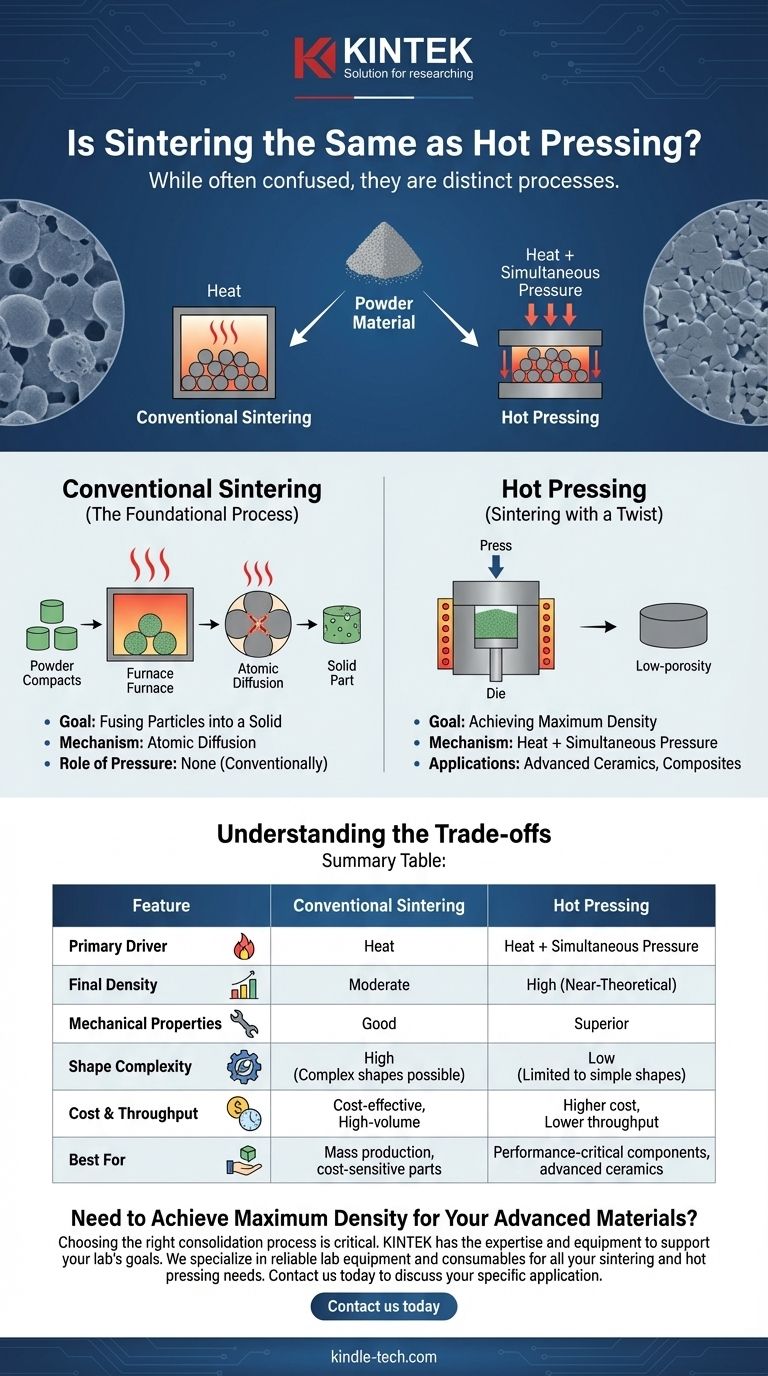
While often confused, sintering and hot pressing are not the same process. They are closely related, but hot pressing is a specific, advanced type of sintering. The core difference is that conventional sintering relies almost exclusively on heat to fuse particles, whereas hot pressing applies both high temperature and significant external pressure simultaneously to achieve densification.
The fundamental distinction lies in the application of external pressure. All hot pressing is a form of sintering, but not all sintering is hot pressing. Conventional sintering uses heat to bond powder particles, while hot pressing uses both heat and pressure concurrently to force the particles together, resulting in a denser final product.
