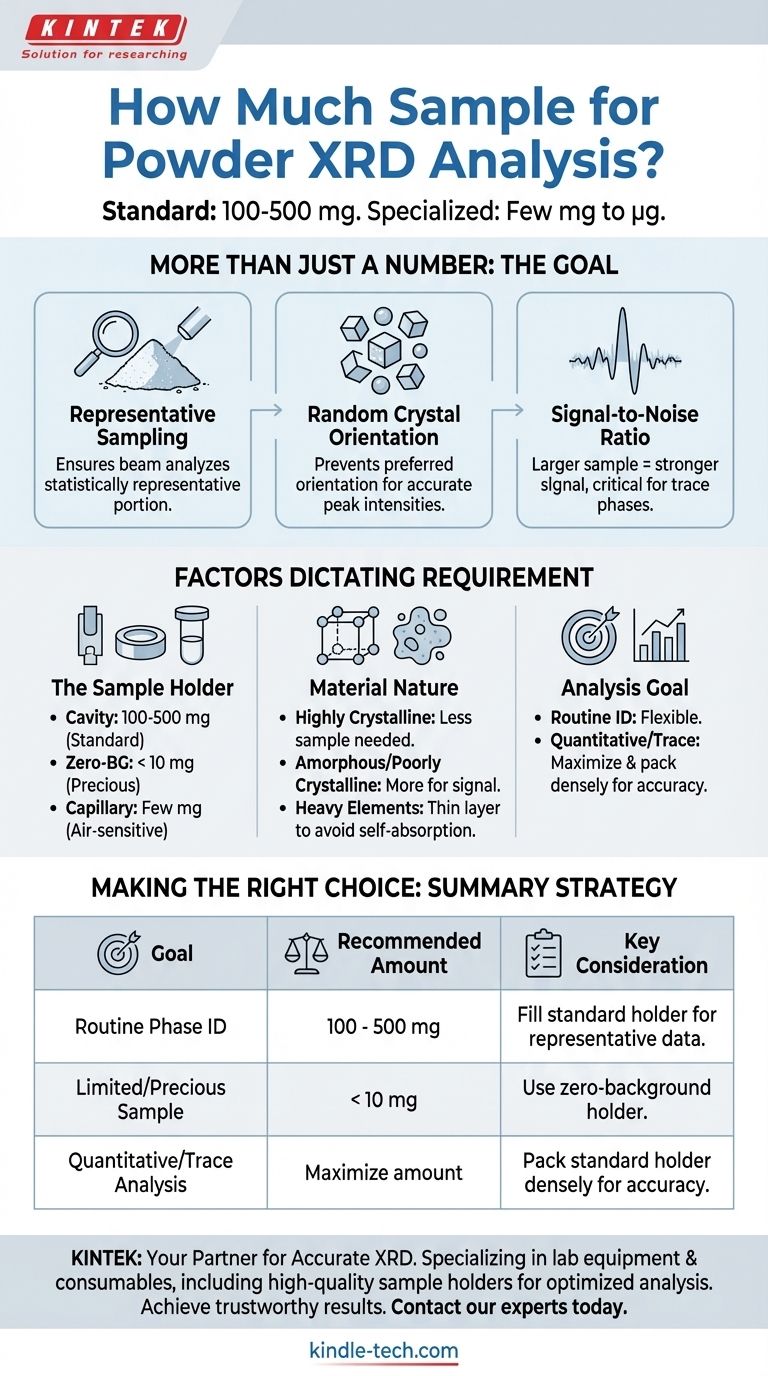
For standard powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), you typically need between 100 and 500 milligrams of a finely powdered sample. This amount is sufficient to completely fill a conventional sample holder, which is the most common setup for routine analysis. However, with specialized holders and techniques, successful analysis is possible with just a few milligrams or even micrograms of material.
The ideal sample quantity is not a fixed weight, but the minimum amount required to achieve a sufficient volume and random particle orientation. This ensures the X-ray beam analyzes a statistically representative portion of your material, producing a high-quality and reliable diffraction pattern.

Why Sample Amount is More Than Just a Number
The primary goal of sample preparation in powder XRD is to present a specimen to the X-ray beam that accurately represents the bulk material. The required mass is simply a means to that end.
The Goal: Representative Sampling
The X-ray beam only illuminates a small area of your sample. To obtain a true diffraction pattern of your material's crystal structure, the beam must interact with a massive number of crystallites.
A larger sample volume increases the probability that the beam is sampling a truly representative portion of the material, avoiding misleading results caused by localized impurities or unusual crystal formations.
