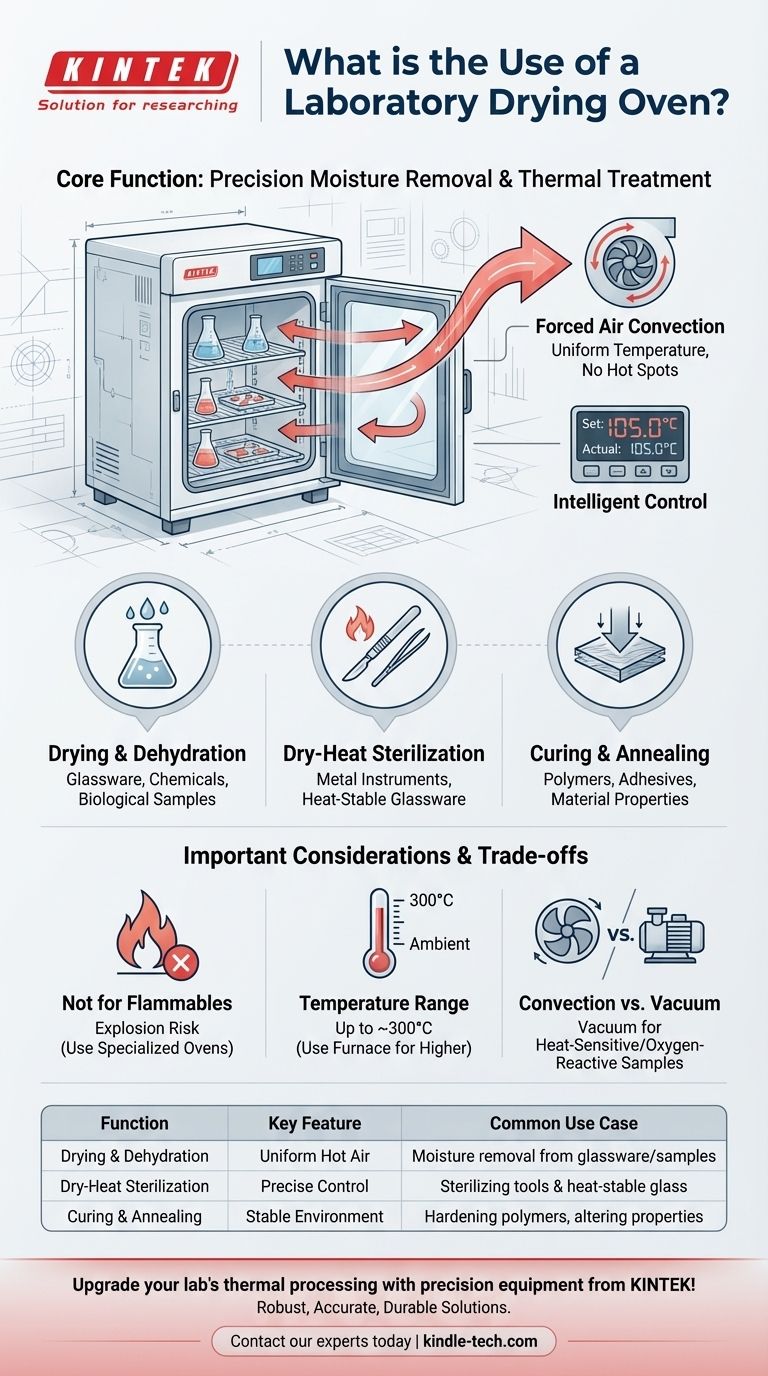
At its core, a laboratory drying oven is a precision instrument for removing moisture and applying thermal treatment. It is used to dry, sterilize, cure, or harden materials and lab equipment by circulating thermostatically controlled hot air. Unlike a conventional oven, its primary design goal is to achieve exceptional temperature uniformity throughout its chamber.
The crucial function of a laboratory drying oven isn't just heating; it's providing a stable, uniform, and precisely controlled thermal environment. This consistency is essential for repeatable and reliable scientific results, from drying delicate samples to sterilizing equipment.

The Core Principle: Forced Air Convection
A drying oven operates on a simple but critical principle: circulating heated air to ensure every item in the chamber experiences the exact same temperature. This is a significant step up from a simple static heater.
How It Achieves Uniformity
Most laboratory drying ovens use a centrifugal fan (or "wind wheel") to actively circulate air. The air is drawn across heating elements and then forced throughout the chamber.
This process eliminates hot spots and cold pockets, ensuring that a sample on the top shelf is the same temperature as one on the bottom.
The Role of Precision Control
Modern units feature an intelligent temperature controller, often with a digital PID (proportional-integral-derivative) display. This allows a user to set and maintain a precise temperature, often within a fraction of a degree.
This level of control is non-negotiable for sensitive scientific protocols where temperature fluctuations could ruin an experiment.
The Mechanism of Drying
As the hot, dry air circulates, it absorbs moisture from the surfaces of glassware or from within samples. Vents in the oven allow this now-moist air to exit, while fresh, dry air is drawn in to be heated, continuing the cycle.
Primary Applications in the Laboratory
While the function is simple, the applications are diverse and fundamental to daily lab work. Each relies on the oven's ability to maintain a uniform temperature.
Drying and Dehydration
This is the most common use. It is essential for drying glassware after washing, removing residual moisture from chemical powders before weighing, or dehydrating biological samples for analysis.
Dry-Heat Sterilization
The oven is used to sterilize heat-stable items, such as metal instruments (forceps, scalpels) and certain types of glassware. The high, dry heat effectively kills microorganisms over a set period.
Curing and Annealing
In materials science and engineering labs, drying ovens are used to cure polymers, adhesives, and epoxies. They are also used for annealing processes that require holding a material at a specific temperature to alter its properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A drying oven is a specialized tool, and it's critical to understand its limitations for both safety and procedural success.
Not for Flammable or Volatile Substances
A standard laboratory drying oven is not explosion-proof. Heating volatile or flammable solvents can cause vapors to build up and ignite, leading to a fire or explosion. Specialized ovens are required for such applications.
Temperature Range vs. a Furnace
Drying ovens typically operate in a range from slightly above ambient temperature to around 300°C (572°F). For processes requiring much higher temperatures, such as ashing or certain metallurgical work, a muffle furnace is the appropriate instrument.
Convection vs. Vacuum Ovens
For samples that are heat-sensitive or may react with air (oxidize), a vacuum oven is a better choice. By removing air, a vacuum oven allows moisture to be pulled out at a much lower temperature, protecting the sample from thermal degradation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating method is key to ensuring the integrity of your work.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture from stable glassware or chemicals: A standard forced-air convection drying oven is the perfect, most efficient tool.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing metal instruments or non-volumetric glassware: A drying oven provides a reliable and simple method for dry-heat sterilization.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive powders or oxygen-reactive samples: You must consider a vacuum oven to prevent sample damage and unwanted chemical reactions.
Ultimately, understanding the specific role of a drying oven empowers you to execute thermal processes with safety, accuracy, and repeatability.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Feature | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Drying & Dehydration | Uniform Hot Air Circulation | Removing moisture from glassware and samples |
| Dry-Heat Sterilization | Precise Temperature Control | Sterilizing metal tools and heat-stable glassware |
| Curing & Annealing | Stable Thermal Environment | Hardening polymers or altering material properties |
Upgrade your lab's thermal processing with precision equipment from KINTEK!
Whether you need reliable drying, consistent sterilization, or controlled curing, the right oven is crucial for repeatable results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust drying ovens designed for accuracy and durability.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect drying solution for your laboratory's specific needs and ensure your thermal processes are safe, efficient, and reliable.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results



















