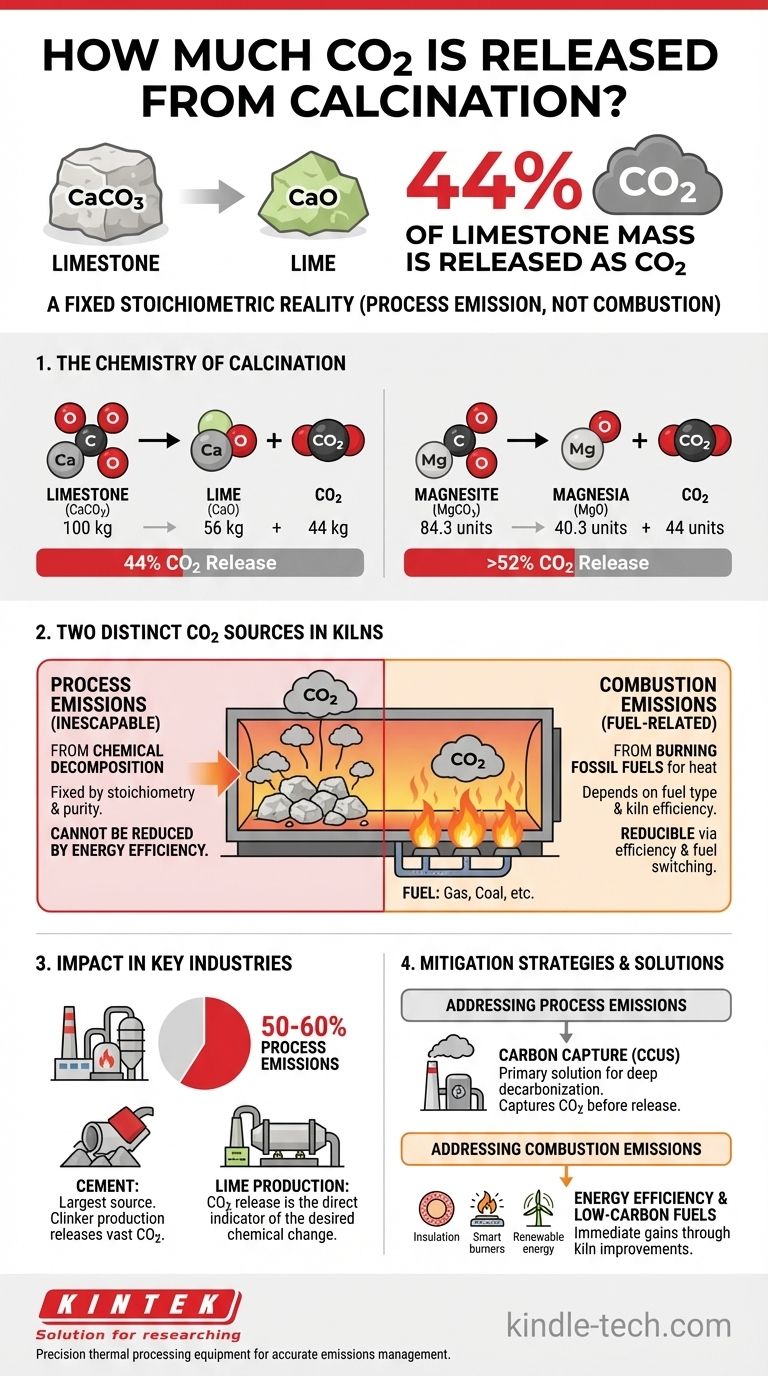
The calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate) releases 44% of its mass as carbon dioxide. For every 1,000 kg of pure calcium carbonate that is processed, 440 kg of CO2 is unavoidably released as a direct result of the chemical transformation.
The core principle to understand is that CO2 released during calcination is a process emission, not a combustion emission. It is liberated directly from the raw material's chemical structure, making it an inescapable part of the reaction, independent of the fuel used for heating.

The Chemistry of Calcination: A Stoichiometric Reality
Calcination is a thermal decomposition process. When certain materials, particularly carbonates, are heated to a high temperature, they break down into a new solid (usually an oxide) and release a gas.
Calcium Carbonate (Limestone)
The most common industrial example is the calcination of limestone (CaCO3) to produce lime (CaO).
The balanced chemical equation is: CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
By looking at the atomic masses (Ca≈40, C≈12, O≈16), we can see that 100 units of CaCO3 break down into 56 units of CaO and 44 units of CO2. This 44% mass ratio is a fixed chemical fact.
