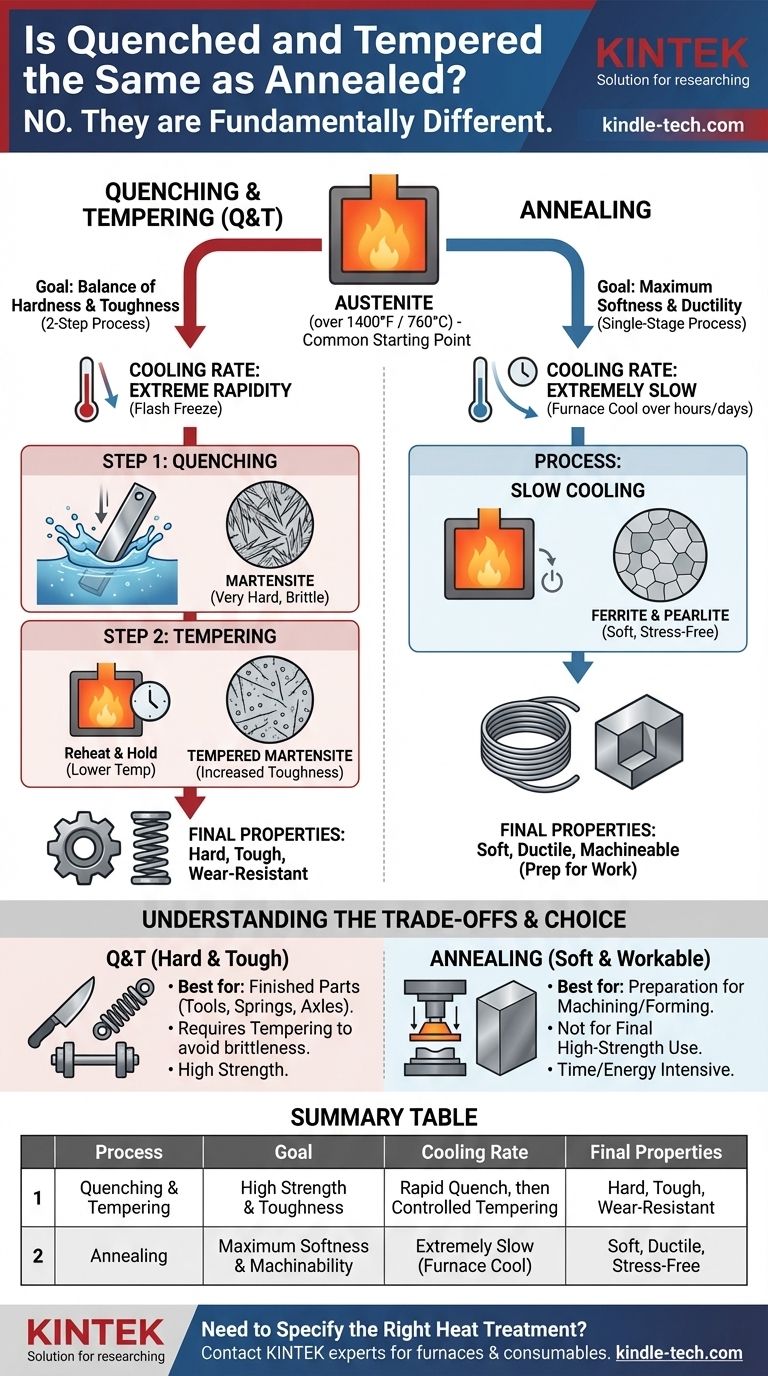
No, quenching and tempering is fundamentally different from annealing. While both are heat treatment processes for steel, they use opposite methods to achieve opposite goals. Quenching and tempering is a two-step process designed to create a final product with a specific balance of high hardness and toughness. Annealing, in contrast, is a single-stage process designed to make steel as soft, ductile, and machineable as possible.
The critical difference is the cooling rate and the intended outcome. Quenching and tempering uses rapid cooling to create hardness, followed by reheating to add toughness. Annealing uses extremely slow cooling to induce maximum softness, preparing the material for further work.

The Goal of Heat Treatment: Manipulating Microstructure
To understand these processes, you must first understand that heat treatment is about controlling the internal crystal structure, or microstructure, of the steel. The arrangement of iron and carbon atoms at a microscopic level dictates the material's final properties.
The Role of Carbon and Iron
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. At room temperature, the carbon is locked within the iron's crystal structure in various ways. By applying heat, we can change how that carbon is distributed.
The Critical Transformation Temperature (Austenite)
When you heat steel above a specific critical temperature (typically over 1400°F or 760°C), its crystal structure changes into a form called austenite. Austenite has a unique ability to dissolve carbon atoms uniformly, much like sugar dissolving in hot water. This austenitic state is the necessary starting point for both processes.
