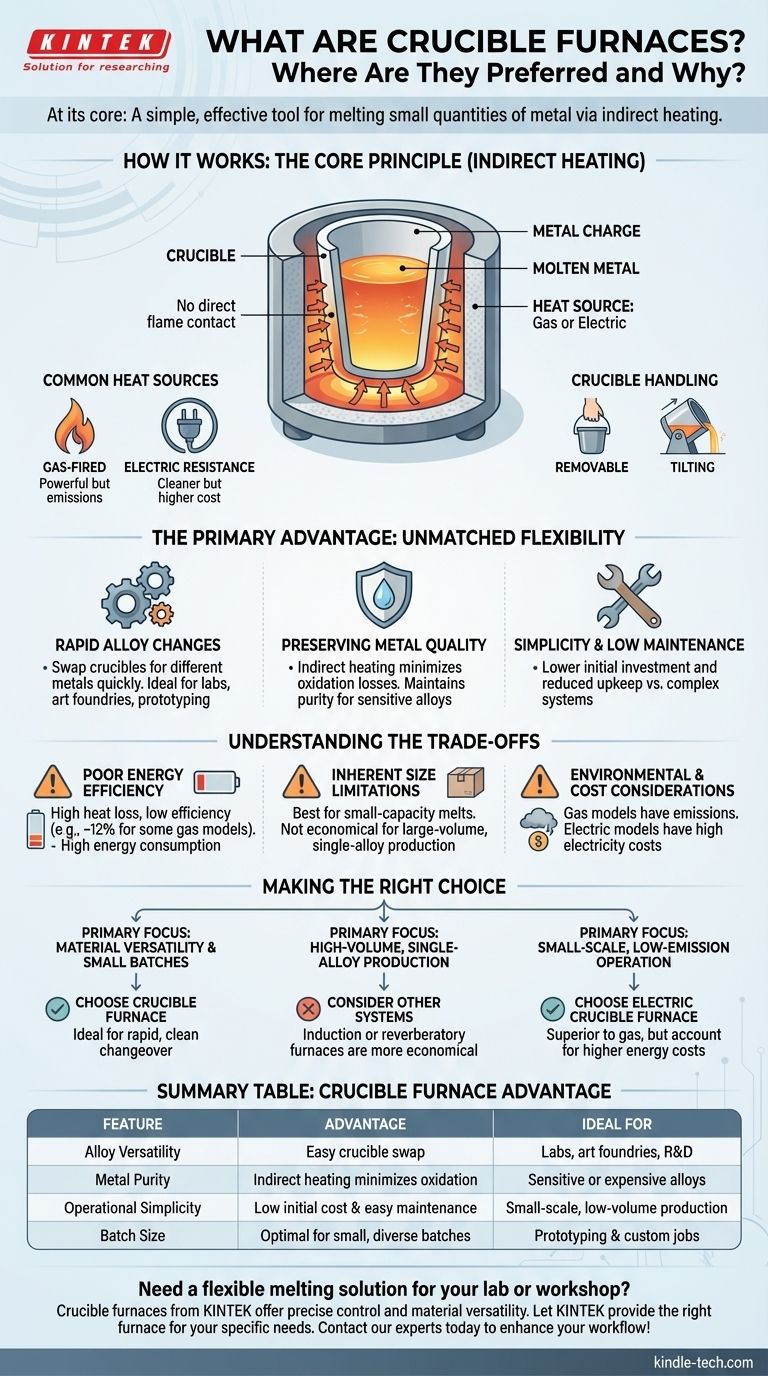
At its core, a crucible furnace is a simple and effective tool for melting small quantities of metal. It operates by heating a separate, removable container called a crucible, which holds the metal charge. This method of indirect heating makes it exceptionally versatile for a wide range of materials and applications.
While often criticized for their low energy efficiency, crucible furnaces are indispensable in settings where flexibility is paramount. Their ability to handle small, diverse batches of metal quickly and cleanly is a strategic advantage that outweighs their higher operational cost for specific tasks.

How a Crucible Furnace Works
A crucible furnace's design is defined by its simplicity. The fundamental principle is to heat a container, not the metal directly, which provides significant control over the melt.
The Core Principle: Indirect Heating
The metal to be melted is placed inside the crucible, a pot typically made from ceramic or other refractory materials. This crucible is then placed inside the furnace, where it is heated by an external source, such as a gas burner or electric elements. The heat transfers through the crucible wall to melt the metal inside, preventing direct contact between the flame and the alloy.