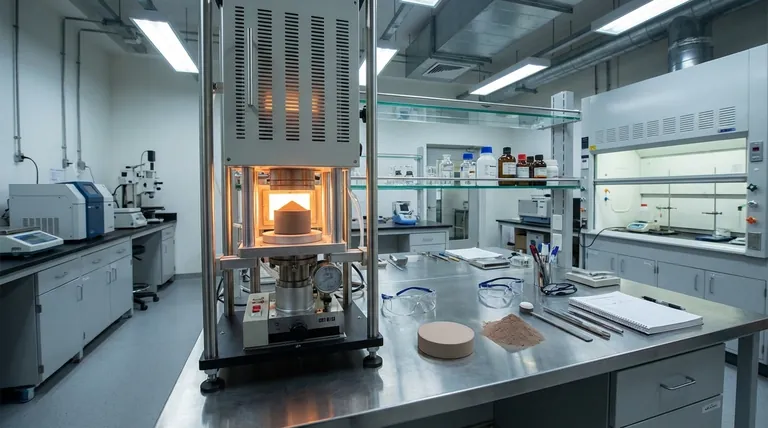

What is Sintering? (The Foundational Process)
Sintering is a thermal treatment process for compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
The Goal: Fusing Particles into a Solid
The primary goal of sintering is to bond individual powder particles together. This process reduces the porosity of the initial powder compact and significantly increases its strength and density.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works by heating a material to a temperature below its melting point. This thermal energy activates atoms, causing them to diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles, forming solid "necks" or bridges that fuse the particles into a coherent, solid piece.
The Role of Pressure: None (Conventionally)
In its most common form, known as "pressureless" or conventional sintering, the powder is first compacted into a desired shape at room temperature. This "green" part is then heated in a furnace, where densification occurs without any externally applied pressure.
What is Hot Pressing? (Sintering with a Twist)
Hot pressing, also known as hot pressing sintering, is a specialized technique that combines the shaping and sintering steps into a single operation.
The Goal: Achieving Maximum Density
Hot pressing is used when the goal is to achieve near-theoretical density and superior mechanical properties. It is particularly effective for materials that are very hard and difficult to densify using conventional sintering alone, such as advanced ceramics or composites.
The Mechanism: Heat + Simultaneous Pressure
In hot pressing, the powder is placed in a die, which is then heated while a uniaxial (single-direction) pressure is applied. The combination of heat and pressure dramatically accelerates the densification process. Pressure aids in particle rearrangement and plastic deformation, closing pores more effectively.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these methods involves clear trade-offs in performance, cost, and complexity.
Final Density and Mechanical Properties
Hot pressing consistently produces parts with higher final density, lower porosity, and, as a result, superior mechanical properties like strength and hardness compared to conventional sintering.
Processing Time and Temperature
Because pressure assists the densification process, hot pressing can often be performed at lower temperatures or for shorter durations than conventional sintering to achieve an equivalent density.
Shape Complexity and Geometry
Conventional sintering holds a major advantage for complex shapes. Powders can be formed into intricate geometries (e.g., via injection molding) before being sintered. Hot pressing is largely restricted to simple shapes like cylinders or blocks due to the limitations of the uniaxial die.
Cost and Throughput
Hot pressing equipment is more complex and expensive. The process is typically slower on a part-by-part basis, making it less suitable for high-volume manufacturing. Conventional sintering is far more scalable and cost-effective for mass production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material requirements and production goals will determine the correct process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production of complex shapes where some porosity is acceptable: Conventional sintering is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical properties for a performance-critical component with a simple geometry: Hot pressing is the necessary method.
- If you need to densify advanced ceramics or composite materials that do not sinter well under heat alone: Hot pressing provides the necessary force to achieve consolidation.
Understanding the distinct roles of heat and pressure is the key to selecting the ideal consolidation method for your material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Sintering | Hot Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Driver | Heat | Heat + Simultaneous Pressure |
| Final Density | Moderate | High (Near-Theoretical) |
| Mechanical Properties | Good | Superior |
| Shape Complexity | High (Complex shapes possible) | Low (Limited to simple shapes) |
| Cost & Throughput | Cost-effective, High-volume | Higher cost, Lower throughput |
| Best For | Mass production, cost-sensitive parts | Performance-critical components, advanced ceramics |
Need to Achieve Maximum Density for Your Advanced Materials?
Choosing the right consolidation process is critical for your material's performance. Whether your project requires the cost-effective scalability of conventional sintering or the superior density of hot pressing, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your lab's goals.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for all your sintering and hot pressing needs. Let our experts help you select the ideal solution to enhance your research and development.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover how we can help you achieve better results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are the fundamentals of spark plasma sintering process? Unlock Rapid, High-Performance Material Consolidation
- What is the role of a graphite mold during vacuum hot press sintering? Achieve Perfect Ceramic Densification
- What is the process fundamentals of spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Consolidation
- What is spark plasma sintering technique? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temp Materials Consolidation
- What role does axial pressure play during vacuum hot pressing of Lithium Niobate? Optimize Density & Grain Size
- What Role Does the Hydraulic Loading System Play in Ti/Al Composite Forming? Master Solid-State Diffusion Bonding
- What core challenges does a vacuum hot press furnace address? Achieve Superior WCp/Cu FGM Structural Integrity
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace play? Achieve 99.6% Density in Al2O3-TiCN/Co-Ni Ceramics



















