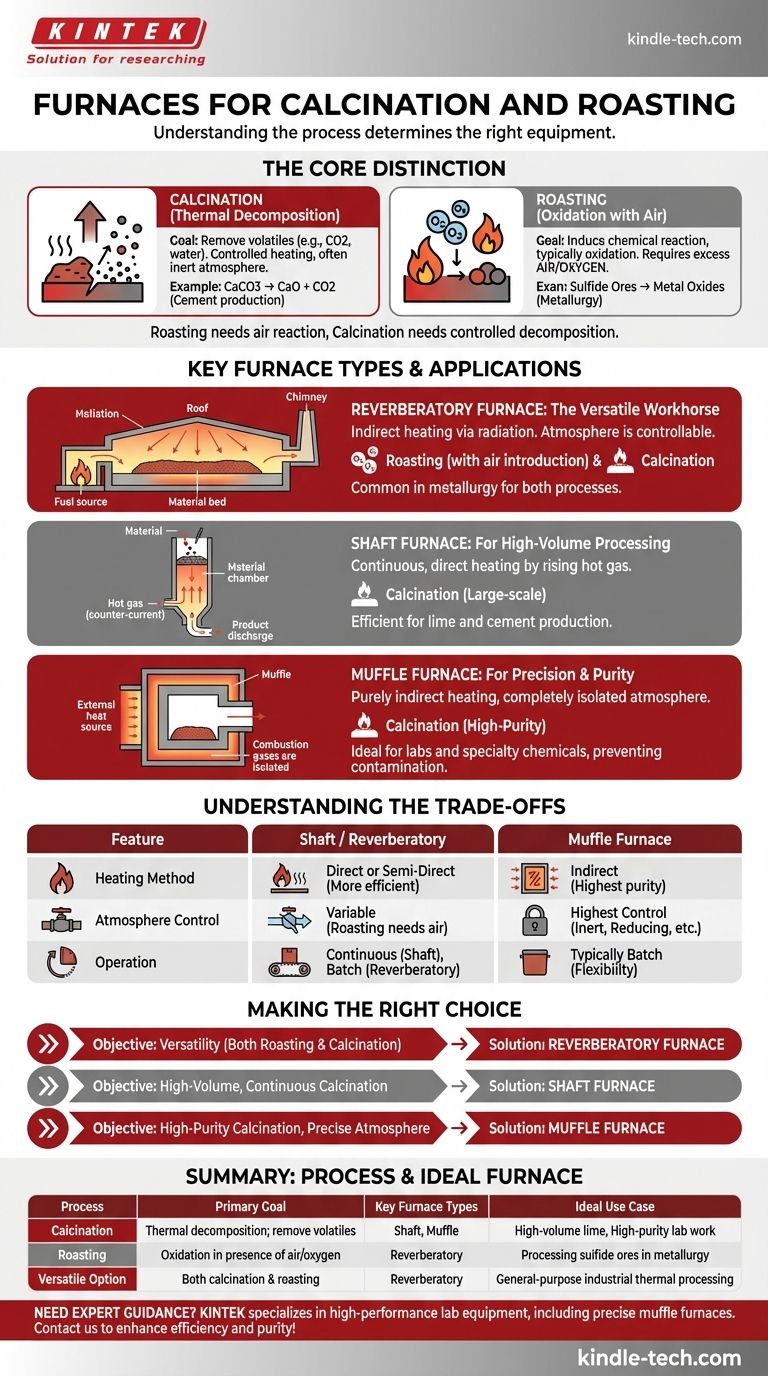
To be direct, both calcination and roasting can be performed in a reverberatory furnace. However, calcination is a more specific thermal process that can also be carried out in specialized equipment like muffle furnaces and shaft furnaces, depending on the material and desired outcome.
The choice of furnace is not arbitrary; it is dictated by the fundamental goal of the process. Roasting requires reaction with air, while calcination demands controlled heating to decompose a material, making furnace design and atmosphere control the critical factors.

