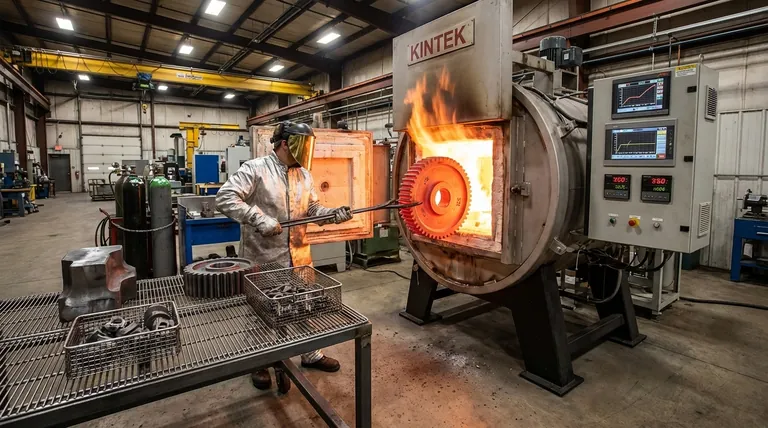
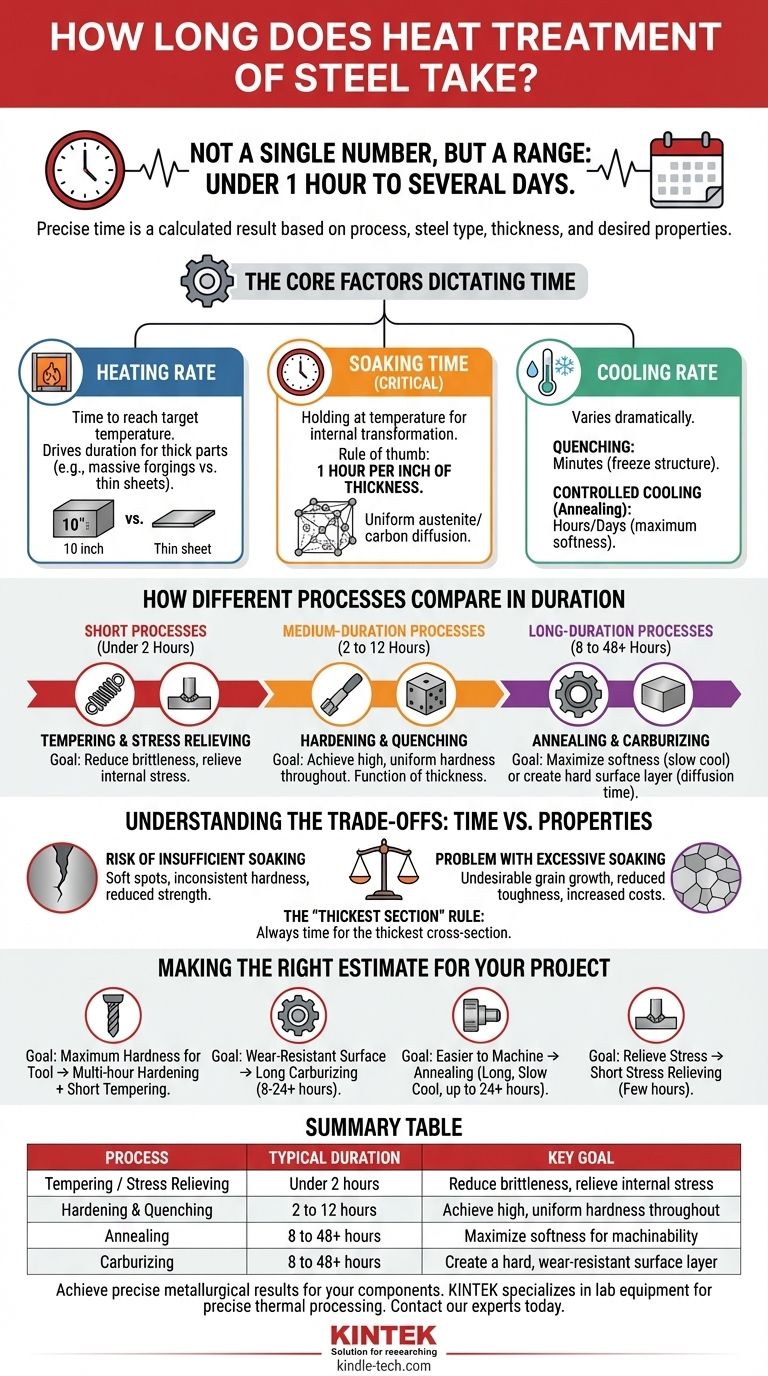
The duration of steel heat treatment is not a single number, but a range that spans from under an hour to several days. The precise time is a calculated result based on the specific process being used, the type and thickness of the steel, and the final mechanical properties required. Simple processes like tempering can be quick, while processes like carburizing or annealing can be extremely time-intensive.
The time required for heat treatment is an outcome, not an input. It is dictated entirely by the metallurgical goal, the thickness of the part, and the specific transformation required within the steel's crystal structure.

