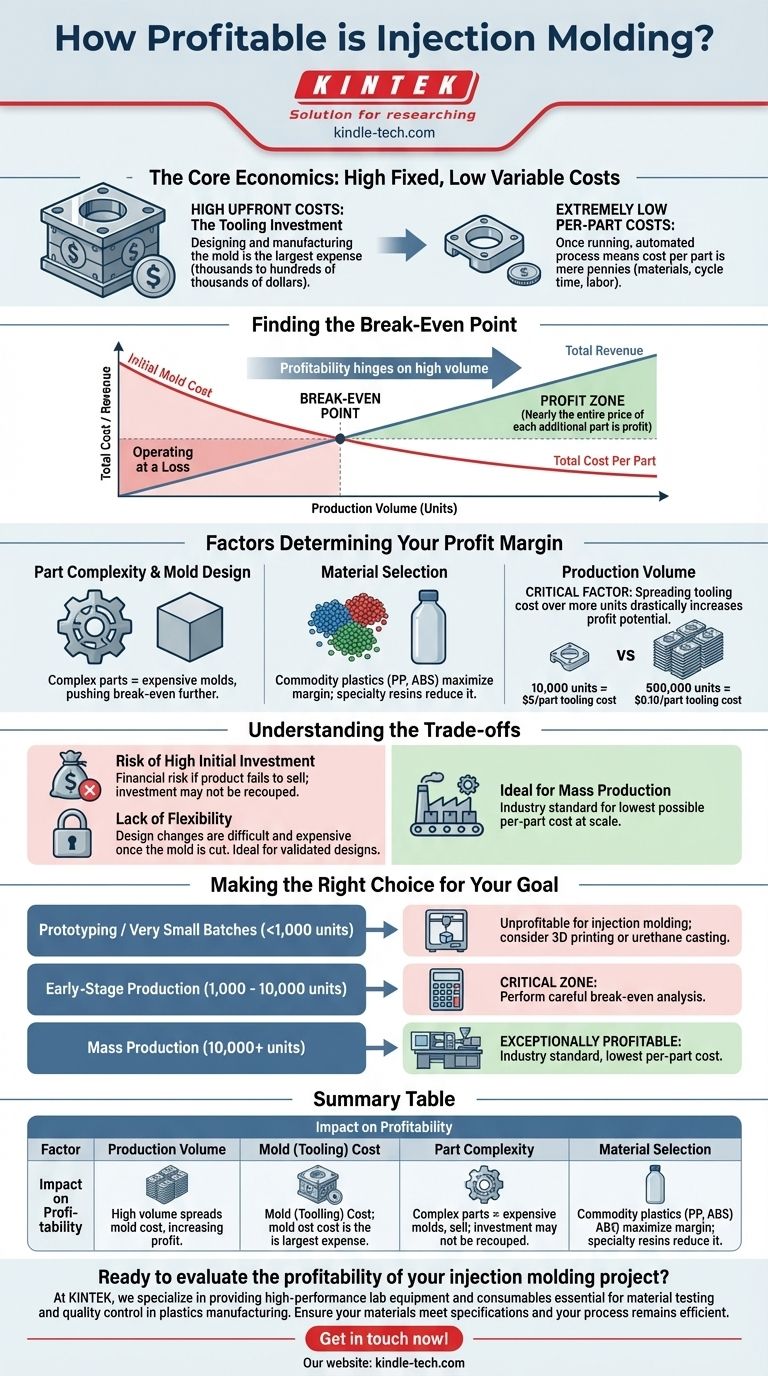
At the right scale, injection molding is one of the most profitable manufacturing methods available for plastics. Its profitability, however, is entirely dependent on producing a high volume of parts, because the significant upfront investment in mold tooling must be spread across many thousands of units to become cost-effective.
The core principle is simple: Injection molding involves a massive initial cost for the mold (tooling) and an extremely low cost for each part produced. Therefore, profitability is not inherent to the process itself but is achieved when production volume is large enough to make the initial investment negligible on a per-part basis.

