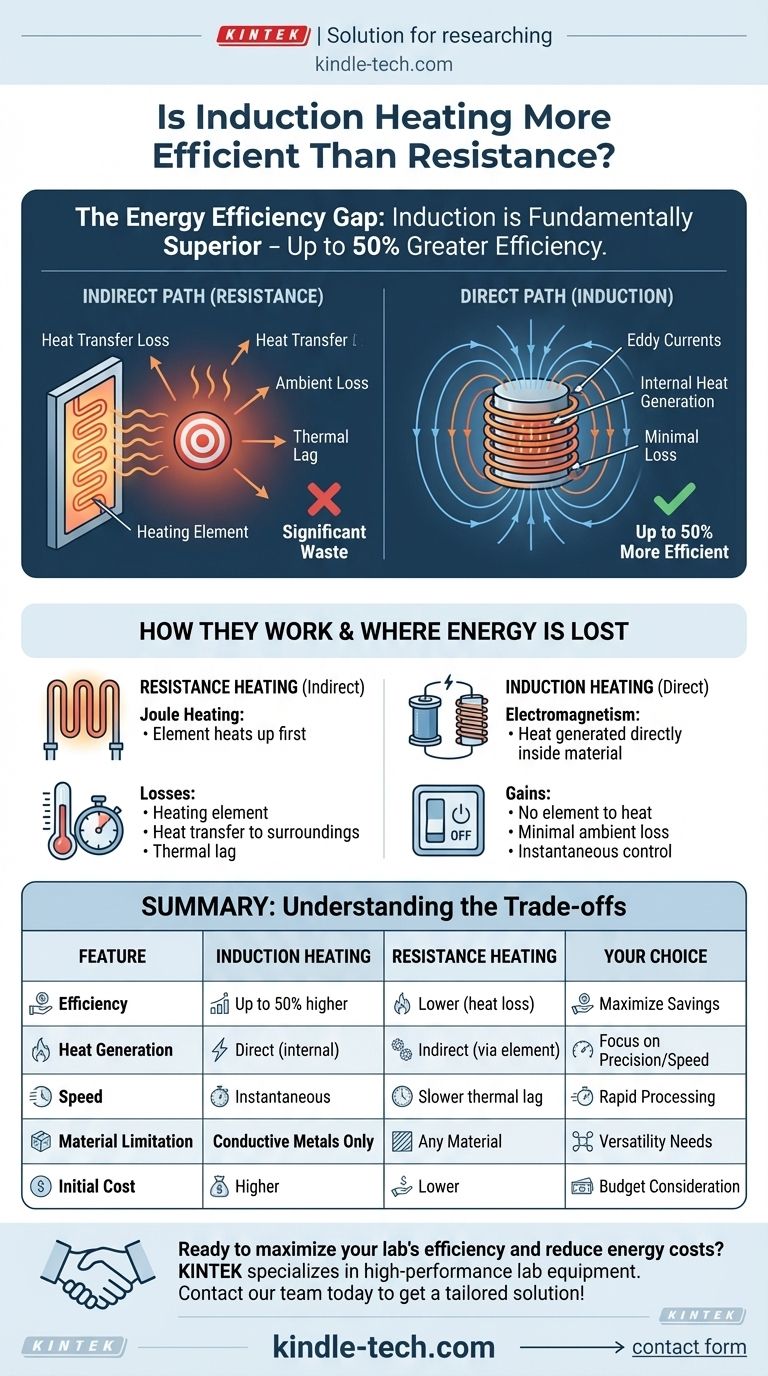
When it comes to pure energy efficiency, induction heating is fundamentally superior to resistance heating. The process generates heat directly within the target material, which can result in up to 50% greater efficiency compared to resistance methods that heat an external element and then transfer that energy, leading to significant waste.
The core difference lies in the method of heat generation. Induction heating is a direct process where the workpiece becomes its own heat source, while resistance heating is an indirect process that loses significant energy to the surrounding environment.

How Each Heating Method Works
To understand the efficiency gap, we must first understand the fundamental physics behind each process. The distinction is between direct and indirect energy transfer.
How Resistance Heating Works: The Indirect Path
Resistance heating is the principle behind a conventional electric stove or a space heater.
An electric current is passed through a high-resistance material, often called a heating element. As the current struggles to flow, it generates intense heat (Joule heating). This heat must then be transferred to the target material through conduction, convection, or radiation.
How Induction Heating Works: The Direct Path
Induction heating uses electromagnetism to heat conductive materials without any direct contact.
A high-frequency alternating current flows through a copper coil, creating a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field. When a conductive workpiece (like a steel pan) is placed within this field, it induces electrical currents, called eddy currents, directly within the metal. The material's own resistance to these swirling currents generates precise, instantaneous heat from the inside out.
The Source of the Efficiency Gap
The "how" directly explains the "why." The efficiency difference is not a small optimization; it's a result of two completely different approaches to generating heat.
Where Resistance Heating Loses Energy
The indirect nature of resistance heating is its primary weakness. Energy is wasted at multiple points:
- Heating the Element: A significant amount of energy is first used just to bring the heating element itself to the target temperature.
- Heat Transfer Loss: Heat radiates from the element in all directions, not just into the workpiece. Much of this energy is lost to the surrounding air and equipment.
- Thermal Lag: The process is slow to start and slow to stop, as the element must heat up and cool down, wasting energy during these transition periods.
Why Induction Is More Efficient
Induction heating bypasses the biggest sources of waste.
- Direct Generation: Nearly all of the electrical energy is converted directly into heat inside the part being heated. There is no intermediate element to heat first.
- Minimal Ambient Loss: Since the coil itself does not get hot (only the workpiece does), very little heat is lost to the environment.
- Instantaneous Control: The heating action starts and stops almost instantly, eliminating energy waste from warming up or cooling down.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While more efficient, induction heating is not the universal solution. Its advantages come with specific limitations that make resistance heating the better choice in certain scenarios.
The Material Limitation of Induction
The single greatest limitation of induction is that it only works on materials that are electrically conductive, such as metals. It is particularly effective on ferromagnetic metals like iron and steel. It cannot be used to heat glass, ceramics, or plastics directly.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Induction heating systems, with their high-frequency power supplies and custom-designed coils, are significantly more complex and carry a higher initial investment cost than simple resistance heaters.
Application Versatility
Resistance heating is far more versatile. It can heat solids, liquids, and gases regardless of their electrical properties. For applications like a large industrial oven that needs to maintain a stable air temperature, resistance elements are often simpler and more practical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision depends entirely on your material, budget, and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is speed and precision on conductive metals: Induction heating is the clear winner due to its rapid, direct, and highly controllable nature.
- If your primary focus is heating non-conductive materials or minimizing initial cost: Resistance heating offers unmatched versatility and a much lower barrier to entry.
- If your primary focus is maximizing long-term energy savings in metal processing: The superior efficiency of induction provides a strong return on investment by drastically reducing operational energy costs.
Ultimately, choosing the right technology requires matching the method's strengths to your specific application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Heating | Resistance Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Up to 50% higher | Lower due to heat loss |
| Heat Generation | Direct (inside the material) | Indirect (via an element) |
| Speed | Instantaneous | Slower thermal lag |
| Material Limitation | Conductive metals only | Any material |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
Ready to maximize your lab's efficiency and reduce energy costs? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced induction heating systems. Our experts can help you select the right technology to accelerate your processes and achieve significant long-term savings. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace



