The Core Factors Dictating Heat Treatment Time
To understand duration, you must first understand the three fundamental stages of any heat treatment cycle: heating the steel to a target temperature, holding it there (soaking), and cooling it back down at a controlled rate.
The Heating Rate
The first variable is simply the time it takes to bring the entire mass of the steel part up to the specified temperature. A thin sheet of steel will heat through in minutes, whereas a massive 10-inch thick forging block can take many hours to reach a uniform temperature from its surface to its core.
Furnace capacity and efficiency also play a role, but the primary driver is the part's cross-sectional thickness.
The Soaking Time
This is the most critical phase and a major determinant of the total cycle time. Soaking is the period where the steel is held at the target temperature to allow for internal changes to occur.
This isn't just about being hot; it's about giving the crystalline structure of the steel time to transform. For hardening, this means allowing the structure to become uniform austenite. For case hardening, it means allowing carbon atoms to physically diffuse into the surface.
A common industry rule of thumb for hardening is to soak for one hour per inch of thickness, but this is only a starting point. The specific steel alloy and the desired outcome will refine this requirement.
The Cooling Rate
The final stage's duration varies dramatically by process.
- Quenching is extremely fast. Submerging a hot part in water, oil, or polymer coolant takes only minutes and is designed to "freeze" a hard microstructure in place.
- Controlled Cooling, by contrast, is very slow. For annealing, the goal is maximum softness. This often involves letting the steel cool down slowly inside the furnace over 8 to 24 hours, or even longer for critical applications.
How Different Processes Compare in Duration
The chosen heat treatment process is the single biggest factor in estimating time.
Short Processes (Under 2 Hours)
Tempering and stress relieving are typically fast. These are lower-temperature processes performed after hardening or heavy machining. They don't require major structural transformation, but rather serve to reduce brittleness or internal stresses.
Medium-Duration Processes (2 to 12 Hours)
Hardening and quenching (also called through-hardening) falls into this range. The cycle is dominated by the heating and soaking time, which is largely a function of the part's thickness. A one-inch-thick tool might take a few hours, while a six-inch-thick die block will take significantly longer.
Long-Duration Processes (8 to 48+ Hours)
Annealing and carburizing are the most time-consuming processes. Annealing's duration is defined by its extremely slow cooling rate.
Carburizing is a diffusion process where time directly equals depth. Creating a shallow "case" of high-carbon, hard steel on the surface might take 4-8 hours. Achieving a very deep, wear-resistant case on a large gear could require a furnace cycle of 24, 36, or even more hours.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Time vs. Properties
Attempting to shorten a heat treatment cycle without understanding the consequences can lead to failed parts. The duration is prescribed for specific metallurgical reasons.
The Risk of Insufficient Soaking
If the soaking time is too short, the steel's core may not fully transform. This results in "soft spots" or inconsistent hardness across the part, rendering it unfit for its intended use. The part will not have the strength or wear resistance it was designed for.
The Problem with Excessive Soaking
Longer is not always better. Holding steel at a high temperature for too long can cause undesirable grain growth within the metal. Large grains can reduce the steel's toughness and make it more susceptible to cracking or fracture under impact. It also consumes significant energy and furnace time, increasing costs.
The "Thickest Section" Rule
A common pitfall is calculating time based on a part's average thickness. The heat treatment cycle must always be timed for the thickest cross-section of the component to ensure it is heated, soaked, and cooled properly all the way through.
Making the Right Estimate for Your Project
Use your end goal to guide your time expectations.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness for a tool: You are looking at a multi-hour hardening and quenching cycle, followed by a shorter tempering cycle to reduce brittleness.
- If your primary focus is creating a wear-resistant surface on a gear: You must plan for a long-duration carburizing process, potentially 8 to 24 hours or more, depending on the required case depth.
- If your primary focus is making a raw component easier to machine: An annealing cycle is necessary, and you should budget for a long, slow cool-down period that could span an entire day.
- If your primary focus is simply relieving stress after welding: A stress-relieving cycle is relatively short, often requiring only a few hours depending on the part's size.
By understanding these key variables, you can move from asking "how long will it take?" to confidently estimating what is required to achieve your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Process | Typical Duration | Key Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Tempering / Stress Relieving | Under 2 hours | Reduce brittleness, relieve internal stress |
| Hardening & Quenching | 2 to 12 hours | Achieve high, uniform hardness throughout |
| Annealing | 8 to 48+ hours | Maximize softness for machinability |
| Carburizing | 8 to 48+ hours | Create a hard, wear-resistant surface layer |
Achieve precise metallurgical results for your components.
Estimating heat treatment time is critical for project planning and achieving the desired mechanical properties in your steel parts. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise thermal processing, serving industries from tool manufacturing to aerospace.
Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for controlled heating, soaking, and cooling cycles, whether you're working on thin sheets or massive forgings. Let us help you optimize your process for consistent hardness, durability, and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific steel heat treatment needs and find the ideal solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering



