Common Heat Sources
Crucible furnaces are generally heated in one of two ways. Gas-fired furnaces are common and powerful but produce emissions. Electric resistance furnaces are cleaner, offering near-elimination of emissions and very low metal oxidation, but often come with higher energy costs.
Crucible Handling
Furnaces can be designed for removable crucibles, which are lifted out for pouring. This is common in smaller operations and for alloys that require precise pouring. Other designs use a stationary crucible and the entire furnace is tilted to pour the molten metal.
The Primary Advantage: Unmatched Flexibility
The reason crucible furnaces remain vital in modern metalworking is not efficiency, but flexibility. They solve a specific set of problems that large-scale furnaces cannot.
Rapid Alloy Changes
This is the crucible furnace's defining feature. Because the metal is contained within a discrete crucible, switching from melting aluminum to bronze requires little more than swapping out the pot. This makes them ideal for environments that require frequent changes in material, such as labs, art foundries, and prototyping shops.
Preserving Metal Quality
The indirect heating method minimizes oxidation losses. The metal is not directly exposed to the combustion gases, which helps maintain the purity and intended properties of the alloy. This is especially critical when working with sensitive or expensive metals.
Simplicity and Low Maintenance
The straightforward design of a crucible furnace translates to lower initial investment and reduced maintenance costs compared to more complex systems like induction furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To use a crucible furnace effectively, you must understand its significant limitations. The choice to use one is always a conscious trade-off between flexibility and operational cost.
Poor Energy Efficiency
Crucible furnaces are not energy-efficient. A significant amount of heat is lost to the furnace structure and the surrounding environment, with some fuel-fired models operating at efficiencies as low as 12%. This results in high fuel or electricity consumption per pound of metal melted.
Inherent Size Limitations
This technology does not scale well for mass production. The design is best suited for small-capacity melts. Attempting to use crucible furnaces for large-volume, single-alloy production is highly uneconomical.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
Gas-fired crucible furnaces produce emissions that may require costly pollution control measures to meet environmental regulations. While electric models solve the emissions problem, their higher electricity consumption can lead to substantial operational expenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a crucible furnace depends entirely on your operational priorities. It is a specialized tool, not a one-size-fits-all solution.
- If your primary focus is material versatility and small batches: A crucible furnace is the ideal choice due to its rapid and clean changeover capability.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, single-alloy production: The high energy cost of a crucible furnace makes other systems, like induction or reverberatory furnaces, a far more economical solution.
- If your primary focus is running a small-scale, low-emission operation: An electric crucible furnace is superior to a gas-fired model, but you must account for its higher energy costs in your budget.
Ultimately, the crucible furnace is the definitive choice when the need for operational flexibility outweighs the demand for maximum energy efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Crucible Furnace Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Alloy Versatility | Easy crucible swap for different metals | Labs, art foundries, R&D |
| Metal Purity | Indirect heating minimizes oxidation | Sensitive or expensive alloys |
| Operational Simplicity | Low initial cost and easy maintenance | Small-scale, low-volume production |
| Batch Size | Optimal for small, diverse batches | Prototyping and custom jobs |
Need a flexible melting solution for your lab or workshop?
Crucible furnaces from KINTEK offer the precise control and material versatility you need for small-batch metal melting. Whether you're in R&D, jewelry making, or prototyping, our equipment ensures clean melts and rapid alloy changes.
Let KINTEK, your lab equipment specialist, provide the right furnace for your specific needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a crucible furnace can enhance your workflow and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can you use the same crucible for different metals? Why dedicated crucibles are essential for metal purity and safety.
- What is a sintered glass filter used for? Achieve Precise, Chemical-Resistant Filtration
- Why are high-purity alumina ceramic crucibles used for hot-dip aluminum coatings? Ensure Purity and Thermal Stability
- What is the maximum temperature for a carbon crucible? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- Is a crucible a lab equipment? A Guide to High-Temperature Containers for Labs and Foundries
- Why are glassy carbon crucibles preferred for molten chloride salt? Maximize Purity in High-Temperature Experiments
- Why is a glass sintered crucible required for pulp separation? Achieve 100% Precision in Wood Fractionation
- Why must high-purity graphite crucibles be treated in a vacuum oven and pre-baked? Ensure Pure Molten Salt Experiments



















