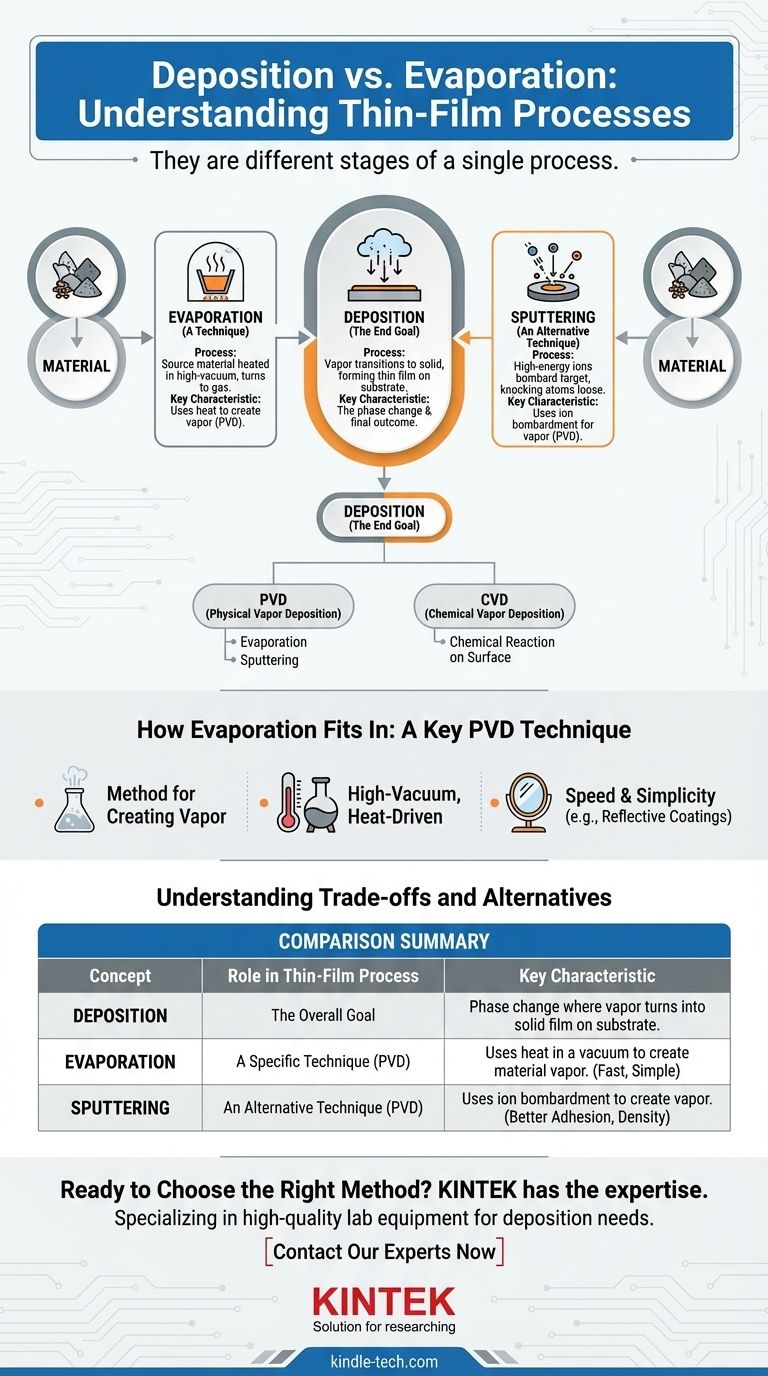
No, deposition and evaporation are not the same thing. They represent two different stages of a single overarching process. Deposition is the final outcome of a material settling onto a surface, while evaporation is one specific technique used to get the material into a vapor state so that deposition can occur.
Think of deposition as the overall goal: applying a thin film of material onto a substrate. Evaporation is simply one of the tools, or techniques, you can use to achieve that goal, alongside other methods like sputtering.

What is Deposition? The End Goal
The Fundamental Process
Deposition is a process where a material in a gas or vapor state transitions into a solid state, forming a thin, stable film on a surface (known as a substrate). It is fundamentally a phase change.
The Core Purpose
The primary goal of deposition is to create a highly controlled layer of material. These thin films are critical components in manufacturing semiconductors, optical lenses, mirrors, and countless other advanced technologies.
Two Major Categories
Nearly all deposition techniques fall into one of two families: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This distinction is based on how the material is prepared before it lands on the substrate.
How Evaporation Fits In: A Key PVD Technique
Evaporation as a Method
Evaporation is a cornerstone technique within the Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) family. It is a method for creating the vapor that will ultimately be deposited.
The Mechanism
In this process, a source material (like aluminum or gold) is heated in a high-vacuum chamber. The heat causes the material to boil or sublime, turning it directly into a gas. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses on a cooler substrate, forming the desired solid film.
Common Applications
Thermal evaporation is often chosen for its speed and simplicity. It is widely used for creating reflective coatings on mirrors, metallizing plastics, and forming electrical contacts in simple electronic devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
Sputtering: The Other Major PVD Technique
Sputtering is another common PVD method. Instead of heat, it uses high-energy ions to bombard a target made of the source material. This bombardment physically knocks atoms loose, which then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
Key Difference: Evaporation vs. Sputtering
As your reference notes, sputtering is often slower than evaporation. However, it can produce films with better adhesion and density. The choice between them depends entirely on the required properties of the final film.
What About Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)?
It's important to distinguish PVD methods like evaporation from CVD. In CVD, precursor gases are introduced into a chamber, and they undergo a chemical reaction directly on the hot substrate surface. This reaction is what forms the solid film, rather than simple condensation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To speak about these processes accurately, it's crucial to use the right term for the right context.
- If your primary focus is the overall process: Use the term deposition to describe the general act of creating a thin film on a surface.
- If your primary focus is the specific technique: Use the term evaporation or sputtering to explain exactly how the material vapor is being generated.
- If your primary focus is categorization: Remember that evaporation is a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), a major class of deposition technology.
Understanding this hierarchy—deposition as the goal and evaporation as one of the methods—clarifies the entire landscape of thin-film technology.
Summary Table:
| Concept | Role in Thin-Film Process | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition | The overall goal | The phase change where vapor turns into a solid film on a substrate. |
| Evaporation | A specific technique (PVD) | Uses heat in a vacuum to create material vapor for deposition. |
| Sputtering | An alternative technique (PVD) | Uses ion bombardment to create vapor, often for better film adhesion. |
Ready to Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method for Your Project?
Understanding the nuances between deposition, evaporation, and sputtering is critical for achieving the precise film properties your application demands. Whether you need the speed of thermal evaporation or the superior adhesion of sputtering, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your laboratory's thin-film research and production.
We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and film quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition



