Ensuring Random Crystal Orientation
Powder XRD theory assumes that the microscopic crystals (crystallites) in your sample are oriented in every possible direction randomly. This ensures that for every set of crystal planes, some crystallites will be perfectly aligned to diffract the X-ray beam.
If you have too little sample, it becomes difficult to achieve this randomness, leading to a phenomenon called preferred orientation, which systematically alters the intensity of diffraction peaks and can lead to incorrect conclusions.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio
A larger, well-packed sample generally produces a stronger diffraction signal relative to the inherent background noise from the instrument and sample holder.
This is especially critical when you are looking for phases present in small quantities (trace phases) or when your material is weakly crystalline.
Factors That Dictate Your Sample Requirement
While 100-500 mg is a general guideline, the true amount you need depends on several practical factors.
The Sample Holder
This is the most significant factor. A standard cavity holder (e.g., 1-2 cm in diameter and 0.5 mm deep) requires a certain volume to be filled, which corresponds to the 100-500 mg range for most materials.
Specialized zero-background holders, often made of a single silicon crystal, are designed for very small quantities. You can simply dust a thin layer of powder onto them, often requiring less than 10 mg.
Capillary mounts are used for air-sensitive samples or for certain instrument geometries and require only a few milligrams to fill the thin glass tube.
The Nature of Your Material
Highly crystalline materials diffract X-rays efficiently and may produce a strong pattern even with a small amount of sample.
Conversely, amorphous or poorly crystalline materials produce very broad, weak signals and benefit from a larger sample volume to improve the signal-to-noise ratio.
Materials containing heavy elements (like lead or tungsten) strongly absorb X-rays. In these cases, using too much sample can actually weaken the signal due to self-absorption, and a thinner layer may be preferable.
The Goal of the Analysis
If you are simply performing a routine phase identification on a major component, you have more flexibility.
For precise quantitative analysis or searching for trace phases, maximizing the sample amount and ensuring perfect preparation is critical for obtaining the high-quality, statistically reliable data needed for an accurate result.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Problem of Too Little Sample
Using an insufficient amount of sample for your chosen holder is one of the most common sources of poor-quality XRD data.
Poor Particle Statistics
When the X-ray beam interacts with too few crystallites, the resulting diffraction pattern can appear "spotty" or "noisy." The peaks may be misshapen and have incorrect relative intensities because you have not sampled enough crystal orientations.
The Risk of Preferred Orientation
With a very thin layer of sample, platy or needle-shaped crystals may preferentially lie flat on the holder surface instead of being randomly oriented. This dramatically increases the intensity of certain peaks and reduces others, which can lead to misidentification of the material.
Dominance of Background Signal
If the sample is too sparse, the weak signal from your material can be overwhelmed by the background scatter from the sample holder itself. This makes it extremely difficult to identify minor peaks or analyze weakly diffracting materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your experimental goals should guide your sample preparation strategy. Consider the best approach based on your specific analytical question.
- If your primary focus is routine phase identification: Use a standard sample holder and aim for the 100-500 mg range to ensure high-quality, unambiguous data.
- If your primary focus is working with a precious or limited sample: Use a zero-background sample holder and ensure the powder covers the area the X-ray beam will hit, accepting a potential compromise in signal-to-noise.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis or trace phase detection: Use a sufficient amount of finely ground powder to completely and densely pack a standard holder to maximize statistical accuracy and minimize orientation effects.
Ultimately, thoughtful sample preparation is the foundation of trustworthy and insightful XRD analysis.
Summary Table:
| Sample Goal | Recommended Amount | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Routine Phase ID | 100 - 500 mg | Fill standard holder for representative data |
| Limited/Precious Sample | < 10 mg | Use zero-background holder |
| Quantitative/Trace Analysis | Maximize amount | Pack standard holder densely for accuracy |
Ensure your XRD analysis starts with the right sample preparation.
At KINTEK, we understand that accurate results depend on proper technique from the very beginning. Whether you're working with abundant materials or rare, precious samples, having the right equipment and consumables is crucial for achieving reliable data.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. We provide a range of high-quality sample holders—from standard cavity types to specialized zero-background options—designed to help you optimize your XRD analysis regardless of your sample quantity or analytical goals.
Let us help you achieve trustworthy and insightful results. Contact our experts today to discuss the best sample preparation solutions for your specific XRD application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- Why is sieve analysis important? Ensure Consistent Quality and Performance of Your Materials
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
















