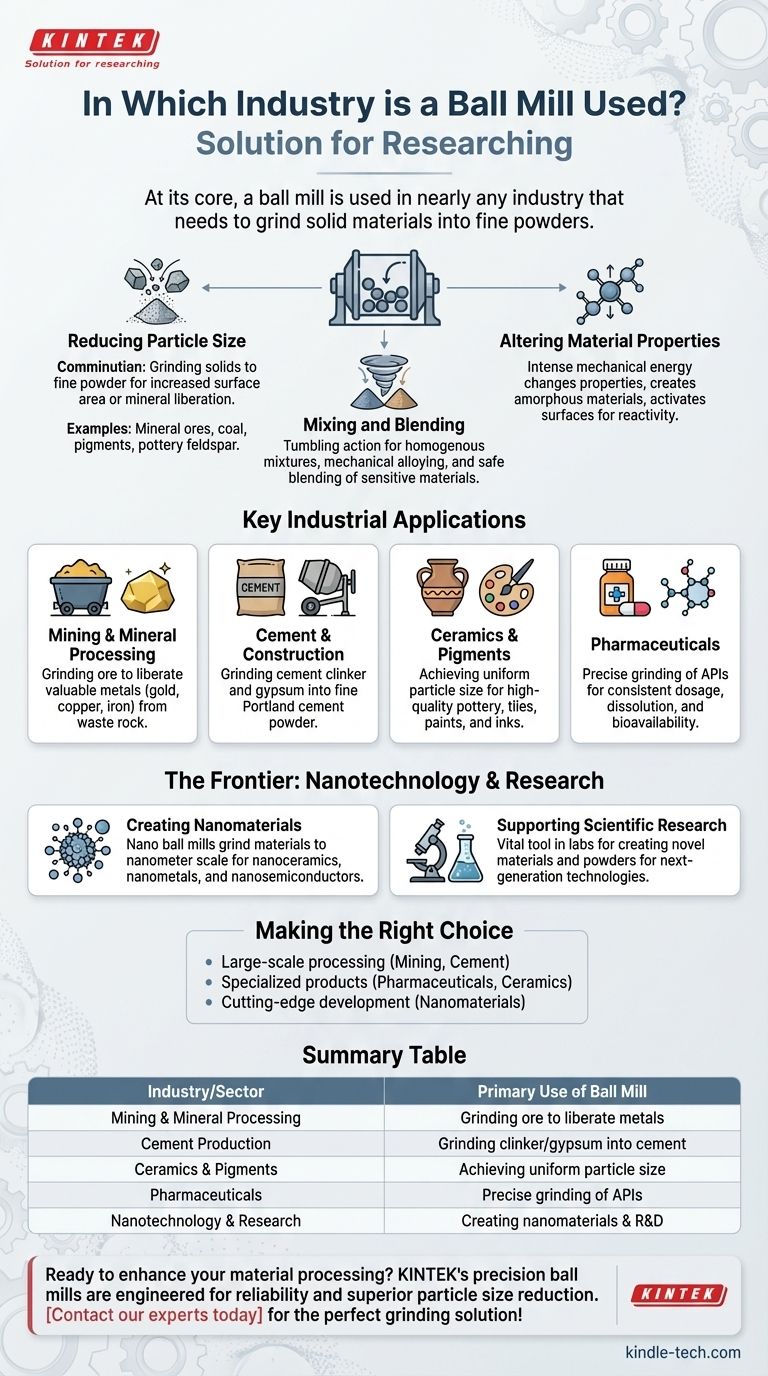
At its core, a ball mill is used in nearly any industry that needs to grind solid materials into fine powders. This includes large-scale industrial sectors like mining, cement production, and ceramics, as well as highly specialized fields such as pharmaceuticals, nanotechnology, and scientific research. Its fundamental purpose is particle size reduction, a critical step in processing a vast range of materials.
A ball mill is not defined by a single industry, but by its core function: transforming coarse solids into fine, uniform powders. This simple, powerful capability makes it an indispensable tool for everything from manufacturing concrete to developing advanced nanomaterials.