The Core Economics of Injection Molding
To understand the profitability of injection molding, you must first understand its two-part cost structure: a high fixed cost followed by a low variable cost.
High Upfront Costs: The Tooling Investment
The single largest expense by a wide margin is the creation of the mold, also known as the tool. This is a precision-machined block of steel or aluminum that serves as the negative of your final part.
Designing and manufacturing this tool can cost anywhere from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars. This initial investment is the primary barrier and the reason the process is unprofitable for small runs.
Extremely Low Per-Part Costs
Once the mold is created and installed, the ongoing production cost for each individual part is incredibly low. The main costs are the plastic resin (pellets), the machine's cycle time, and labor.
Because the process is automated and fast, the cost per part can be mere pennies, allowing for significant profit margins after the initial tooling cost is paid off.
Finding the Break-Even Point
Profitability hinges on reaching the break-even point. This is the number of parts you must produce and sell to cover the initial investment in the mold.
Before you reach this point, you are operating at a loss. After you surpass it, nearly the entire price of each additional part becomes profit.
Factors That Determine Your Profit Margin
While volume is the primary driver, other factors directly influence your final profit margin.
Part Complexity and Mold Design
A simple part requires a simple mold, which is less expensive. A highly complex part with intricate features or undercuts requires a much more complex and expensive mold, pushing your break-even point further out.
Material Selection
The cost of the plastic resin itself is a key variable cost. Common commodity plastics like Polypropylene (PP) or ABS are inexpensive.
However, high-performance engineering polymers or custom-colored resins can significantly increase the per-part cost, which eats into your margin.
Production Volume
This remains the most critical factor. Spreading a $50,000 tooling cost over 10,000 units adds $5 to the cost of each part. Spreading that same cost over 500,000 units adds only $0.10 to each part, dramatically increasing the potential for profit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Injection molding is a powerful tool, but it is not the right solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to making a profitable decision.
The Risk of High Initial Investment
The primary risk is financial. If your product fails to sell in the numbers you projected, you may never recoup the significant cost of the mold, resulting in a substantial loss.
Lack of Flexibility
Once a steel mold is cut, making design changes is extremely difficult and expensive. The process is ideal for a finalized, validated design, not for a product that is still evolving. This inflexibility is a major trade-off for its low per-part cost at scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision must be based entirely on your projected production volume.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or very small batches (under ~1,000 units): Injection molding is almost certainly unprofitable; consider alternatives like 3D printing or urethane casting instead.
- If your primary focus is early-stage production (1,000 - 10,000 units): This is the critical zone where you must perform a careful break-even analysis to see if the investment is justified.
- If your primary focus is mass production (10,000+ units): Injection molding is the industry standard and becomes exceptionally profitable, offering the lowest possible per-part cost.
Ultimately, profitability in injection molding is a strategic calculation of scale.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Profitability |
|---|---|
| Production Volume | High volume spreads mold cost, lowering per-part cost and increasing profit. |
| Mold (Tooling) Cost | High initial investment; profitability requires high volume to break even. |
| Part Complexity | Complex parts require expensive molds, pushing the break-even point higher. |
| Material Selection | Commodity plastics (e.g., PP, ABS) maximize margin; specialty resins reduce it. |
Ready to evaluate the profitability of your injection molding project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables essential for material testing and quality control in plastics manufacturing. Whether you're prototyping or scaling to mass production, our solutions help ensure your materials meet specifications and your process remains efficient.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs and discover how we can support your path to profitable production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What technical characteristics are required for specialty pressure molds used in the compaction of Li10GeP2S12? Expert Tips
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- How does a stainless steel pressure die ensure the quality of the electrolyte layer? Unlock Precision Battery Assembly
- Why are custom pressure molds used during the hot pressing process for solid polymer electrolytes?
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?



