Defining the Processes: Calcination vs. Roasting
Understanding the difference between these two thermal treatments is the key to selecting the right equipment. Though both involve heating, their objectives are fundamentally different.
What is Calcination?
Calcination is a thermal decomposition process. Its goal is to heat a solid material to a high temperature in a controlled atmosphere to drive off volatile components.
This is done to remove absorbed water, carbon dioxide, or other volatile substances. A prime example is the production of cement, where calcium carbonate is calcined to produce calcium oxide (lime) and carbon dioxide.
What is Roasting?
Roasting, on the other hand, is a process of heating a solid in the presence of excess air or oxygen.
The goal of roasting is not just to decompose the material, but to induce a specific chemical reaction, typically oxidation. It is a common step in processing sulfide ores, converting them into more easily reducible metal oxides.
Key Furnace Types and Their Applications
While a reverberatory furnace is a common answer, it is not the only one. The three primary furnace configurations each serve a distinct purpose.
The Reverberatory Furnace: The Versatile Workhorse
This furnace is designed so that the material is heated without coming into direct contact with the fuel source. Heat is radiated from the roof and walls onto the material bed.
Its design allows for sufficient control over the atmosphere, making it suitable for both roasting (by introducing air) and calcination. This versatility makes it a common choice in metallurgy.
The Shaft Furnace: For High-Volume Processing
A shaft furnace is a tall, vertical chamber where material is fed in from the top and moves downward. It is heated by a counter-current flow of hot gas rising from the bottom.
This configuration is extremely efficient for large-scale, continuous calcination processes. Its most prominent application is in the production of lime and cement.
The Muffle Furnace: For Precision and Purity
In a muffle furnace, the material being heated is placed inside a separate chamber, or "muffle," which is then heated from the outside.
This complete isolation from combustion gases provides a highly pure, precisely controlled atmosphere. It is the ideal choice for calcination where preventing contamination is critical, such as in laboratory settings or for specialty chemical production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between these furnaces comes down to balancing efficiency, purity, and process requirements.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
Shaft and reverberatory furnaces use a more direct method of heat transfer from combustion gases. Muffle furnaces use purely indirect heating, which ensures purity but can be less energy efficient.
Atmosphere Control
Roasting fundamentally requires an oxidizing atmosphere (air). Calcination might require an inert, reducing, or specific gas atmosphere. A muffle furnace offers the highest degree of atmosphere control, making it superior for sensitive calcination tasks.
Batch vs. Continuous Operation
Shaft furnaces are designed for continuous, high-throughput operation, making them industrial powerhouses. Reverberatory and muffle furnaces are often better suited for batch processing, offering more flexibility for smaller or varied loads.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct equipment, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is versatility for both roasting and calcination: The reverberatory furnace is a proven and widely used solution.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous calcination for bulk materials: A shaft furnace or rotary kiln is the most efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity calcination with precise atmosphere control: The muffle furnace is the only option that guarantees isolation from combustion byproducts.
Ultimately, the material's specific chemical and physical requirements will always dictate the correct thermal processing technology.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Furnace Types | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermal decomposition; remove volatiles | Shaft Furnace, Muffle Furnace | High-volume lime production, high-purity lab work |
| Roasting | Oxidation in presence of air/oxygen | Reverberatory Furnace | Processing sulfide ores in metallurgy |
| Versatile Option | Both calcination & roasting | Reverberatory Furnace | General-purpose industrial thermal processing |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right furnace for your calcination or roasting process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces for precise, contamination-free thermal processing. Our experts can help you choose the ideal solution to enhance efficiency, purity, and throughput. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and air oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- What are the conditions for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety, Performance, and Longevity
- What is done by ashing in muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Inorganic Content Analysis
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a normal furnace? Ensuring Sample Purity with Indirect Heating
- Is a furnace endothermic or exothermic? Uncover the Science of Home Heating



