Magnesium Carbonate (Magnesite)
A similar reaction occurs for magnesium carbonate (MgCO3), which is calcined to produce magnesia (MgO).
The equation is: MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
Here, approximately 84.3 units of MgCO3 break down into 40.3 units of MgO and 44 units of CO2. This means that for magnesite, over 52% of the initial mass is released as CO2.
The Source of the Carbon Dioxide
It is critical to recognize that this CO2 was chemically locked within the stone itself. The high heat simply provides the energy needed to break the chemical bonds and release the gas that was already present in the material's molecular structure.
Process Emissions vs. Combustion Emissions
In any real-world kiln, there are two distinct sources of CO2, and failing to differentiate them leads to significant confusion in emissions management.
Process Emissions (The Inescapable CO2)
This is the CO2 released from the chemical decomposition of the carbonate feedstock, as described above. It is determined entirely by the stoichiometry of the reaction and the purity of the raw material.
Combustion Emissions (The Fuel-Related CO2)
This is the CO2 generated by burning fossil fuels (like natural gas, coal, or petcoke) to achieve the high temperatures (often >900°C) required for calcination. This portion of emissions depends on the fuel type and the thermal efficiency of the kiln.
Why This Distinction Is Crucial
You can reduce combustion emissions by improving kiln insulation, using more efficient burners, or switching to low-carbon fuels. However, you cannot reduce process emissions through energy efficiency. The CO2 from the stone will be released regardless of whether you heat it with natural gas, electricity, or concentrated solar power.
Calcination's Impact in Key Industries
The stoichiometric release of CO2 makes calcination a major focus for industrial decarbonization efforts.
The Cement Industry
Cement manufacturing is the largest single source of calcination emissions globally. The production of clinker, the key ingredient in cement, involves calcining enormous quantities of limestone.
Process emissions from calcination account for 50-60% of the total CO2 footprint of modern cement plants. The remainder comes from fuel combustion.
Lime Production
The entire purpose of a lime kiln is to produce CaO from CaCO3. Therefore, the release of CO2 is not just a byproduct but a direct indicator that the desired chemical transformation has occurred.
Common Pitfalls and Mitigation Strategies
Understanding the nature of calcination emissions is key to developing effective strategies to manage them.
The Inefficiency Trap
A common mistake is believing that making a kiln more energy-efficient will eliminate its CO2 emissions. While this is a critical step for reducing combustion emissions, it does absolutely nothing to stop process emissions.
The Role of Carbon Capture
Because process emissions are chemically unavoidable, the primary technological solution for deep decarbonization in sectors like cement and lime is Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS). This technology captures CO2 from the flue gas before it enters the atmosphere.
Alternative Materials
Long-term research focuses on developing alternative building materials that do not rely on carbonate calcination, thereby designing the problem out of the process entirely.
How to Quantify CO2 for Your Process
Your approach to measuring and managing CO2 will depend on your specific objective. Use the principles of stoichiometry as your foundation.
- If your primary focus is accurate emissions reporting: You must calculate process emissions based on the mass and chemical composition of your carbonate feedstock, then separately calculate combustion emissions based on fuel consumption data.
- If your primary focus is emissions reduction: Target combustion emissions first through energy efficiency and fuel switching for immediate gains, while evaluating carbon capture as the long-term solution for the unavoidable process emissions.
- If your primary focus is process design and mass balance: Account for the significant mass loss (44% for pure limestone) from your solid feedstock as it converts to gas, as this will fundamentally impact material flows and product yield calculations.
Understanding the fixed, stoichiometric nature of calcination emissions is the first and most critical step toward managing the carbon footprint of these essential industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Material | Chemical Reaction | Approx. CO2 Released (by mass) |
|---|---|---|
| Limestone (CaCO3) | CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 | 44% |
| Magnesite (MgCO3) | MgCO3 → MgO + CO2 | >52% |
Need precise thermal processing equipment to manage your calcination process and its emissions? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and kilns designed for accurate temperature control and process efficiency. Whether you're in R&D, cement, or lime production, our equipment helps you achieve optimal results while providing the data needed for accurate emissions accounting. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your specific calcination and decarbonization goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is the primary function of an industrial rotary tube furnace? Master Tungsten Powder Hydrogen Reduction
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotary furnace? Maximize Uniformity & Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity



