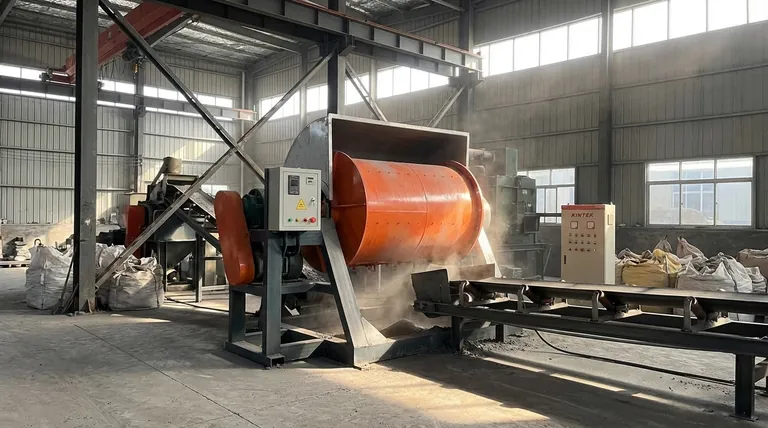

The Core Function: Why a Ball Mill is So Versatile
A ball mill's value comes from its ability to reliably perform a few critical material processing tasks. Understanding these functions explains its widespread adoption.
Reducing Particle Size
The primary use of a ball mill is comminution, or the reduction of solid materials from a larger size to a fine powder. This is essential for increasing surface area, freeing minerals from ore, or creating a consistent mixture.
Examples of materials ground this way include mineral ores, coal, pigments, and feldspar for pottery.
Mixing and Blending
Beyond just grinding, the tumbling action inside a ball mill is an effective method for mixing and blending different powdered materials into a homogenous mixture.
This process is used for tasks like mechanical alloying, where different metal powders are fused, and even for safely blending sensitive materials like explosives.
Altering Material Properties
The intense mechanical energy inside a ball mill can do more than just shrink particles; it can change the fundamental properties of a material.
This can be used to create amorphous materials (solids lacking a crystalline structure) or to activate a material's surface, making it more reactive for subsequent chemical processes.
A Look at Key Industrial Applications
While the function is universal, the application of ball milling is tailored to the specific goals of each industry.
Mining and Mineral Processing
In the mining industry, ball mills are a cornerstone of mineral liberation. They grind down large rocks and crushed ore to a fine powder, which allows for the efficient separation of valuable metals like gold, copper, and iron from the waste rock.
Cement and Construction
The production of Portland cement, a key ingredient in concrete, relies heavily on ball mills. They are used to grind cement clinker—a hard, nodular material—along with gypsum into the fine grey powder we recognize as cement.
Ceramics and Pigments
Achieving a uniform, fine particle size is critical for high-quality ceramics and vibrant pigments. Ball mills provide the necessary consistency to produce everything from pottery and tiles to paints and inks.
Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry requires precise control over particle size to ensure proper drug dosage, dissolution rates, and bioavailability. Ball mills are used to grind active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to meet these strict specifications.
The Frontier: Nanotechnology and Research
Modern, high-energy ball mills have pushed the technology into advanced scientific and research applications.
Creating Nanomaterials
The preparation of nanomaterials is a classic modern application. Nano ball mills can grind materials down to the nanometer scale, enabling the production of nanoceramics, nanometals, and nanosemiconductors.
Supporting Scientific Research
In labs focused on materials science, energy, and biomedicine, ball mills are a vital tool. They provide researchers with the ability to create novel materials and powders for analysis and experimentation, supporting the development of next-generation technologies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the different applications allows you to see where this technology fits into various production and research workflows.
- If your primary focus is large-scale raw material processing: A ball mill is an essential workhorse for industries like mining and cement that must process thousands of tons of material daily.
- If your primary focus is creating specialized products: The controlled grinding of a ball mill is critical for pharmaceuticals and ceramics, where particle consistency directly impacts final product quality.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge scientific development: High-energy ball milling is a key enabling technology for creating the advanced nanomaterials that drive innovation in materials science.
Ultimately, the ball mill is a foundational tool in material science, enabling progress across a surprisingly diverse range of human endeavors.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Sector | Primary Use of Ball Mill |
|---|---|
| Mining & Mineral Processing | Grinding ore to liberate valuable metals (e.g., gold, copper) |
| Cement Production | Grinding clinker and gypsum into fine cement powder |
| Ceramics & Pigments | Achieving uniform particle size for high-quality products |
| Pharmaceuticals | Precise grinding of APIs for consistent dosage and bioavailability |
| Nanotechnology & Research | Creating nanomaterials and supporting advanced R&D |
Ready to enhance your material processing? Whether you're in mining, pharmaceuticals, or advanced research, KINTEK's precision ball mills are engineered for reliability and superior particle size reduction. Contact our experts today to find the perfect grinding solution for your laboratory or production needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory ball mill used in Co-Ni catalyst research? Optimize CO2 Conversion with Precise Milling
- What is the key role of a planetary ball mill for IZO targets? Achieve Atomic-Level Uniformity in Material Preparation
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a sag mill? A Guide to Primary vs. Secondary Grinding
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- How does a high-energy planetary ball mill facilitate the synthesis of sulfide glassy electrolytes? Achieve Amorphization



















