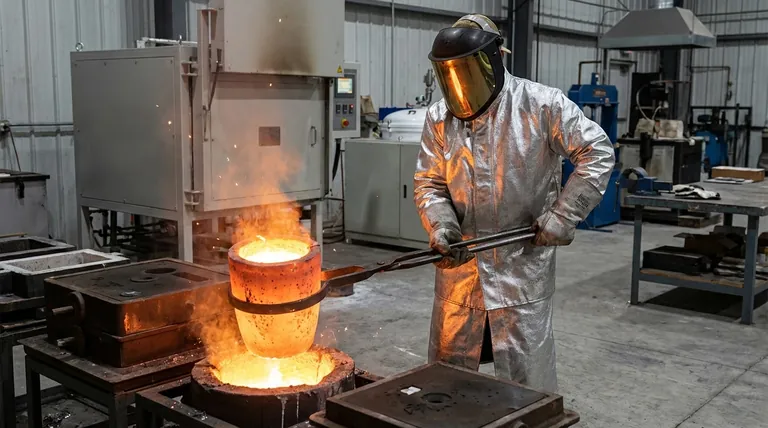
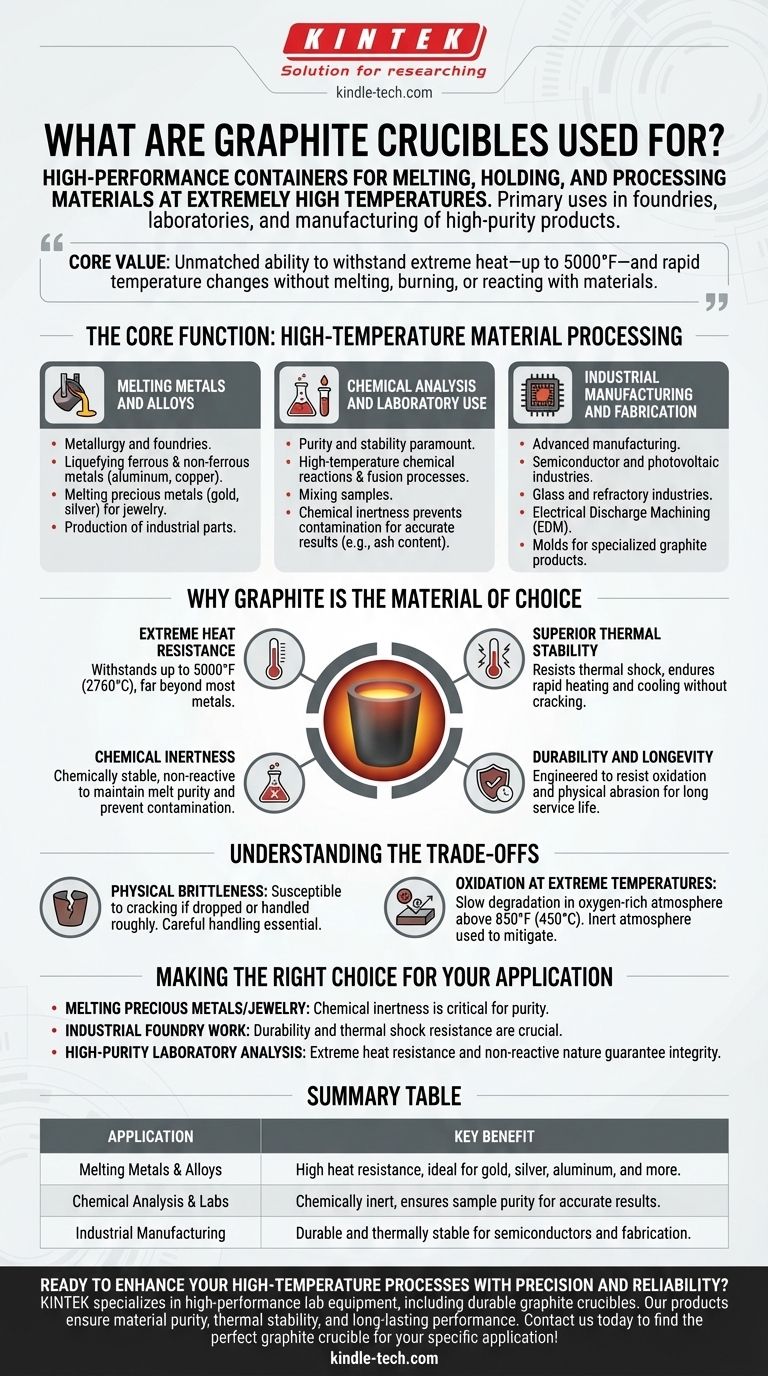
In essence, graphite crucibles are high-performance containers designed for melting, holding, and processing materials at extremely high temperatures. Their primary use is in foundries for melting both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, in laboratories for chemical analysis, and in the manufacturing of high-purity products like semiconductors and jewelry.