Why Cooling Rate is Everything
The properties of the steel are determined by what happens to the microstructure as it cools down from the austenitic state. The speed of this cooling is the single most important variable that separates quenching from annealing.
Process Breakdown: Quenching and Tempering (Q&T)
Quenching and tempering is a two-stage process used to produce parts that are strong, hard, and tough, such as tools, axles, and springs.
Step 1: Quenching for Maximum Hardness
After the steel is heated to its austenitic state, it is cooled with extreme rapidity by plunging it into a liquid like water, oil, or brine. This is the quench.
This "flash freeze" does not give the carbon atoms time to move and form softer structures. Instead, they are trapped, creating a very hard, brittle, and highly stressed microstructure called martensite. A fully quenched part is at its maximum possible hardness but is often too brittle for practical use.
Step 2: Tempering for Toughness
The brittle, martensitic steel is then reheated to a much lower temperature (well below the critical temperature) and held for a specific time. This is the tempering phase.
Tempering relieves the internal stresses from quenching and allows some of the trapped carbon to form tiny carbide particles. This process reduces the overall hardness slightly but dramatically increases the material's toughness and ductility, preventing it from fracturing under load. The final properties are "dialed in" by precisely controlling the tempering temperature.
Process Breakdown: Annealing
Annealing is a process used to put steel into its softest, weakest, and most stress-free state. This is often done to make a material easier to machine or to prepare it for extensive plastic forming, like stamping or deep drawing.
The Single Goal: Maximum Softness
Unlike the two-part goal of Q&T, annealing has one primary objective: to undo previous hardening, refine the grain structure, and relieve all internal stress, thereby maximizing softness and ductility.
The Key Step: Extremely Slow Cooling
After heating the steel to its austenitic state, it is cooled down as slowly as possible. This is most often achieved by simply turning the furnace off and allowing the part to cool down with the furnace over many hours or even days.
This slow cooling gives the atoms ample time to rearrange themselves into their most stable, low-energy state. The resulting microstructure (typically a mix of ferrite and pearlite) is very soft, ductile, and has low internal stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong process can lead to material failure or unnecessary production costs. Understanding the compromises is essential.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Dilemma
A fully quenched, untempered part has immense hardness and wear resistance but is practically useless because it will shatter like glass at the first impact. Tempering is not optional; it is the necessary compromise that trades a small amount of hardness for a massive gain in toughness.
Annealing's Limitation: Not for Final Performance
An annealed part is rarely the intended final product for any application requiring strength. Its softness and low strength make it unsuitable for tools or structural components. It is almost always a preparatory or intermediate step in a manufacturing sequence.
The Cost of Time and Energy
Annealing, with its long furnace cycles, is a very time and energy-intensive process. For this reason, a less precise process called normalizing (which involves cooling in still air) is sometimes used as a more cost-effective alternative when maximum softness isn't required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of heat treatment is dictated entirely by what you need the steel to do.
- If your primary focus is creating a finished part with high strength and toughness (e.g., a knife, axle, or spring): You need the two-step Quench and Temper process to achieve the required mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is preparing a raw material for heavy machining, forming, or bending: You need to Anneal the steel to make it as soft and stress-free as possible before you begin work.
- If your primary focus is simply relieving stress from welding or machining without greatly affecting hardness: You may need a different sub-critical process, like stress relief, which does not involve heating to the full austenitic temperature.
By understanding these fundamental differences, you can move beyond simply following a procedure and begin to dictate the precise performance of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Process | Goal | Cooling Rate | Final Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quenching & Tempering | High strength & toughness | Rapid quench, then controlled tempering | Hard, tough, wear-resistant |
| Annealing | Maximum softness & machinability | Extremely slow (furnace cool) | Soft, ductile, stress-free |
Need to Specify the Right Heat Treatment for Your Application?
Choosing the correct process is critical for part performance and manufacturing efficiency. The expert team at KINTEK specializes in supporting laboratories and manufacturers with the equipment and consumables needed for precise heat treatment. We can help you select the right furnaces and tools to achieve your desired material properties, whether you require the hardness of quenching and tempering or the machinability of annealing.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific steel heat treatment needs and ensure optimal results for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high temperature furnace? Transform Materials with Precision Heat
- How does temperature affect vacuum pressure? Master the Key to System Control
- How are high-performance vacuum furnaces used in helium implantation annealing? Master Material Defect Visualization
- Why is a high-purity gas supply system necessary for ion carburizing? Ensure Precise Surface Integrity and Phase Purity
- What is the function of high vacuum furnaces for Inconel 718? Achieve Peak Superalloy Strength via Micro-Engineering
- Why vacuum furnace? Achieve Absolute Control for Superior Material Quality
- Which heat treatment process increases the strength? Mastering Hardening and Tempering for Superior Steel
- Why is the diffusion bonding process within a vacuum furnace critical for near-alpha titanium alloy materials?



