The core value of a graphite crucible is its unmatched ability to withstand extreme heat—up to 5000°F—and rapid temperature changes. It achieves this without melting, burning, or chemically reacting with the valuable materials it contains.

The Core Function: High-Temperature Material Processing
Graphite crucibles serve as the essential vessel in any process where materials must be heated to a liquid state or analyzed under intense thermal conditions. Their applications span a wide range of industries, from heavy manufacturing to delicate scientific work.
Melting Metals and Alloys
The most common application is in metallurgy and foundries. Graphite's high melting point makes it the ideal container for liquefying metals for casting.
This includes ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals (like aluminum and copper), and precious metals such as gold and silver. It is a foundational tool in jewelry making and the production of industrial parts like valves and plumbing fixtures.
Chemical Analysis and Laboratory Use
In a laboratory setting, purity and stability are paramount. Graphite crucibles are used to hold samples for high-temperature chemical reactions, fusion processes, and mixing.
Their chemical inertness ensures that the crucible itself does not contaminate the sample, which is critical for obtaining accurate results, such as determining the ash content of a substance.
Industrial Manufacturing and Fabrication
Beyond simple melting, these crucibles are integral to advanced manufacturing. They are used in high-temperature furnaces for the semiconductor and photovoltaic industries.
They also play a role in the glass and refractory industries, Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), and even serve as molds for creating other specialized graphite products.
Why Graphite is the Material of Choice
The widespread use of graphite is not accidental. It possesses a unique combination of physical and chemical properties that make it uniquely suited for high-heat applications where other materials would fail.
Extreme Heat Resistance
Graphite does not melt under atmospheric pressure. It maintains its structural integrity at temperatures as high as 5000°F (approximately 2760°C), far beyond the melting point of most metals.
Superior Thermal Stability
A key advantage is its resistance to thermal shock. A graphite crucible can withstand rapid heating and cooling without cracking or breaking, making it reliable for repeated use in demanding industrial cycles.
Chemical Inertness
Graphite is chemically stable and does not readily react with other substances. This non-reactive quality is crucial for maintaining the purity of the melt, preventing contamination that could ruin a precious metal alloy or skew a scientific analysis.
Durability and Longevity
Modern graphite crucibles are engineered to resist oxidation and physical abrasion. This robust nature translates to a long service life, providing excellent value and reliability in both commercial and laboratory settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly effective, it's important to understand the practical limitations of working with graphite crucibles to ensure safety and longevity.
Physical Brittleness
Despite its thermal resilience, graphite can be brittle. It is susceptible to cracking or chipping if dropped or handled roughly. Careful handling is essential to avoid mechanical failure.
Oxidation at Extreme Temperatures
While resistant to oxidation, graphite will slowly begin to degrade in an oxygen-rich atmosphere at very high temperatures (typically above 850°F or 450°C). In many furnace applications, an inert atmosphere is used to mitigate this effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right tool depends entirely on your specific goal. The properties of graphite serve different needs across various fields.
- If your primary focus is melting precious metals or jewelry: Its chemical inertness is the most critical feature, ensuring the purity and value of your final product.
- If your primary focus is industrial foundry work: Its durability and resistance to thermal shock are crucial for withstanding the demands of repeated casting cycles.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory analysis: Its combination of extreme heat resistance and non-reactive nature guarantees the integrity and accuracy of your results.
Ultimately, a graphite crucible is the definitive choice for any application where intense heat and material purity are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Melting Metals & Alloys | High heat resistance, ideal for gold, silver, aluminum, and more. |
| Chemical Analysis & Labs | Chemically inert, ensures sample purity for accurate results. |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Durable and thermally stable for semiconductors and fabrication. |
Ready to enhance your high-temperature processes with precision and reliability?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including durable graphite crucibles designed for melting, analysis, and manufacturing. Our products ensure material purity, thermal stability, and long-lasting performance for laboratories, jewelers, and industrial foundries.
Contact us today to find the perfect graphite crucible for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.
- What does a graphite furnace do? Achieve Extreme Heat and Ultra-Sensitive Analysis
- What is the use of graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Processing for Advanced Materials
- What are the disadvantages of graphite furnace? Key Limitations and Operational Costs
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C



















